question:
A friend from a northern company asked: If the hardened layer of the hard surface gear tooth root is worn, will it have a significant impact on the bending strength of the gear teeth? ‘gear ?
answer:
1. The impact of hardened layer of hard surface gear tooth root on the bending strength of gear teeth.
The hardened layer of the hard surface gear tooth root has been worn away. This situation belongs to excessive wear of the gear teeth. Its specific manifestations include large wear of the working tooth surface material and changes in the tooth surface material. the size of the gear teeth, which of course greatly affects the bending resistance of the gear teeth, the main reasons are:
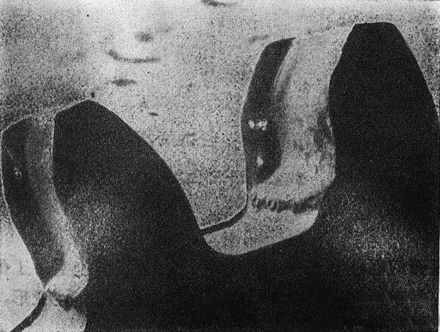
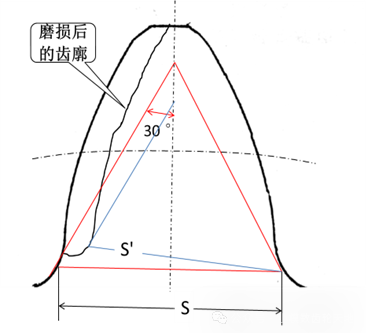
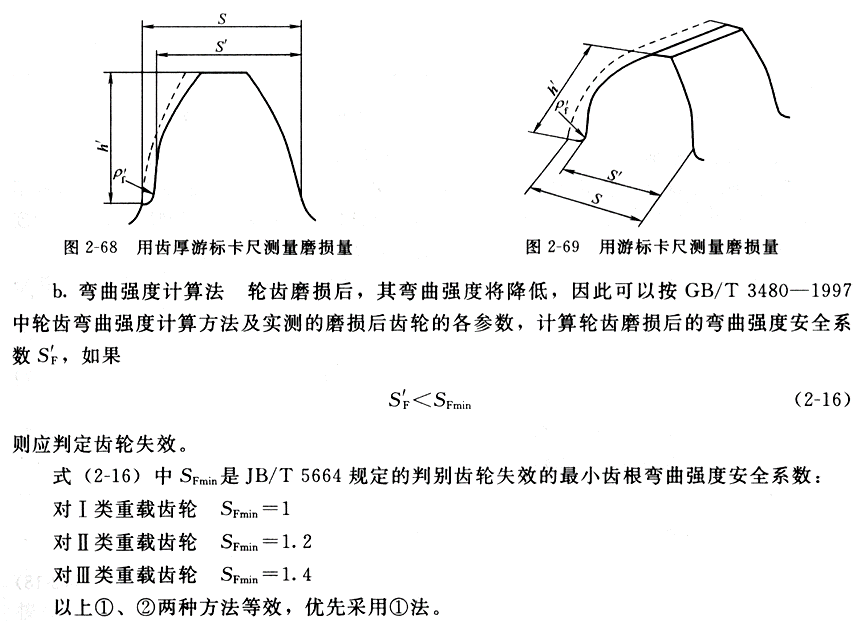
(1) Excessive wear reduces the load-bearing cross-sectional area of the tooth root. Figure 1 shows an example. The dimensional changes of gear teeth after excessive wear are shown in Figure 2. The load size S’ after wear is smaller than the normal load size S, and the bending resistance of the gear teeth will decrease inevitably.
(2) When the hardened martensite layer on the tooth root of the hardened tooth surface is worn away, the residual compressive stress in the tooth root returns to zero, and even residual tensile stress appears, which which is very detrimental to the bending resistance of the gear teeth.
(3) Excessive wear destroys the normal shape of the tooth profile, resulting in significant vibration and noise of the gear system, a sharp increase in dynamic load, and ultimately random breakage of the gear teeth. gear.
(4) Conclusion: Generally, these gears should be scrapped.
Figure 1 Example of excessive gear tooth wear
Figure 2 Gear tooth dimensions after excessive wear
2. Failure criteria for excessive gear tooth wear
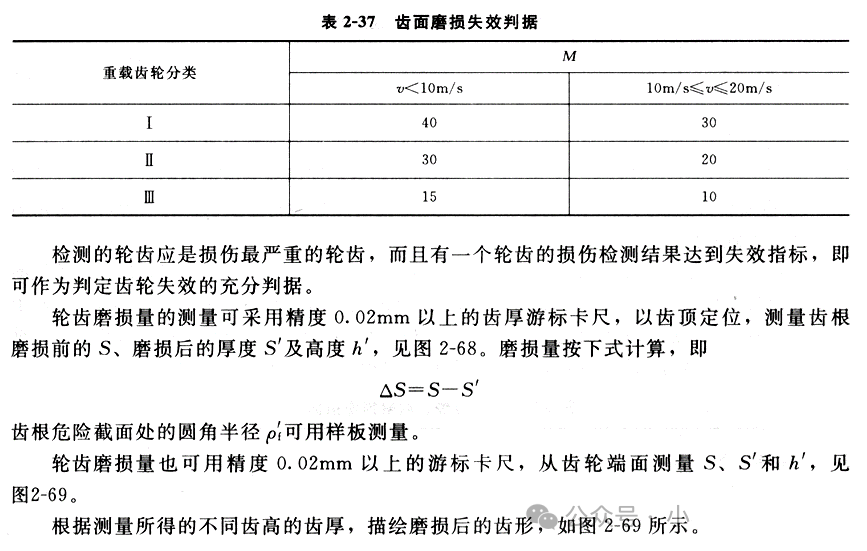
The failure criterion of gear tooth wear is the degree of wear of the gear teeth before the gear can be scrapped. There are two failure criteria for gears: one is the failure criterion for gear bench testing and the other is the failure criterion for industrial product gears. The former is clearly specified in GB/T 3480-1997 “Method for calculating the load capacity of involute cylindrical gears”. It is not suitable for actual product gears in different industries and different working conditions (such as automobile gears, aviation gears, machine tool gears, ship gears, etc.), because the use of these gears is much more complicated than test gears, and it is impossible to formulate product gear failure criteria common to all industries and working conditions. The feasible method is to formulate gear failure criteria consistent with actual industry conditions through a large number of surveys, analysis, calculations and experience summaries based on the actual conditions of each industry.
The following content is taken from JB/T 5664-1991 “Heavy Load Gear Failure Criteria”. See:
Editor-in-chief Zhu Xiaolu. Gear Transmission Design Handbook.[M].Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2010: 73-74.
3. Discussion
(1) JB/T 5664-1991 “Heavy load gear failure criteria” is mainly formulated on the basis of industrial practical experience and lacks rigorous theoretical analysis basis. For example, the standard believes that excessively worn gears can be calculated using GB/T 3480-1997 for the bending strength of gear teeth. However, the determination of the tooth profile coefficient in the calculation will encounter difficulties in the theoretical analysis.
(2) The rationality of using the bearing dimension S’ after wear to calculate the bending resistance of gear teeth is also questionable. It would be more reasonable to use the dimension S’ in Figure 2.
(3) The lubrication system fails, the sealing device is poor, and the oil film cannot be established; the transmission system has high vibration and impact loads, which will cause excessive wear. Particularly on open gear transmissions, excessive wear is common.
(4) Excessive wear of closed gear transmissions with hard tooth surfaces is rarely observed, but when the gear pitch speed is less than 0.5 m/s and it is impossible to establish a oil film, excessive wear may also occur.
(5) The failure criteria and strength calculation of excessively worn gears are still far from perfect and there is still room for further research, which could be studied as a special topic.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.