magnet inThere are also many applications in 3D printing projects. Not only can they be used in entertainment or decorative applications, but they can also be used in quick, swappable modular designs or even for wire bed detection. Of course, it is also important to find practical and safe ways to integrate magnets into printed parts.
In this article, Mohou.com will learn and discuss the role of magnets with everyone.Some possible uses for 3D printing parts and projects, then seamlessly inserting them into your prints in several effective ways.
1. Things to note
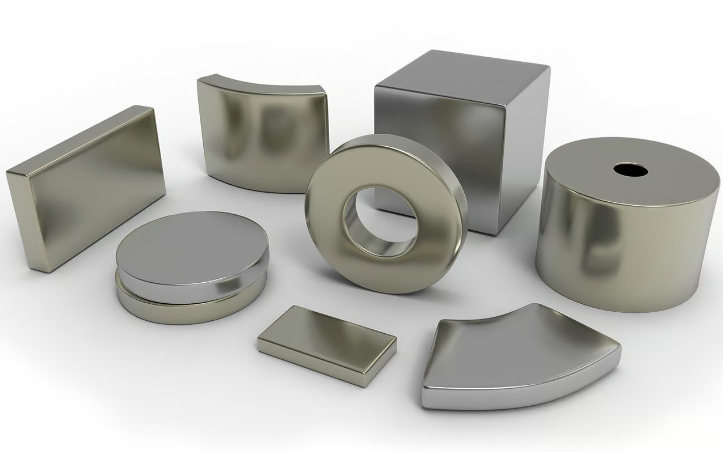
There are many types of magnets (source:Arnold Magnetic)
Before you start using magnets, here are a few things to consider:
shape: Magnets are generally cylindrical or rectangular. Barrel magnets are more popular because they are easy to install (as they allow easier insertion) and are unidirectional. They also come in ring or countersunk form for threaded fits, which we’ll discuss in detail below. Of course, there are many other shapes you can use depending on your application.
size: Choose the appropriate size based on the required strength of the magnet. Larger magnets will obviously be more powerful because they have stronger magnetic fields. Of course, you need to choose the right size and shape for your desired application. For example, if your part is thin but requires a strong magnet, choose a magnet with a large diameter but a small height (i.e. a thin, wide magnet).
Material: Neodymium magnets are very popular because they are very powerful (for their size and weight) and can withstand quite high temperatures depending on the specific type. Typically, you will want to keep a general purpose magnet in place for a long period of time.Below 70°C to maintain its magnetism.
Of course, make sure to insert the magnet with the correct polarity!
2. Adhesive fit
Glue adjustment is the easiest way! (source:Mattia via printables)
Glue installation is the easiest and most convenient way to install magnets. You simply use super glue, epoxy or similar material to secure the magnet into the oversized hole. Although this is the least secure mounting method, it is still strong enough for most applications.
If you choose to glue the magnets into your project, you will need to design slightly larger holes. For example, if you use the diameterFor a 6.00mm circular magnet with a height of 3.00mm, consider modeling the diameter of the hole as 6.30mm and a height of 3.30mm.
Of course you shouldAdjust this value for 3D printer tolerances. If your printer has tight tolerances, consider reducing this value; for looser tolerances, increase this value. This ensures that the magnet can slide in and out of the hole easily.
After printing, add a drop of glue and press the magnet firmly. Then wait for the glue to dry and your piece is ready for use.
3. Respect the adjustment to the press
Example of flexible pressure adjustment (source:Gédéon Ang via All3DP)
Flexible pressure fit takes advantage of plastic’s slight flexibility and flexible design features to“Tighten” the magnet. This is a safe and easy installation method that requires no glue. However, for added safety, it is recommended to also use a drop of glue.
In your design, based onDepending on the tolerances of the 3D printer, the hole is modeled to be exactly the same size as the magnet or slightly larger or smaller. However, you need to model the height of the hole to be slightly higher than the height of the magnet.
Next, add fins or other compatible parts so the hole can be enlarged slightly. For a stronger hold, use fewer, stronger fins. The hole will expand less and provide better grip on the magnet. However, this also depends on the tolerances of the printer. For example, if the hole is too small, you may not be able to insert the magnet at all.

Example of flexible press-fit hole (source:Gédéon Ang via All3DP)
Alternatively, you can model the hole so that the magnet can fit easily. Just add more flexible fins, which will allow the hole to bend more. However, this means that the fixation will be less secure.
The image above is an example design. The design on the left shows a more secure, less conforming fit, while the design on the right shows a more flexible, conforming fit. Feel free to try other fin styles to get a consistent hole pattern and achieve the results you want.
After printing, press the magnet firmly into the appropriate hole.– Use a drop of glue if desired.
3. Tighten
Screws are used to securely mount the magnets (Source:YGK3D via YouTube)
Screw fixing is a very secure installation method. Countersunk screws are used to mount the countersunk magnet very securely to the required component. This method is used when the magnet must be exposed outside the room (i.e. for conductive or other purposes).
For example,PCB Klicky Probe uses threaded magnets to ensure reliability, safety and conductivity. YouTuber YGK3D has a great video showing the entire build.
To design a threaded magnet, create holes or other features in the part for the screws. This can be accomplished by various methods, such as self-tapping holes for screws, holes for thermoset inserts, or slots for nuts.
Once printed, screw the magnet into the part. Then it is ready to use.
4. Integrated
How to install recessed magnets (Source:Gédéon Ang via All3DP)
Here, the magnets are fully integrated into the printed part and cannot be removed or modified once inserted. This stops them from coming loose, but it also means the magnets will be weaker because the plastic will be between the magnets and the surface they are attracted to. Therefore, this method is particularly useful for components requiring magnetic isolation.
To embed magnets, you must hang the print at a specific height. We shared howThere is a guide to doing this in Cura, but all modern slicers allow this setting. You can also monitor the height of the print layer and manually pause the print at a specific height.
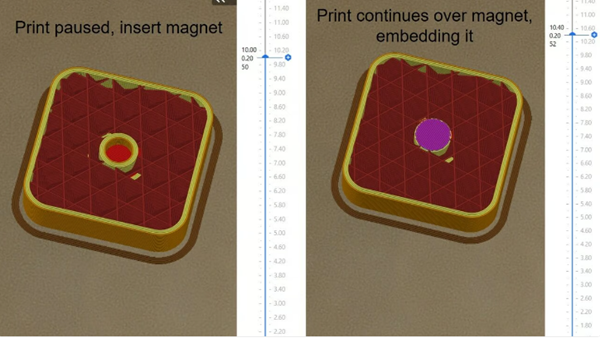
Here’s an overview of how to design and print embedded magnetic holes:
1. Model a hollow hole inside the part for the magnet. Similar to gluing, each hole size (e.g. the diameter and height of a cylindrical magnet) needs to be slightly larger in order to install easily.
2、Sets the height at which printing is stopped when trimming. This height is the layer where the hole is completely printed. For example, in the image above, all layers of the hole have beenPrinting is finished at Z=10.00 mm. At 10.20mm, a layer will be printed above the hole. Therefore, we will pause the printing after finishing the 10.00mm layer.
3. After printing stops, insert the magnet with the correct polarity into the hole.
4. After inserting the magnet, resume printing and printing will continue on the inserted magnet.
You now have a finished part with a built-in magnet hidden from the outside.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.