Stamping die is a special processing equipment used to transform materials into parts (or semi-finished products) during stamping processing.
Classified according to process properties: punching dies, bending dies, drawing dies, forming dies, etc.
Classified according to the degree of process combination: single process mold, composite mold and progressive mold.
a) Forming die b) Drawing die c) Clamping die d) Bulging die
Three elements of stamping production: reasonable stamping technology, advanced molds and efficient stamping equipment.

1. Cutting, punching and cutting
Defects: excessive burrs, deformations, surface scratches, size deviations, missing holes, etc.
1) Excessive burrs: the gap between the convex and concave dies is too large or too small; the cutting edge is worn; guidance accuracy is poor; the positions of the convex and concave matrices are not concentric;
2) Deformation: the distance between the holes is too small; the pressing plate and the concave surface of the model do not match well; the gap is too big, etc.
3) Surface scratches: sliding, pulling, etc. during operation, the sheet metal is scratched when shearing, etc.
4) Dimensions do not match: cargo is not in place; the positioning device is damaged or loose, the position moves, etc.
5) Few holes: the punch is broken; the length of the punch is not sufficient, etc.

Die-cutting, punching and die-cutting products are subject to faulty locations
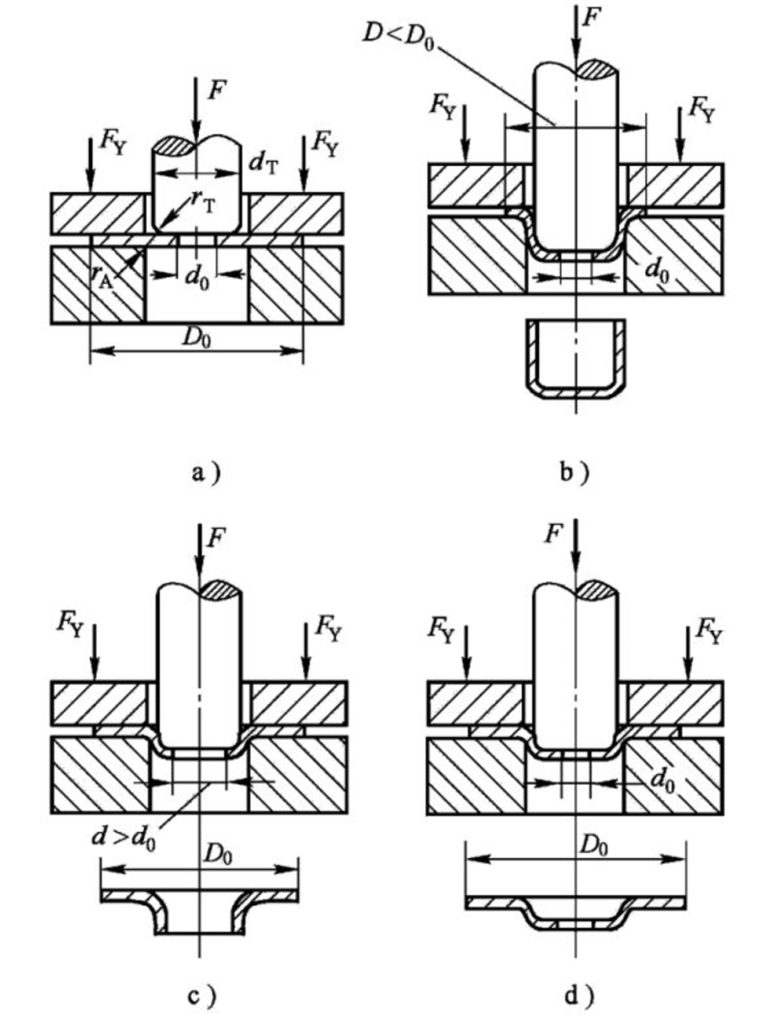
2. Stretch

Designed products are subject to defective locations
3. Flange
Defects: the flange is not vertical, the flange height is inconsistent, the flange is rough, the flange is cracked, etc.
1) The planking is not vertical: the gap between the convex and concave molds is too great.
2) The planking height is inconsistent: the gap between the convex and concave molds is uneven; the positioning is inaccurate; the size of the cutting parts is inaccurate;
3) Edging and roughness: there are scars on the cutting edge; there are impurities on the surface of the part; the hardness of the cutting edge is too low;
4) Flange cracks: burrs are significant during trimming; the gap between the convex and concave molds is too small, there is a sudden change in the shape of the flange.

Flanged products are prone to faulty locations
4. Folding
Defects: unqualified folding angle, cracked folding edge, steps at R folding corner, etc.
1) The bending angle is not qualified: the gap between the convex and concave molds is too large, and the corresponding angle of the convex and concave molds does not match the thickness of the panel material.
2) Broken folding edge: the gap between the convex and concave molds is too small; the folding angle is too small; the punching force is too large and the speed is too fast;
3) There are steps in the bending angle R: the bending angle of convex and concave molds is too large; the exterior angle R is too large;

Folded products are subject to defective locations
5. Waste jump hole
1) The length of the punch is not sufficient. Cut the die according to the sharpness of the punch and add 1mm to the material thickness to replace the punch;
2) The space between the concave molds is too large. Cut the space to reduce the space or use a covering machine to reduce the space.
3) The punch or template has not been demagnetized. Use a demagnetizer to demagnetize the punch or template.
6. Trash blocks the hole
1) The shutter hole is small or the shutter hole is offset and the shutter hole is enlarged to make the shutter smooth;
2) The blanking hole is chamfered, enlarge the blanking hole to remove the chamfer;
3) The knife edge is not tapered, and the wire cutting cone or expansion hole on the back reduces the length of the straight wall;
4) The straight wall of the knife edge is too long, and holes are drilled on the reverse side to shorten the right wall of the knife edge;
5) The cutting edge collapses, resulting in a large blade, and the cutting edge must be blocked and resharpened.
7. Bad cape
1) The cutting edge collapses, making the blade too large and the cutting edge must be sharpened again;
2) The gap between the punch and the die is too large, the wire is cut in the block and the gap needs to be readjusted;
3) The die edge finish is poor and the polished edge has a straight wall;
4) The gap between the punch and the die is too small, register the die again and adjust the gap;
5) The ejection force is too great. Remove the cap in the opposite direction and replace the spring to reduce ejection force.
8. Uneven size
1) positioning offset adjustment;
2) There is single-sided forming, the material is pulled, the pressing force is increased, and the positioning is adjusted;
3) The design error caused the knife to connect unevenly and the cutting insert to recut;
4) It is not allowed to adjust the feeder when feeding;
5) There is an error in calculating the feed step distance. Recalculate the step distance and reset the tool receiving position.
9. The punch is easy to break
1) The closing height is too low and the punch edge is too long. Adjust the closing height;
2) Improper positioning of the material, causing the punch to cut off on one side, adjust the positioning, or break the feeding device due to uneven stress;
3) The waste from the lower die blocks the knife edge, causing the punch to break and punch a large blanking hole to make the blanking smooth;
4) The fixed part of the punch (splint) and the guide part are repaired or recut into blocks to allow the punch to move up and down smoothly (plate punching);
5) The platemaking guide is poor, resulting in stress on the punch on one side and the platemaking space needs to be readjusted;
6) The edge of the punch is too short and this hinders the manufacture of the plate. Replace the punch and increase the edge length.
7) The punch is not secure and moves up and down. Reattach the punch so that it cannot move up and down.
8) The edge of the punch is not sharp and needs to be resharpened;
9) The punch surface is tight and the force is uneven when stripping. Replace the punch;
10) The punch is too thin, too long and not strong enough. Change the punch type.
11) The hardness of the punch is too high and the punch material is incorrect. Replace the punch material and adjust the heat treatment hardness.
10. Iron filings
1) Recalculate the position or folding position of the tie rods if they are misaligned;
2) The bending gap is too small, wring out the iron shavings to readjust the gap, or grind the forming block or forming punch;
3) The bending punch is too sharp and the R corner needs to be cut;
4) There is too little material to connect the knife edge and reconnect the knife edge;
5) The bead is too narrow. Grind it again.
11. Poor germination
1) If the center of the bottom hole and the center of the punch do not coincide, determine the correct center position, or move the punch position, or move it to an upper-lower position, or even move the pre-punching. position or adjust positioning;
2) The gap between the concave molds is uneven, resulting in small cutting gaps on the high side of the sprouting side, or even breakage;
3) The bottom hole of the shoot does not meet the requirements, resulting in recalculation of the height of the shoot and the diameter of the bottom hole, and the diameter deviation of the pre-drilled hole increases or decreases, or even breaks .
12. Bad casting
1) The punch of the forming die is too sharp, causing the material to crack. Repair the R angle of the molding punch and cut the R angle appropriately at the cutting edge.
2) The length of the forming punch is not enough, resulting in forming failure. Calculate the correct punch length and adjust the actual punch length to meet the molding requirements;
3) The forming punch is too long and the material in the forming area is deformed due to pressure. Determine the correct punch length and adjust the actual punch length to meet the requirements until the punch breaks.
4) Insufficient material at the molding area causes cracking. Calculate the unfolding of the material, or cut the angle R, or reduce the molding height;
5) Improper positioning, resulting in poor casting. Adjust the positioning or feeding device;
6) The molding gap is too small, causing the gap to crack or deform.
13. Folding dimensions
1) The mold is not adjusted in place, causing angle errors, resulting in dimensional deviation, wrong closing height or wrong angle difference;
2) Insufficient elasticity results in poor angle and results in size deviation. Replace the spring;
3) Material does not meet requirements, resulting in poor angles, material size changes, or readjustment of gap gaps;
4) Material thickness deviation causes wrong angle, resulting in material dimensional deviation and thickness, so the material needs to be changed or the deviation needs to be readjusted;
5) Incorrect positioning results in size deviation. Adjust the positioning so that the size is correct;
6) Design or processing errors result in repairs by welding and grinding between male bending parts, thereby eliminating gaps between parts, resulting in small bending dimensions;
7) The casting has no R angle and the curvature height is too small under the angle and other normal conditions of the R angle of the casting;
8) The bending dimensions on both sides are too large for the compression ribs;
9) Unilateral bending and pulling of materials causes dimensional instability, increases spring force and adjusts positioning;
10) The gap is unreasonable, causing wrong angles and size deviations to repair the gap;
11) The height of the folding knife is not enough and the folding punch is too short to fit into the folding knife. Increase the height of the folding knife so that the folding punch fits into the position of the folding knife as much as possible, resulting in. in worse angles;
12) The speed is too fast when folding, causing deformation of the bending root. Adjust the gear ratio control and select a reasonable speed;
13) The structure is unreasonable. The folding knife is not inserted into the fixed template. When the folding knife is inserted into the template for stamping, the space becomes larger.
14) The heat treatment hardness of the casting male is not sufficient, causing the pressure line to collapse or the casting male pressure line to be flattened.
14. No unloading
1) Bad positioning or feeding. Adjust the positioning or feeding device;
2) The avoidance position is not sufficient to repair and rectify the avoidance position;
3) The inner guide post is tight, resulting in poor boarding movement. Replace the inner guide post;
4) If the punch is strained or the surface is not smooth, replace the punch;
5) The position of the ejector pin is not reasonable. Rearrange the position of the ejector pin;
6) The ejection force is not enough or the ejection force is not sufficient. Replace the ejector spring or ejector spring;
7) The punch and the plywood do not cooperate smoothly. Repair the plate and plywood so that the punch cooperates smoothly.
8) If the cast slide block does not fit easily, cut the slide block and guide groove to fit easily;
9) The heat treatment of the plate is not suitable and it becomes deformed after stamping for a certain time. Grind the plate again to correct the deformation;
10) The punch is too long or the ejector is not long enough. Increase the length of the ejector or replace it with a punch of appropriate length.
11) Replace the punch if the punch is broken;
12) The template is not magnetized and the part is raised towards the template to demagnetize it.
15. Feeding is not smooth
1) The mold is not installed correctly, causing the material strip, feeder and mold to be readjusted or the feeder adjusted not to be in the same straight line;
2) If the material strip is uneven, adjust the leveling machine or replace the material;
3) Failure to discharge material results in unsatisfactory feeding. Please refer to countermeasures related to not unloading material;
4) The positioning is too tight and adjust the positioning;
5) The guide pin is too tight or the right wall position is too long. Adjust the guide pin;
6) The punch is not securely attached or is too long and interferes with the material belt. Reattach the punch with appropriate length;
7) The ejector pin is too short and the material belt interferes with the forming block. Adjust the length of the ejector pin to avoid interference;
8) The position of the floating block is incorrectly arranged. Adjust the position of the floating block.
16. Bad riveting
1) The mold closing height is inappropriate and the riveting is not in place to adjust the closing height;
2) The workpiece is not placed and the positioning deviation is adjusted;
3) If the part is defective before riveting, confirm the seed hole. Refer to the countermeasures to solve the problem of defective seed holes to confirm whether the riveting hole is chamfered. If there is no chamfer, increase the chamfer.
4) If the riveting punch is not long enough, replace it with a punch of suitable length;
5) If the riveting punch does not meet the requirements, confirm and use a riveting punch that meets the requirements.
17. Missing or installed
1) You accidentally make the wrong punch during assembly;
2) Hallmark without direction mark. Mark the punch with the direction.
18. Wrong screws installed
1) I don’t know the thickness of the model. Understand that the thickness of the model is too long or too short;
2) Insufficient attention and experience in selecting the appropriate screws.
19. Disassembly and assembly of the mold
1) Pin holes are not cleaned. Wipe the pin holes and pins when disassembling the mold, you must first remove the positioning pins, which are easily damaged. When installing the mold, you must first use screws to guide them. then drill the holes for the positioning pins;
2) If the mold assembly and disassembly procedures are incorrect, do not damage the pin hole by dropping the pin.
20. Positioning pin
1) If the hole wall is rough or scratched, making it too tight when assembling the mold, carefully check whether the pinhole is made rough, otherwise the pinhole which cannot be drilled must be reamed;
2) The pin hole is offset or there is no drain hole underneath. Add a drain hole for the locating pin.
21. Spring is too long
1) Did not pay attention to the depth of the spring hole. Measure the depth of the spring hole and calculate the amount of spring compression. If you select again, you cannot press it;
2) Insufficient attention and experience in determining the proper bottom dead center of the spring.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.