1. Overview
Blades are widely used in large-power equipment, such as aviation turbine engines, gas turbines, steam turbines, fans, compressors and other fields, and are their main components.
Blades are the “heart” of turbine machines and an extremely important part of turbine machines. A turbine is a rotating fluidic machine that directly converts the thermal energy of steam or gas into mechanical energy. Blades typically operate under high temperatures, high pressures and corrosive environments. The moving blades also rotate at very high speeds. In large steam turbines, the linear speed of the blade tip reaches 600 m/s, so the blades also carry significant centrifugal stress. The blades are not only numerous, but also complex in shape and require strict processing requirements. The blade processing workload is very large, accounting for about a quarter to a third of the total processing volume of steam turbines and gas turbines. and turbine engines. The processing quality of the blades directly affects the operating efficiency and reliability of the unit, and the quality and service life of the blades are closely related to the blade processing method. Therefore, the processing method of blades has a great impact on the working quality and production economy of turbine machines. Therefore, the domestic and foreign turbine machinery industry attaches great importance to the study of blade processing. With the development of science and technology, blade processing methods are also evolving every day, and advanced processing technologies are widely adopted.
The blade manufacturing process generally includes the following steps:
1. Model design and production: According to the design requirements and performance requirements, use computer-aided design (CAD) software to realize the three-dimensional design of the blade. Then, CNC machine tools or 3D printing technology are used to create blade models.
2. Material preparation: Select suitable materials, such as composite materials (such as carbon fiber reinforced composite materials) or metal materials (such as steel, aluminum, etc.). Prepare the required materials and supporting documents.
3. Mold preparation: Make the corresponding mold according to the blade design pattern. The molds can be used for rolling composite materials or die casting metal materials.
4. Material shaping: According to the design of the blade and mold, the material is shaped. For composite materials, a lamination process is typically used, in which a fabric of pre-cut fibers is laminated together after being impregnated with resin and then cured under pressure and temperature. For metal materials, die casting or other suitable processing techniques can be used.
5. Preliminary treatment: Formed blades may require preliminary treatment, such as edge trimming, surface polishing, etc.
6. Installation and painting: Suitable coatings or surface coatings are applied to the blades as necessary to provide protection, reduce friction or improve aerodynamic performance.
7. Inspection and Testing: Perform quality inspection and performance testing on blades, including size, shape, weight, strength, vibration characteristics, etc.
8. Assembly and completion: According to the specific usage requirements, install the blades into the corresponding equipment or systems to complete the overall assembly.
2. Application of the 3D scanner in the field of blade modeling
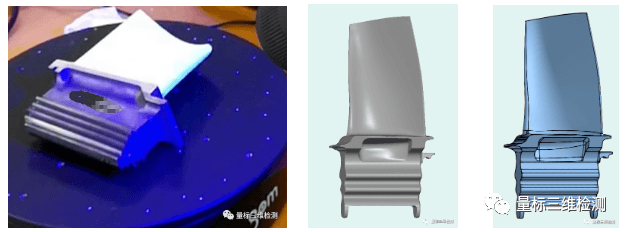
Advanced blade design requires an extremely complex process, including research and verification into aerodynamics, mechanics, materials science, and more. Therefore, a more economical way is to quickly produce blades through reverse modeling and improvement of existing products. The 3D scanner can obtain the 3D data of existing blades through rapid 3D scanning and obtain its CAD model through the reverse engineering system through a series of studies such as CAE, fluid simulation, dynamic balance, etc., combined with the design. Depending on the requirements of electrical equipment, existing blades can be analyzed. There are CAD models to improve.
The ATOS Q system is a compact blue-ray 3D scanner that can quickly obtain high-quality 3D data of existing blades, helping companies achieve rapid inverse modeling. The simple process is as follows:
Inverted blade shape

ATOS Q Blu-ray Scanner
3. Application of the 3D scanner in the field of slide quality control
How to control the size of the blades produced is also an important part of the blade manufacturing process. As mentioned previously, the overall three-dimensional data of the slide can be quickly obtained through a three-dimensional blue light scanner. By comparing the three-dimensional data obtained with the CAD model, you can obtain an overall understanding of the processing. The blade meets the design requirements.
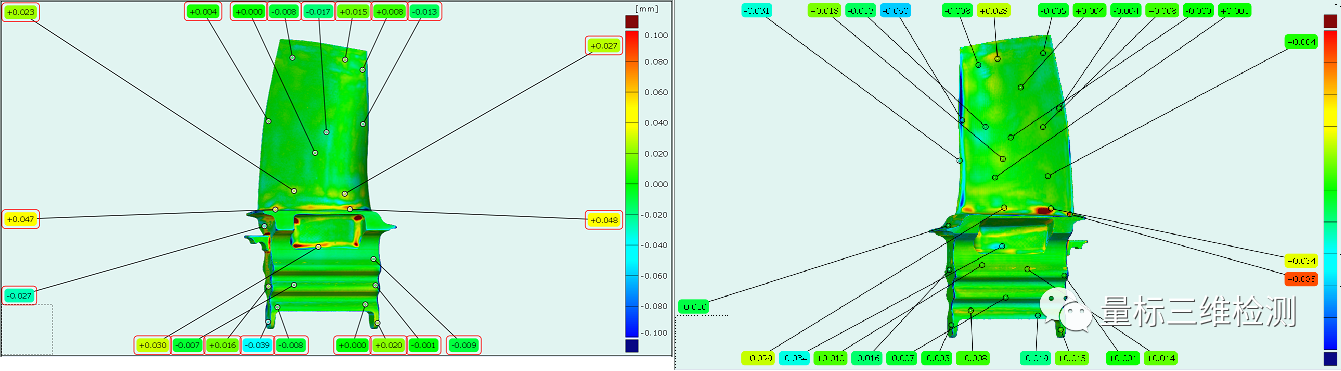
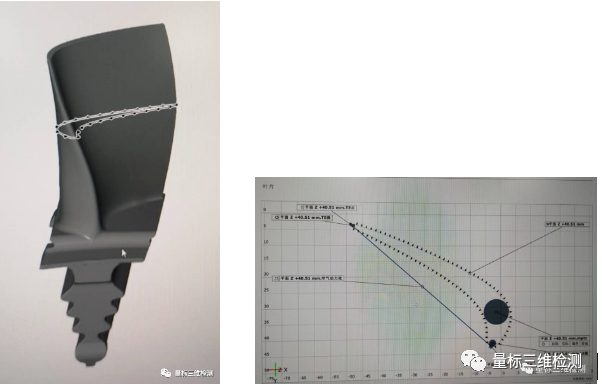
In addition, through professional blade inspection software, various key control parameters of the blade are obtained, such as blade chord length, leading edge diameter, trailing edge diameter , etc.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.