Sheet metal is a complete cold working process for metal sheets (usually less than 6mm), including shearing, punching/cutting/compositing, bending, welding, riveting, splicing, forming (such as automobile bodywork) and other steps. Its particularity is the constant thickness of the same piece. Products processed using sheet metal technology are called sheet metal parts. Different industries usually refer to sheet metal parts differently and they are mainly used for assembly.
Material selection
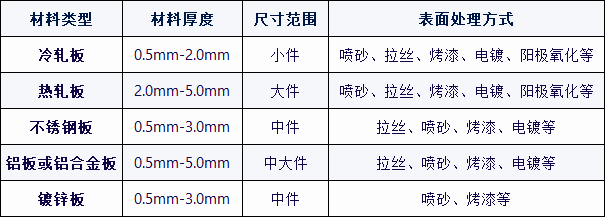
Common materials used in sheet metal processing include cold-rolled sheets, hot-rolled sheets, galvanized sheets, aluminum sheets, aluminum profiles, stainless steel sheets, etc. The following is an introduction to these materials:
Cold Rolled Sheet Metal: The brand name SPCC is the abbreviation of cold rolled steel sheet made of ordinary carbon structural steel. After cold rolling and annealing, the hot plate becomes a cold plate. It has good processing performance and is widely used.
Hot rolled sheet: SPHC brand, which is a low-end material easy to rust, and the thickness is generally above 3mm. Usually used to make hinge products.
Galvanized sheet: divided into hot-dip galvanized sheet and electrogalvanized sheet. Hot-dip galvanized sheet is a layer of zinc coated on the surface of the cold plate, generally called hot-dip galvanized sheet. Electrogalvanized sheets form a uniform and dense galvanized layer on the surface of steel sheets through electrolysis. Galvanizing is an inexpensive and cost-effective anti-corrosion method. About half of the zinc produced worldwide is used in the galvanizing process.
Aluminum plate or aluminum alloy plate: low density, anti-corrosion, typical products: refrigerator drain pan and evaporator fins, etc.
Stainless steel and stainless iron: belong to alloy materials, have good anti-rust and anti-corrosion properties, and have a beautiful surface. Usually used to make exterior parts, such as refrigerator door shells and gas stove tops.
Commonly used surface treatments for sheet metal include:
Drawing: Place the material between the upper and lower spool wheels of the drawing machine and drive the material through the upper and lower abrasive belts, removing traces on the material surface. Depending on the abrasive belt, the thickness of the marks. will be different. The main function is to beautify the appearance. Generally, brushed surface treatment is only considered for aluminum materials.
Sandblasting: The wind force of the sandblasting machine hits the sand particles on the surface of the workpiece, forming a dense layer of hollows on the surface of the workpiece. The main function is to remove dirt on the surface of the workpiece and increase adhesion. of the workpiece surface and provide a method for subsequent surface treatment.
Paint and powder spraying: The best known is automobile painting. Through spraying, high temperature baking, etc., a layer of paint of different colors is sprayed on the surface of the material to beautify the appearance and increase the anti-corrosion performance of the material. The painted surface is non-conductive and painting is not permitted in areas with EMC requirements.
Electroplating: Through chemical reactions, a layer of other metals is attached to the surface of the material to increase the anti-corrosion properties of the metal and achieve a certain beautifying effect. Plating mainly colored zinc, blue and white zinc, black zinc, chrome plating, etc.
Anodizing: Oxidizes the metal on the surface of the part to form a dense protective film on the surface of the part to increase the corrosion resistance of the part. There are generally two methods: chemical oxidation and anodizing.
Common sheet metal defects include:
Dents: May be caused by mold issues or problems during the stamping process.
Scratches: These can be caused by operational problems, such as malfunction or friction between parts.
Rust: May be caused by improper protection or storage.
Indentation: This could be due to a mold problem or a problem during the stamping process.
Wrinkles: These can be caused by problems during operation, such as malfunction or material rebound.
Deformation: It can be caused by hardware problems or improper storage.
Cracking: This could be due to hardware issues or problems during the stamping process.
Misalignment: This may be due to problems during operation, such as malfunction or poor fit between parts.
Blocking holes: This may be due to problems during operation, such as malfunction or poor fit between parts.
Empty: This may be due to hardware issues or improper storage.
File Marks: This may be due to problems during operation, such as malfunction or marks left from using files to repair during retouching.
Polishing Marks: May be caused by problems during the polishing process, such as excessive polishing or improper selection of polishing materials.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.