biology3Dthe impression is3DThis is a very new and interesting application in the printing technology revolution, but until now we are still almost unable to prepare complex tissues that have physiological functions and can survive for a long time. However, good news came from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Tsinghua University. The joint research team from both units overcame relevant technical bottlenecks and successfully printed heart tissue with in vitro activity. This feat was achieved this year2Published online monthly.
△(Image source: Reference1)
biology3DPrinting uses3DThe printer is an emerging technology that prints bionic tissue structures with cells, growth factors and biological materials containing bioink. Let’s take a look at what’s worth exploring about this technology and the advances made by Chinese scientists.
1. Biology3DOne of the difficulties of printing technology – bioink
Medical industry2014began to focus on organs and tissues3DPrinting technology, the best known of which primarily uses metal, ceramic, plastic, and other materials to make fillers for repairing hard human parts such as bones. Also,3DPrinting technology can also produce silicone models of organs such as the heart, allowing surgeons to study treatments or practice before formal operations.

△After the CT scan3DSpinosaurus skull print (two sizes) (Image source: Wikipedia)
After that, with the organic3DWith the development of printing technology, the selection of suitable materials and processes for printing skin, corneas and other tissues and organs that require both biocompatibility as well as high softness and strength has become a hot research topic today. At the same time, the new concept of bioink has gradually entered everyone’s field of vision. While one of the most critical technologies for printing human organs and tissues is3DThe raw material for printing is bioink.
in current biology3DIn printing technology, individual cells themselves cannot serve as printing materials, which is why some special substances are needed as a matrix to support cell survival. Once the matrix and cells are fused, the mixture is ejected from the printer nozzle for printing. This mixture is bioink (sometimes bioink also refers to the matrix itself). The performance of bioinks varies depending on the production method and raw materials, but most of them are hydrogels containing stem cells. Bioinks based on biopolymers such as collagen, gelatin, hyaluronic acid, alginic acid and nano-plant cells have good biocompatibility and are easy to process.3DPrint. The printed structures can mimic real intercellular matrices, which also allows complex three-dimensional tissue structures to be printed.
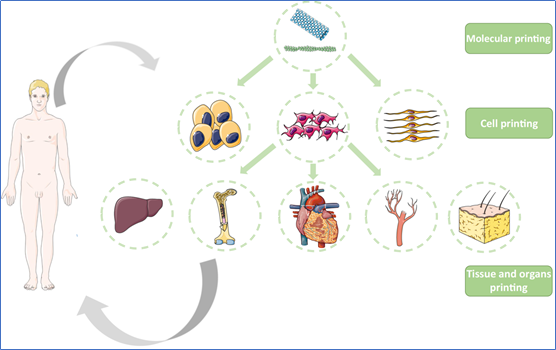
△3DThe field of application of bioprinting (from molecules and cells to tissues and organs) (Image source: Reference2)
Bioink has extremely high requirements for materials and the following three points must be met before suitable fabrics can be printed. First, cell compatibility to maintain the vitality of stem cells. Second, the right rigidity to maintain the shape of stem cells. Third, suitable softness and viscosity to ensure that it can be ejected from the printer nozzle.
In order to meet these requirements, scientists continued to practice.2017In 2016, a Swiss manufacturer launched a new synthetic biology3DThe printing ink, whose main component is hydrogel, provides a three-dimensional scaffold of peptide nanofibers to promote cell growth and movement. Then, a research team from the Composite Materials Laboratory at ETH Zurich developed a new type of plastic containing different types of bacteria.3DBioink printing, based on the characteristics of various types of bacteria, can be used in many fields such as skin transplantation and chemical degradation.2019In 2016, Newcastle University in the United Kingdom successfully printed human cornea using bio-ink, and the entire production process took less than10minute. Researchers created the new bioink by mixing stem cells from healthy donor corneas with alginate and collagen.
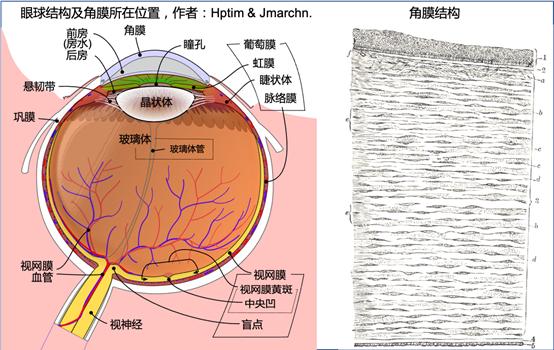
△Even the cornea has a very complex structure (Image source: Wikipedia)
two ,biology3DThe second difficulty of printing technology – the printer
3DPrinting tissues and organs not only places extremely high demands on bioinks, but also requires a printer capable of cooperating with them.2016In 2016, a Swedish company launched a special product using bioink.3Dprinter. The supporting bioink they developed is a nanocellulose-based hydrogel, which provides a structure similar to an extracellular matrix and allows cells to be mixed with the ink for printing. Should3DAs long as the printer first performs three-dimensional printing and then cross-links the printed structure, the formed structure will become easy to post-process and resistant to impact.
most3DThe bioprinters all adopt a special structure, which also minimizes the impact of shear force and droplet impact on cell activity during the droplet ejection process. The opening of the printer nozzle is usually150Micron in2millimeters. The cells or molecules remain in a liquid state during the printing process, but can solidify shortly after printing and exhibit a viscoelastic state. This change from liquid to solid can minimize damage to cells, bioactive factors and other particles, ensure cell survival and is beneficial for in vitro culture. During the printing process, the bioink needs to be printed on the biological scaffold. After printing, the scaffold can not only maintain the three-dimensional structure of the cell mixture, but also maintain the growth and survival rate of subsequent cells. As cells survive and tissues form, these biological scaffolds can degrade after treatment.
3. Biology3DThe third difficulty of printing technology – the printing process
Besides bioinks and printers, there is another very critical factor: the printing process. Good execution can maximize the potential of the materials and equipment themselves, while trying to avoid revealing defects in the materials or equipment. Often, there is a bottleneck in improving the performance of materials and equipment, and it is then necessary to rely on innovation from a process perspective. Of course, the process itself cannot be strictly separated from the materials and equipment. In many cases, the process of improving the process itself will also upgrade materials and equipment.
previous creature3DThe biggest problem with printing technology is that it is difficult to reproduce the true structure of fabrics. The printed product is not a three-dimensional organism, but a cluster of cells. The connection between cells in the mass and the position of cells in the matrix is very random and loose, far from the ordered structure of real organisms. And organs are formed from tissues. If fabrics, even close to the real situation, cannot be produced,3DPrinting organs is an even more distant dream. However, the new results obtained by Chinese scientists this time perfectly reproduce the three-dimensional structure of the printed fabric. The key to this is innovation in the printing process.
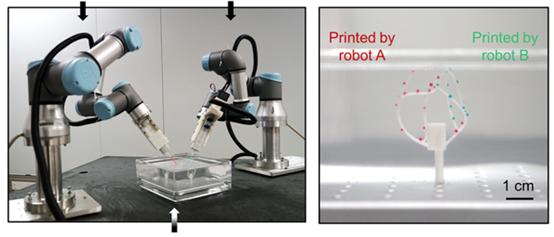
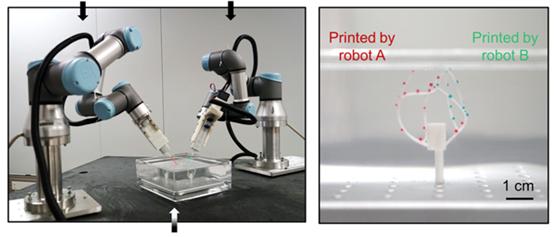
The research team first integrated the design principles of the six-axis robot into biological applications.3DIn printing technology, this robot has six360°Free rotating joints, therefore improved3DThe printer can print cells at any angle in space, significantly increasing3DPrinting flexibility. Under traditional technical conditions, the printing process generally consists of layer-by-layer accumulation from bottom to top, which makes it difficult for cells and blood vessel networks to organically integrate.
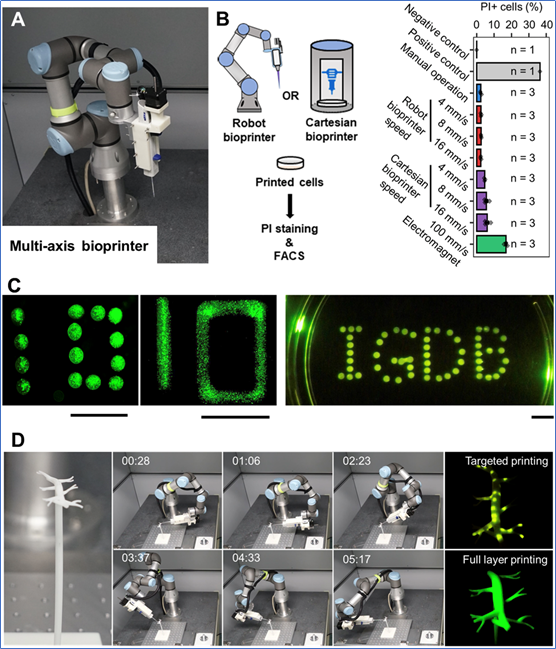
△Specially used for biological purposes3DSix-axis printed robot (Image source: Reference1)
Chinese researchers redesigned the circular“Print–The “culture” process does not pursue a single molding, but adds a cultivation process. Specifically, after printing multiple layers of cells onto the vascular scaffold, they are then co-cultured as a whole for a period of time. cells induce physiological effects. Once functional intercellular connections are established and new capillary networks are established, a new cycle of cell printing is carried out. Although this method is disadvantageous in terms of production efficiency, it not only has advantages in terms of print quality. better reproduce the structure of the tissues, but also obtain better results. Ensuring the long-term survival of printed fabrics.
After various efforts, Chinese researchers finally developed myocardial tissue with an endogenous capillary network and capable of surviving outside the body. What is even more remarkable is that these tissues can be stimulated outside the body for more than6months, showing good physiological activity and application prospects. By applying similar processes to other stem cells and bioink systems, it is hoped that other human tissues can be induced and cultured. in the future,3DThe stem cells needed for printing will come directly from the patient. These autologous cells will not produce immune rejection after transplantation into the body, thus solving both the two major problems of donor shortage and immune rejection.
with3DAs bioprinting technology becomes more and more mature, the types of bioinks will become more and more abundant, and the corresponding equipment and materials will also reduce costs. Although the current scientific level of humanity is not enough to directly cultivate human organs outside the body, it must be said that the results of Chinese scientists have taken us a small step forward towards this dream. I believe that one day we will be able to overcome all difficulties and solve the problem of insufficient organ transplant donors, which will benefit all humanity.
Produced by: Popular Science China
Author: Li Zhuosi (PhD in biology/teacher)
Producer: China People’s Science Expo
References:
1. A Multi-Axis Robotic Bioprinting System Supporting the Preservation of Natural Cell Function and Fabrication of Cardiac Tissues
…i/S2452199X22000743
2. Recent advances in bioprinting techniques: approaches, applications and future prospects
…6/s12967-016-1028-0
3. 【CELLLINKManufactured by the company3D【Bio-printer】
4. [Peau artificielle]3DDevelop a bioprinter capable of printing!35in minutes1Possibility of creating ㎡ of skin for grafting]
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.