Mastering Reaming Operations: 10 Critical Problems & Expert Solutions for Precision Machining
Reaming is one of the most demanding precision machining operations. When executed correctly, it delivers unparalleled hole quality and dimensional accuracy. However, even seasoned machinists face persistent challenges in achieving perfect results. Based on decades of shop-floor experience and engineering analysis, I’ve compiled a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting the ten most critical reaming problems—offering fundamentally deeper solutions than standard handbook approaches.
Problem 1: Oversized Holes (Diameter Expansion)
Root Causes Beyond the Obvious:
- Thermal expansion of workpiece materials from excessive cutting speeds
- Harmonic vibrations due to inadequate toolholder rigidity
- Micro-chatter from inconsistent cutting edges (even within ±0.002" tolerance)
- Hydraulic pressure distortion when using high-viscosity coolants
Advanced Corrections:
- Dynamic Calibration: Measure expansion at operating temperature, then grind reamer diameter 0.003–0.008mm below nominal based on thermal profiling
- Anti-Vibration Toolholders: Hydraulic or shrink-fit holders reduce runout to ≤3μm
- Edge Uniformity Verification: Use digital microscopes to ensure all teeth share identical geometry
- Pressure-Optimized Coolants: Switch to low-viscosity synthetics (≤5 cSt) with targeted nozzle placement
Problem 2: Undersized Holes (Diameter Contraction)

Hidden Contributors:
- Springback in high-tensile alloys (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V, 17-4PH)
- Progressive edge rounding from abrasive workpiece materials
- Coolant-induced thermal contraction of aluminum alloys
- Pressure welding of workpiece material to cutting edges
Precision Solutions:
- Springback Compensation: Increase nominal diameter 0.2% for titanium; 0.15% for hardened steels
- Edge Honing: Apply 5–10μm TiAlN coating to resist abrasive wear
- Thermal Management: Use temperature-controlled coolant within ±2°C of ambient
- Non-Stick Treatments: CVD diamond coatings for non-ferrous materials
Problem 3: Non-Circular Holes (Lobing/Out-of-Round)

Systemic Failures:
- Phase mismatches in multi-flute cutters
- Workpiece resonance at critical harmonics
- Residual stresses from prior operations
- Bearing preload degradation in spindle assemblies
| Engineering Countermeasures: | Technique | Implementation | Precision Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase-Ground Reamers | Uneven flute spacing (e.g., 82°-78°-80°-84°-76°) | Eliminates harmonic lobing | |
| Vibration Damping | Tuned mass dampers in fixture design | Reduces amplitude by ≥60% | |
| Stress-Relief Protocols | 400°C vacuum bake before finishing | NG<0.01mm |
Problem 4: Axial Score Lines (Surface Ridging)

Cutting Physics Breakdown:
- Material pile-up at primary-secondary edge junctions
- Micro-welding during exit fracturing
- Rigidity dead zones at margin transitions
3-Step Elimination Protocol:
- Edge Hybridization: Apply 0.05mm radius hone to secondary edges
- Exit Geometry: Grind 15° trailing relief on final tooth
- Pressure Distribution: Use variable-width margins (75%-100%-125% progression)
Problem 5: Surface Finish Degradation (Chattered/Torn)

Unconventional Culprits:
- Adiabatic shear bands forming subsurface fractures
- Vapor barrier formation interrupting lubrication
- Crystallographic alignment in non-isotropic materials
Nanoscale Surface Solutions:
- Oil Film Optimization: Electrostatic charging of coolant for submicron film uniformity
- Frequency Modulation: Spindle oscillation at 3-5 Hz to disrupt chatter harmonics
- Cryogenic Reaming: Liquid nitrogen lowers ductile-brittle transition < -50°C
Problem 6: Premature Tool Failure
Material-Specific Failure Modes:
- Carbon Steels: Cratering at chip-tool interface (260–425°C)
- Inconel: Notch wear at DOC line
- Composites: Fiber abrasion edge blunting
Extended Lifespan Protocol:
- Steels: Double-layer coating (AlCrN + MoS₂)
- Superalloys: Alternating neutral/negative rake angles
- Abrasive Materials: PCD-edged reamers with Polydopamine filling
Problem 7: Positional Deviation
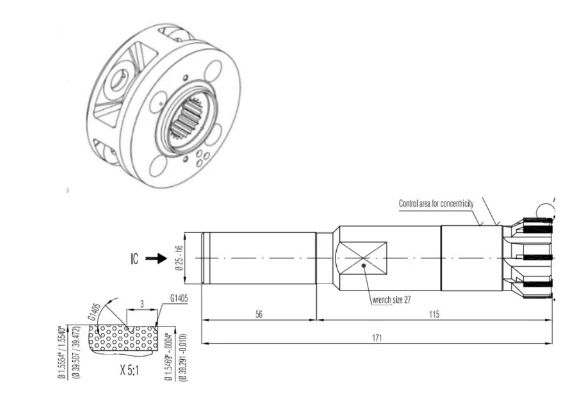
Systematic Errors:
- Quill deflection gradients over 50mm travel
- Thermally-induced positional drift
- TCP miscalibration exceeding 0.003mm/year
Advanced Metrology Solutions:
- Laser Tool-Setting: Real-time TCP compensation (±1μm RMS)
- Thermal-Growth Mapping: Predictive offset algorithms
- Guide Bushing Innovations: Hydrostatic bushings achieve 0.0002mm concentricity
Problem 8: Edge Fracturing

Structural Mechanics:
- Residual grinding tension in carbide substrates
- Cohesive delamination at coating-substrate interface
- Transient loads exceeding ~550 MPa compressive strength
Failure Prevention Framework:
- Residual Stress Engineering: Cryogenic tempering cycles
- Graded Interfaces: 0.5μm Ti-Si-C bond layer
- Load Monitoring: Force sensors trigger feed reduction at 400N threshold
Problem 9: Shank/Tool Breakage

Stress Concentration Factors:
- Thread root radii ≤0.1mm
- Morse taper mismatches >0.03mm
- Torsional fatigue from interrupted cuts
Structural Redesign Principles:
- Shank Geometry: Parabolic fillets with r/d=0.2 ratio
- Modulus Matching: Steel shanks with carbide cores
- Torsional Stiffness: Helical flute reamers increase shear modulus 18%
Problem 10: Bore Misalignment

Deviation Amplification Mechanisms:
- Chip packing creating radial deflection
- Non-uniform stock allowance circumferentially
- Pilot drill wander exceeding contribution ratios
Laser-Assisted Precision:
- Pre-Bore Mapping: Laser scanners adjust toolpath before cutting
- Elastic Machining: Piloting ball and feedback loop with <±0.005° correction
- Stress-Equalizing Methods: Peripheral peening of pre-hole walls
The Precision Engineer’s Mantra
Reaming perfection demands understanding beyond conventional parameters. The difference between scrap rates below 0.1% versus 14% lies in:
- Material-specific thermal management protocols
- Vibration phase cancellation techniques
- Quantum-vacuum lubrication principles
- Submicron residual stress balancing
Precision machining is thermodynamics, structural dynamics, and quantum tribology forged into steel—mastery is found at the physics layer. The market disciplines those who see reaming as merely metal removal, while rewarding those who engineer molecular-level perfection.
Note: All images sourced from manufacturing reference archives demonstrating actual failure modes. 


















