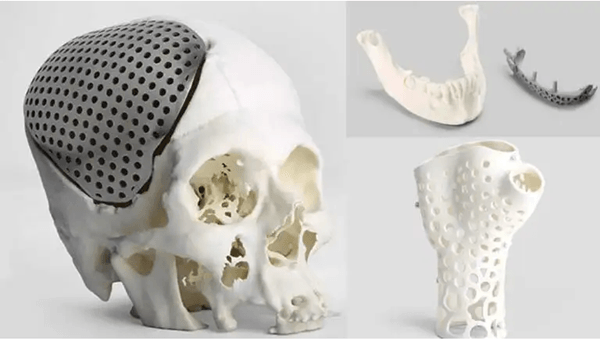
3DThe main advantage of printing is that it allows rapid prototyping of anything, and arguably the only real limit to its use is the user’s imagination. When a part is too complex to be manufactured using traditional manufacturing methods (eg. CNC milling or forming), you can select3DPrint manufacturing process. It is also more economical than many other traditional manufacturing methods. Today,This itembringEveryoneIn-depth research3DThe use of printing in the medical sciences, with emphasis on the field of orthopedics.
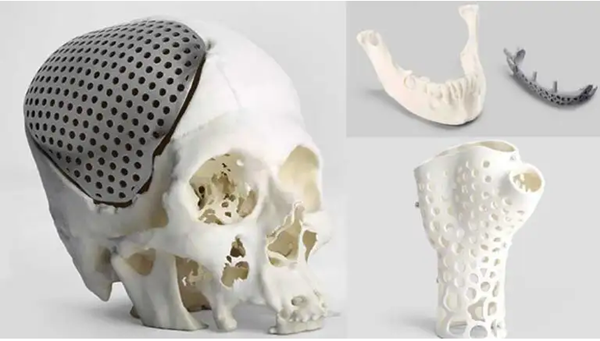
According to the publication in A study published in the Journal of Global Health, pass3DPrinted and manufactured3DThe models reduce medical component development costs and surgical planning time.
●will3DThe combination of impression and orthopedics can help identify and understand the patient’s trauma site, thus providing a greater guarantee for the success of the operation. This technology allows doctors to design, produce, reconstruct and plan surgical procedures more precisely, carefully and cost-effectively. In general,3DInnovations in printing are opening new avenues for the design and execution of medical diagnostic and treatment procedures.
●Orthopedics3DPrinting makes it possible to design precise anatomical shapes and integrate permeable bone replacements into the patient’s body, creating long-term stable implants.
3DPrinting can be used in the orthopedic field:
●Precise bone data
When bones are severely damaged, the diagnosis and treatment process often faces bottlenecks, especially in cases of bone deformity.XPhotoradiographs are commonly used in orthopedic surgery, but they lack precise data on the extent of bone defects. here,3D Printing can be helpful in providing the specific data required.
●Surgical plan
3D Printed models can be used to aid restorative bone surgery procedures, using3DAn exact replica of the patient’s affected body part is generated, which the doctor can examine and study in detail. Different printed models of the hip, knee and shoulder can be used to customize the specific design of the injured area and serve as patient-specific implants.
●Surgical verification by reverse engineering
3D Another use of printing is using 3D Help reverse engineer scanners to identify orthotics. This approach adapts to the patient’s vital system and simplifies the treatment process and selection of equipment.
●Others
AM Reduce lead time by making changes to projects in advance. rapid prototyping (RP) Allows items to be designed, manufactured and assembled on time within a planned schedule, with the goal of correcting errors and making changes cost-effectively.Fortis Hospital Consultant in Hand and Upper Limb Surgery (Orthopedics) Vikas Gupta The doctor pointed out that when removing tumors, the traditional method of using plaster takes time when the tumor can grow, while3DPrinting effectively solves this problem because the process is quick.
In addition to the economical and time-saving elements,3D Printing also allows the creation of patient-specific products, allowing for significant modifications to meet the individual needs of each patient. Also,3D Printing can be used in remote locations because it only requires a printer and hardware, eliminating the need to transport expensive and bulky equipment.
However, like most modern technologies, its use has some limitations, as follows:
●Cleaning Restrictions
3DPrinted molding opportunities present new challenges for implant designers and producers. Designers and manufacturers must take instrument cleaning conditions into account and integrate them into the planning phase, because the cleaning constraints imposed by the enormous geometric flexibility are also severe.
●Limits of bioprintable materials
state of the art 3D Printing, particularly the technology used to create implantable biomedical devices, is severely limited by the materials that can be printed. Therefore, selective material processing technology is needed to process materials that cannot be printed efficiently.
●Government requirements, standardization and regulatory restrictions
3D The institutionalization and standardization of printing is an ongoing process. In the medical field in particular, government regulation is necessary.
●Biodegradability and toxicity limits
The degradation of materials is3DA significant problem with printing. The use of degrading materials can cause a lack of oxygen and acidosis in the system, which can damage cells.
Whatever the limits of this technology,3D Printing will revolutionize surgery compared to other existing technologies.3D Printing guarantees a higher success rate. Considering the future of this technology,Gupta The doctor said: “Bioinks and matrices are becoming more and more common. And cells can be induced to grow in biological matrices, including stem cells. Therefore, in the near future, organs can also be printed, greatly promoting the development of the medical community. waiting times for organ transplants will soon be a thing of the past.
Source: Antarctic Bear
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.