3DPrinting is an emerging manufacturing technology based on digital models that stacks materials layer by layer to create physical objects. This technology will have a profound impact on traditional process flows, production lines, factory models and industrial chain combinations. the manufacturing industry. With the EU 3DPrinting Standardization Roadmap Released, International Organization on3Dprints the development of a series of standards, and the United StatesFDAabout3DThe introduction of a series of specifications such as printing technical documents,3DPrint gradually acquired its own language and its own universal direction.
3DThe application of printing technology in the research, development and manufacturing of medical devices has continuously promoted the innovative development of medical devices, thus forming a “3DPrint “medical device” products and receive them in the near future5Its use has gradually become widespread over the years.3DMedical device printing primarily uses materials such as metals and polymers, which enable personalized customization of devices and fabrication of precise microstructures.3DWhile printing provides “personalization,” it also carries unique risks. The traditional method of monitoring standardized products can be difficult to apply.3DThere is also a lack of analysis and assessment methods and standards for the process, quality and risks of printed medical devices, making3DThe regulation of printed medical devices faces many challenges.
Establish a medical examination3DCertification standards, regulations and rating systems for printing products
For medical purposes3DFor the further industrial application of printing products, all relevant institutions must work together and the superstructure must play a leading role.
Medical3DThe first advances in printing took place in the fields of orthopedics and dentistry, where it is now maturing. So, from2010In 2006, it was proposed for orthopedic and dental products3DPrint medical implant regulations.
Currently, the National Medical Products Administration has approved four types of3DPrint standard products. The National Medical Products Administration prioritizes its use in mature or proven fields, such as orthopedics and dentistry, with components for customized products manufactured by different provinces.
Since additive manufacturing products include customized products, the State Drug Administration plans to establish a comprehensive evaluation system. Currently, the National Medical Products Administration has formulated40Guiding principles on obtaining registration certificates for medical devices, including7principles related to additive manufacturing. In the future, relevant standard systems, regulatory systems, guiding principles, technical registration documents and beacon systems will be established to focus on developing clinical applications and achieving breakthroughs.
My country’s “Measures for Supervision and Administration of Production of Medical Devices” lists the safety and effectiveness of medical devices as the main requirements. Currently, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) mainly based on reasonable decisions and effective scientific evidence to control risks and ensure that medical products can be used safely and effectively, thereby improving public health. For new medical devices in the field of additive manufacturing, corresponding regulatory science must be established to verify the performance of registered products. Important tasks that must be completed prior to registration include conducting multicenter clinical trials and medical research, as well as producing summarized, peer-reviewed products published in scientific publications to provide an important basis for registration. clinical practice. Such research and production will facilitate the development of innovative products and facilitate monitoring of the entire use of the product during its clinical application.
The Scientific Institute of Medical Device Regulation of Sichuan University is the world’s first academic institution to deal with regulatory issues related to medical devices. Its mission is to establish regulatory science for medical devices through pre-verification and risk control. This regulatory science should cover the entire life cycle of a medical product based on contextual information about users, product developers and company risk controls.
There are differences between national and international regulations regarding personalized products. In the UK, the fundamental management philosophy for custom devices is that apart from material issues, the entire production process for additive manufacturing is the responsibility of the surgeon, including CT scanning of clinical patients (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image data acquisition, fabrication, clinician validation and subsequent clinical application.
The goal of Chinese companies is to obtain the registration certificate issued by the State Food and Drug Administration before entering the market. The current situation in the United Kingdom shows that my country should issue clear registration guidelines for personalized medical devices as soon as possible and accelerate clinical transformation. Relevant registration guidelines should take into account technical feasibility and create practical benefits for all parties.——Especially patients. The reproducibility of medical additive manufacturing and the characterization of the finished product produced (whether for humans, animal models or cellular models) must be achieved in a standardized manner. This topic deserves further consideration and discussion in future research and development and clinical applications.
All new technologies and materials–especially3DThree types of printed medical products – all must be systematically evaluated and approved by regulatory agencies before clinical use. Medical additive manufacturing technology is still in its early stages of exploration. at present,3DThere are still several major challenges to overcome in the clinical application of printing technology in the field of orthopedics and dentistry: risk responsibilities are not clearly defined and deadlines for registration and d clinical approvals are too long. Indeed, it is difficult to evaluate the expected clinical effects of such products,3DThis is especially true for printed products. In addition, the product quality control system is not yet perfected. Although the goal of clinical research initiated by preclinical scientists is not clinical registration, the relevant management processes and quality control systems must meet the corresponding surgical medical requirements.
3DPrinting medical device quality control points
For3DThe performance and safety of printed medical devices are the most important aspects. To ensure safety, it is necessary to control all aspects from the early stages of design and manufacturing, i.e. product quality control.3DQuality control of printed medical devices involves many links in the manufacturing process and production management, including medical-industrial interaction, quality control of raw materials, management of printing equipment, process parameters processing, management of the post-treatment process and quality control of the finished product. The link has different requirements.
1 Medicine-industry interaction
Doctor-worker interaction is a connection with patients3DOne of the remarkable features of printed medical devices, which differ from non-personalized medical devices, is that standardization, efficient interactive information, close cooperation and well-recorded documents are very important. The key links and their constituent elements in the whole process of doctor-engineer interaction should be precisely defined and how to effectively control these elements should be studied.
“Guiding Principles for Technical Review for Registration of Custom Additively Manufactured Medical Devices for Passive Implantable Oral Bones, Joints and Hard Tissues” (2019year70“No.)” also clarified that products must meet the requirements of medical-industrial interaction6requirements, including design software?printing equipment?raw materials?Checking the printing process?Post-processing methods and verification?product testing,and request a custom design?The interaction capabilities between medical engineers and additive manufacturing medical devices are confirmed in three aspects: product delivery and use.
2 Quality control of raw materials
Quality control of raw materials is the basis for ensuring the quality of printed products, and their purity and performance are even more crucial. Raw materials currently involved in additive manufacturing of medical devices are mainly used for3DPrinted metal powders include medical titanium alloys, medical pure tantalum, and medical nickel-titanium alloys.
Metal3DThe printing raw material is in the form of a spherical powder. Therefore, it is necessary to characterize the raw material in terms of roundness, sphericity, fluidity, tap density, bulk density, etc., and check whether its physical and chemical properties meet the requirements. for the production of medical devices. Furthermore, for3DThe use of old recycled powders in printing requires the manufacturer to explain and verify the mixed powder, verify the impact of the printing environment on the powder, demonstrate process stability and clinical acceptability, and judge the The impact of powder recycling on the printing process and the potential impact of the results would not otherwise allow the use of recycled powder materials.
3 Managing printing devices
The printing device is implemented3DPrinting critical materials for the production of medical devices. The stability of the equipment operation and the stability of the printing process determine whether the batch-to-batch variation of the product is within the acceptable range. The printing parameters of printing equipment must undergo strict verification procedures to ensure the workability and stability of the printing process. The rationality and effect of equipment modifications should also be checked.
4 Verification of the processing process and management of the post-processing process
Preliminary printed products must undergo necessary post-processing, such as thermal stress removal, surface roughness treatment, and powder residue removal. These post-treatments are important guarantees to guarantee the reasonable mechanical properties and biocompatibility of the product. Currently, the “Medical Additive Manufacturing” standard “Metal powder cleaning method and cleaning effect verification for powder bed fusion casting process” is in the approval stage, mainly forEstablish standards for the technical content of “common procedures for cleaning residual metal powders” and “methods for verifying the cleaning effect”. Manufacturers may implement cleaning processes and demonstrate cleaning compliance in accordance with the provisions set out therein.
5 Quality control of the finished product and assessment of risks linked to the application of the product
3DIn addition to meeting post-manufacturing performance requirements, printed medical devices must also consider the possible impact on human health when interacting with the human body. by3DTaking the printing of titanium alloy implants as an example, in order to evaluate the precipitation of metal ions, the China Central Inspection Institute formulated the “Additive Manufacturing Medical Products”3DThe “Method for Evaluation of Metal Ion Precipitation in Titanium Alloy Printed Implants” has been submitted for approval. The standard specifies the morphology of the sample used for the tests and the metal ions to be detected (Of、Al、Vand impurity elementsFe) and other content.
Other areas of concern include: control of physical properties (mechanical properties and fatigue properties), chemical properties (control of chemical composition, microstructure) and biocompatibility. Biocompatibility should be based onGB/T16886A comprehensive assessment of the requirements of the series of standards.
A series of policies favor3DIntegration of printing technology and the real economy
2015Year2In September, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Finance jointly released the National Additive Manufacturing Development Plan (2015—2016Year)”, proposed to2016In 2019, China will initially establish a relatively complete additive manufacturing industrial system, and the overall technical level will keep pace with the international level.
2015Year5In March, the State Council issued the “Made in China”2025》Plan, which clearly considers the additive manufacturing industry as an axis of development and promotes the rise of China.3DResearch, development and application of printing technologies and equipment. As an important part of intelligent manufacturing,3DPrinting technology made in China2025“1+X“Mentioned in several plans. 3DBusinesses in the printing sector will also benefit from support from the national special list system.
2016Year12In March, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology approved the establishment of the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Center, which includes Xi’an Jiaotong University, the University of Aeronautics and Beijing Astronautics, Northwest Polytechnic University, Tsinghua University and Huazhong University of Science and Technology.5Universities and equipment, materials, software and R&D, etc.13key companies created and carried out jointly3DImpression of common technological research, standard formulation and industrialization. At the same time, the Wuxi General Administration of Product Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine approved the Wuxi Product Quality Supervision and Inspection Center to prepare for the establishment of the National quality monitoring and inspection center for additive manufacturing products to carry out testing, certification and other related products. services.
2017Year11In September, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, etc.12The department published the “Action Plan for the Development of Additive Manufacturing” (2017—2020Year)”, made it clear that2020In 2018, the annual revenue of China’s additive manufacturing industry exceeded200billion, with an average annual growth rate of30%That’s all.3DThe development of printing technology requires the improvement of research, development and industrialization capabilities of key technologies such as materials, processing equipment and core components, as well as the promotion of innovative applications in key industries.
medical action plan 3DThe development of printing technology has clarified the direction to improve the quality and process performance of special materials for medical additive manufacturing, improve the material design and microstructure design technology of personalized medical devices, to improve the quality performance and reliability of additive manufacturing equipment and core components. , and at the same time, we must actively explore “3DPrint+New “medical” demonstration application model, targeting needs for personalized medical devices, rehabilitation equipment, implants, soft tissue repair, etc. in the medical field, and promoting the improvement of personalized medical additive manufacturing products in terms of classification, clinical trials, registration, market access, etc. Policies and regulations, research and determination of3DPrint medical billing standards and medical insurance payment standards for products and services. At the same time, establish and improve the additive manufacturing standard system, testing and certification system and talent training system.
3DPrinting technical specifications for medical device registration opens avenues to market
3DThe clinical use of printed medical devices has historically been restricted by regulations and policies. There are no relevant standards for approval and registration in most countries.3DPrinted products mainly include clinical ancillary products such as tumors, organ models and surgical guides. They only need to be filed and are not subject to strict approval and registration control.2017In 2016, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) published “3D“Technical Guide on Medical Device Printing” to standardize related product manufacturing activities, clarify the medical product additive manufacturing process and associated test operational specifications, and3DSpecific technical requirements are proposed for core processes such as printing methods, design, workflow, manufacturing process, material control, post-processing, testing and quality management , etc.3DPrinting medical devices provides a basis for approval and registration and opens channels for products to market.
3DEnlarged image of basic medical device printing process
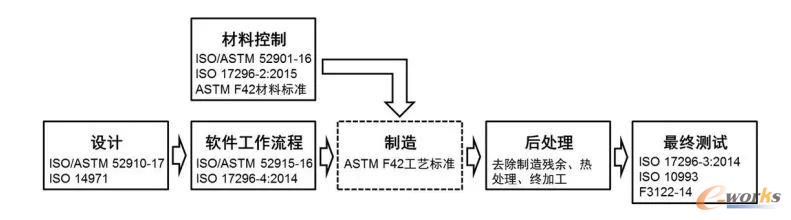
3DBasic Medical Device Printing Process
2018Year2In September, the State Food and Drug Administration (CFDA) published draft comments on the “Guiding Principles for Technical Review of Registration of Customized Additive Manufacturing Medical Devices,” which clarified the relevant operations and data requirements for registration approval , and clarified the requirements for registration approval.3DSpecific requirements are proposed for the use of printed products, product performance, clinical trials, quality management, etc., with particular emphasis on confirming medical-industrial interaction conditions and capabilities, And3DThe production and verification process of printed medical devices, including testing of printing equipment, processes, post-processing, raw materials and final products, must be strictly controlled. The qualifications and capabilities of personnel in product design and development, delivery and use. must be confirmed and guaranteed.3DPrinting products are used safely and effectively in clinical practice. Furthermore, it is emphasized that a database must be established on the health status of patients throughout the life cycle of the product, in order to evaluate the durability of the device and the traceability of medical accidents. The introduction of this approval and registration specification means that the Chinese medical field3DThe printing industry is one step closer to having formal technical review guidelines for3DPrint medical device registration, approval and marketing to eliminate barriers.
outlook
In general,“3D“Printed medical device standardization” can be divided into three concepts:3DPrinting, medical devices, standardization.3DPrinting is the technology of manufacturing products, medical devices are products, and standardization is about making products meet requirements. Only products that meet the requirements can be applied in practice and realize the significance of the product.
At present, considering the systematic and extensive characteristics of standardization work, we must continue to promote3DStandardizing medical device printing requires advancing many aspects of the work simultaneously, including:1) Promote the industrialization process of Chinese additive manufacturing technology;2) Strengthen exchanges and cooperation between China and other countries and organizations in standardization work;3), all stakeholders in this field make constructive suggestions to Chinese regulatory authorities to establish relevant laws and regulations;4) All stakeholders in the field provide technical support for the formulation of regulatory guidelines such as special risk analysis and risk control;5) Regulatory authorities further establish standards for technology and methods, raw materials, equipment and processes.
This shows that industry and standards are interdependent. Industry cannot be separated from the direction of standards, and standards cannot become castles in the air without being separated from industry. Secondly, production, education, scientific research, inspection institutions, medical units, standardization agencies and regulatory authorities are all important parts of this field. All parties can achieve synergy and integration in terms of functions and resource advantages according to different divisions of labor. and jointly promote growth. The development of standardization work for medical device manufacturing materials.
exist“2020During the “National Medical Device Safety Publicity Week” event, the Food and Drug Administration demonstrated the eight dimensions of quality control formed by the latest components of additive manufacturing medical device product evaluation, including performance and characteristics, which are divided into three at once. The main categories are product-based, manufacturing-based, and user-based methods, which provide relatively comprehensive and systematic guarantees.3DPrint medical devices with quality and meet user needs.
These can serve as entry points to help medical device manufacturers better understand seemingly complex standardization work from scratch. There is an old saying in China calledThe meaning of “remaining unchanged in the face of all changes” is reflected in standardization work. Although products are customized, work processes and operating methods can still be standardized, and standardized processes are used to standardize various product customizations. Understanding these concepts, combined with continued knowledge of regulations and3DPrinting technology, enterprises can better innovate products according to standardized requirements, truly use new technologies to come up with new products and meet approval requirements.
Extend product development to a longer process, from experimental research to production application, even in the laboratory, to3DResearch on printed medical devices must also consider industrialization and clinical transformation as an important principle throughout the R&D process. Products should not remain at the scientific research stage just for the sake of publishing articles. Similarly, from scientific research to industrial stage, the requirement for medical device companies is that when a product is developed3DWhen printing medical device products, regulatory approval and certification cannot be the end goal. Product certification is only the beginning of application, and application effectiveness is the ultimate pursuit of medical device products.
For3DRegarding the future development of the supervision and standardization of printed medical devices, “quality” and “risk” will continue to be the two key words that will continue to be explored in this field, and the first task remains to establish a system fuller set of guiding principles. , standards and regulations. RIGHT3DBuilding a standardization and supervision system for printed medical devices has been listed as one of the important tasks and plans of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan. These systems can continually expand the scope horizontally, so that standards cover more types of technologies and products, and continually expand the depth vertically, extending and improving more details on specific products and technologies.
source:Additive manufacturing Ringier
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.