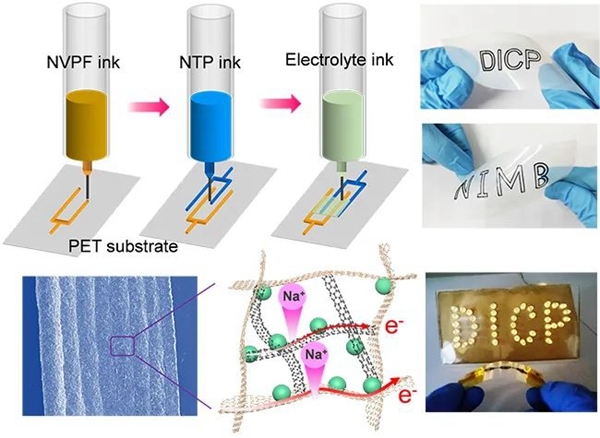
2022Year8moon24Recently, after proposing a new customizable printing strategy for aqueous zinc-ion hybrid capacitors, the research group on two-dimensional materials chemistry and energy applications of the State Key Laboratory of Catalytic Fundamentals of the Institute of Dalian Chemical Physics (Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics)508Group) Wu Zhongshuai’s team recently achieved another breakthrough in the development of sodium-ion microbatteries.3DA breakthrough in printing. The team of researcher Wu Zhongshuai and associate researcher Zheng Shuanghao developed an electrode ink capable of forming a three-dimensional conductive network and an electrolytic ink with high ionic conductivity, which significantly improved3DImprint electron and ion transmission efficiency in high-capacity microelectrodes to develop high-capacity, high-throughput, flexible sodium-ion microbatteries.
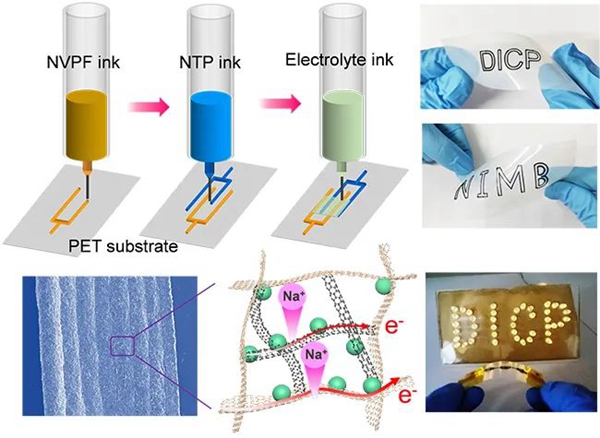
The development of wearable electronic products and microelectronic devices has promoted research into high-performance, multifunctional, customizable, and flexible microenergy sources. Planar sodium-ion microbatteries are considered a promising new microenergy source due to their advantages of abundant sodium resources, low cost, and rapid transmission of sodium ions. At present, microelectrodes prepared by micromachining technology for sodium-ion microbatteries generally have limited thickness (10mm), which makes its surface capacity less than0.04mAh/cm2it is difficult to meet the demand for higher surface capacity. To this end, it is necessary to develop an efficient and feasible strategy to construct sodium-ion microbatteries with three-dimensional structure (electrode thickness >100mm) to make full use of limited space. However, in thick electrodes, due to high curvature, long ion diffusion paths and insufficient use of electrode materials, electrons are hindered./The rapid transport and conversion of ions makes it difficult to construct high-performance sodium-ion microbatteries.
In this work, the team succeeded3DPrinting and construction of planar sodium-ion microbatteries with high surface specific capacitance and high throughput. The team achieved this by preparing a3DPrinting electrode ink,3DPrint thick electrodes (thickness up to1200mm) has a three-dimensional porous conductive framework structure, which promotes the kinetic rate of ion transmission, reduces the electron transmission distance in thick electrodes, and effectively improves the electrochemical performance of sodium-ion microbatteries. The prepared sodium-ion microbattery operates at low current density2mA/cm2show when4.5mAh/cm2high surface capacity and7.33mWh/cm2high surface energy density. Thanks to the construction of an efficient conductive network in thick electrodes and the high ionic conductivity of the gel electrolyte, the microbattery operates at high current densities.40 mA/cm2I still have3.6mAh/cm2high surface capacity and6000Long loop cycle stability. In addition, thanks to the porous structure of the microelectrode capable of withstanding mechanical stress and the strong interfacial interaction between the ionic liquid gel electrolyte and the substrate, the sodium-ion microbattery exhibits excellent mechanical flexibility. This work shows3DPrinting high-performance planar microbatteries has potential applications in wearable and wearable microelectronics.
In the process of building printable microelectrochemical energy storage devices, Wu Zhongshuai’s team has already developed a variety of printing technologies, such as spray printing of micro supercapacitors (Av. Maître.,2017;ACS Nano,2017), screen printing micro supercapacitor, lithium-ion/Zinc-manganese micro-battery (Energy Environment. Sci.,2019;Natl. Sci. Round.,2020; Av. Maître.,2021;Little,2021), inkjet printing micro supercapacitor and integrated self-powered temperature sensing system (Av. Energy material.,2021),3DPrinting micro supercapacitors and zinc-ion hybrid capacitors (J. Energy Chem.,2021;Av. Energy material.,2022)。
Relevant search results include“3D printing flexible sodium-ion microbatteries with ultra-high areal capacity and robust flow capability“, published in “Advanced Materials” (Advanced materials)superior. The first author of this work is the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics508Doctoral student in the Ma Jiaxin team. The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Chinese Academy of SciencesAFunded by the “Key Technologies and Transformative Clean Energy Demonstration” Category Pilot Project, the Cooperation Fund of the Institute of Clean Energy Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and other projects. (arts/Tu Ma Jiaxin, Zheng Shuanghao)
Article link:
Source: Chinese 3D Printing Network
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.