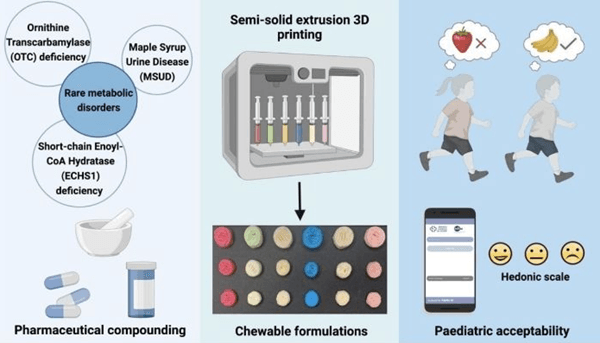
3D printing transforms the manufacture of drugs by providing personalized solutions to improve the treatment and experience of patients. Traditionally, personalized drugs have been formulated, which is a manual, laborious process and subject to errors. However, as mentioned above, 3D printing becomes a promising technology in the field, overcoming these limits by offering the possibility of producing drugs fully adapted to the specific needs of each patient. A new study led by Lucía Rodríguez Pombo, researcher at the University of Santiago de Compostela (USC), confirms the effectiveness of 3D printing technology in the clinical manufacture of personalized drugs, especially for pediatric patients.
This is calledResearch on “the clinical 3D printing application in the preparation of personalized drugs” focuses on the application of 3D printing in the manufacture of clinical drugs. Under the direction of teachers Carmen Álvarez and Professor Álvaro Goyanes, Lucía Rodríguez Pombo explored two major technologies: semi-solid extrusion technology and 3D volume printing technology for the first time in the pharmaceutical field.

The design of 3D printed drugs takes into account the needs of patients and of course the taste preferences of patients.
In this study, the possibility of implementing the two technologies in hospitals has been evaluated, highlighting their ability to produce personalized pediatric drugs whose shape, taste and dosage can be adjusted according to the specific needs of each patient . In particular, the first time that the integration of two different formulas in a single printed drug helps to improveCompliance with treatment in children aged 6 to 14.
With helpESS Technology and 3D printing volume to make personalized medicines
Judging by the results obtained by these two technologies, it is obvious that they represent significant progression in the field of personalized medicine. Studies have shown that semi-solid extrusion (Sse) can be used to print pills to treat rare diseases such as maple diabetes (MSUD), a rare genetic metabolic disease. In addition, the use of 3D volume printing “marks an important step in the pharmaceutical field, as this technology has never been used to test printing drugs,” said Lucía Rodríguez Pombo in his article. The doctoral thesis reveals that 3D volume printing makes it possible to produce high quality personalized drugs in a few seconds.
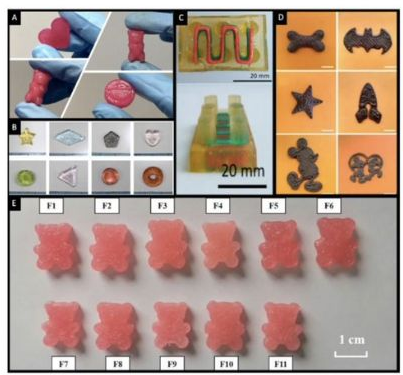
Semi-solid extrusion has been used to print various forms of drugs, including certain gelatin or chocolate drugs.
In addition to focusing on personalization, the study also representsImportant advances in the supervision of 3D printing and clinical implementation. With technologies such as semi-solid extrusion and 3D volume printing, it can inaugurate a new era of more effective drugs. These innovations not only help optimize the use of resources, but also promote therapeutic membership by creating more attractive and practical drugs, especially for pediatric patients.
The document also discusses the regulatory impact and the opportunities of these technologies in the clinical integration of hospitals with a view to obtaining a broader application in the field of health care.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.