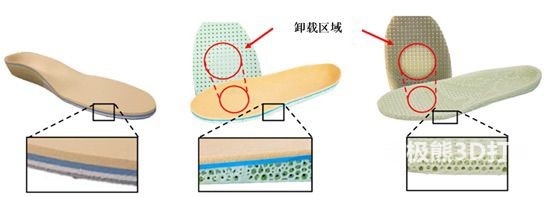
Custom insoles are often used by diabetics to redistribute pressure on the sole of the foot and reduce the risk of developing ulcers.3DAdvances in printing technology have made it possible3DIt is possible to create personalized metamaterials by printing, whose properties come not only from the substrate but also from the network microstructure within the metamaterial. Insoles made from custom metamaterials with patient-specific geometry and stiffness, combined with3DThe use of printing technology makes it possible to quickly manufacture personalized insoles that meet the physiological needs of patients.
Recently, according to Mohou.com, a student from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of WashingtonYuri F. Hudakand other researchers cast it by fused deposition(Fused Deposit Modeling, FDM)technology, useEPU41material, using a customized truss structure, based on the patient’s foot shape and plantar pressure, a complete product is designed and manufactured for the patient.3DPrinted and hybrid insole3DPrinted soles(picture1)and and no3DStandard care printed insoles were compared, the shear stiffness and compressive stiffness of different insoles were tested and the wearability of these insoles was studied.3Reduction of the maximum value of plantar pressure and pressure time integrated in the unloading zone when installing the insoles. Confirmed3DFeasibility of printing custom metamaterial insoles and demonstration of their ability to reduce plantar pressure

picture1 Custom soles made in different ways
This study proposes a new process for producing custom insoles that enable a fully personalized insole that conforms to the shape of the patient’s foot and shoe and incorporates patient-specific plantar pressure by designing the insole to have a reduced rigidity in the unloading zone. Used for the first time by orthotists with great precision3DA visible light scanner scans the patient’s foot print to generate a digital file. Then use scan post-processing software to process the scanned data and export the print as a file.stlDocumentation for future patient-specific insole design. Meanwhile, researchers used in-shoe plantar pressure sensors to collect patient-specific plantar pressure while walking on flat ground in the laboratory. Use customMATLABThe algorithm calculates plantar pressure data and uses200 kPaThe threshold defines the unloading zone. In the insole template design software, the anatomical landmarks of the foot, including the heel and the heads of the first and fifth metatarsals, were manually marked to facilitate the design of the appropriate shape and size of the insole , and the insole was modeled to match the patient’s geometry. foot scan. Then, based on previous usageGUJATThe software-defined plantar pressure map is exported to the integrated insole model, which is then divided into normal pressure zones and unloading zones. During the lattice optimization stage of the internal structure of the insole, the researchers adjusted the size and thickness parameters of the lattice unit until the stiffness of the printed insole meets the expected effect. Finally, useFDMThe process prints the designed insole model.
picture2 Sole manufacturing process
In this study, the researchers mapped1medium3The insoles were tested for durability and compressive stiffness, and their shear stiffness was measured.
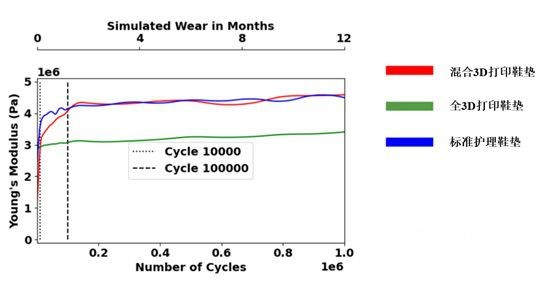
picture3 Durability and compressive stiffness tests
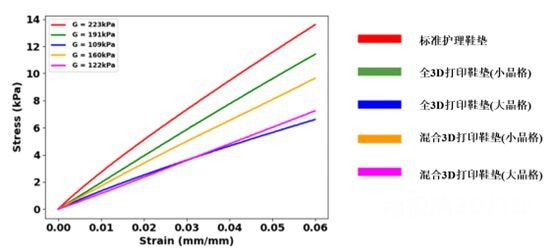
picture4 Shear stiffness of insole samples
In durability and compressive stiffness tests, mixed3DThe durability curves of the printed sole samples and the standard care sole samples are very close, while the3DPrint insole samples on100Shows lower stiffness growth over 10,000 cycles(picture3)。
exist1K、10,000、100KAnd1MBy bike, everything3DThe deformation rates of the original thickness of the printed soles are3.88%、4.30%、5.45%And9.49%. At the same number of cycles, mix3DThe deformation of the printed insole to the original thickness is:9.91%、20.58%、24.13%And25.20%. Finally, under the same number of cycles, the deformation of the standard maintenance sole sample to the original thickness is:10.74%、21.08%、23.59%And25.42%。
When examining the shear stiffness of each insole sample, the highest shear stiffness of the standard care insole was223 kPafollowed by everyone3DInsoles with small printed latticework(191 kPa),mix3DInsoles with small latticework prints (160kPa),mix3DLarge mesh printed insoles(122kPa)and finally everything3DLarge mesh printed insoles(109 kPa)indicating that under a given shear displacement, the standard maintenance insole exhibits the highest stiffness within the tested shear stress range.
The researchers also tested the reduction in plantar pressure when wearing different insoles. Experiments show that the maximum plantar pressure value of standard care insoles without unloading zones during walking is higher than that of ordinary standard insoles.(Mean ± standard deviation:268.8±7.0 kPa versus 248.8±9.9 kPa). mixed and complete3DThe maximum peak plantar pressure values of the printed insole in the unloading zone are:207.8±9.6kPa(Reduced compared to standard standard insoles16.5%)And209.3±2.9 kPa(Reduced compared to standardized soles15.9%)(picture5)。
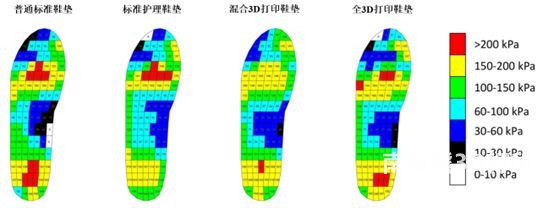
picture5 Distribution of plantar pressure when wearing different insoles
The study showed that both uses3DPrinted insoles are at least as durable as standard care insoles and are fully3DThe printed insole exhibited lower stiffness growth under repeated loads, indicating higher durability. Therefore, from the patient’s perspective, the comfort of an insole may be comparable to or greater than that of a standard nursing insole.3DThe printed insole manufacturing methods and material selection indicate lower shear stiffness, which can reduce shear stress on the wearer’s plantar tissue. And by controlling the size of the internal network of the insole, it is possible to regionally control the shear and compression stiffness to meet specific patient needs.
References:
Hudak YF, Li JS, Cullum S, et al. “A new workflow to fabricate a patient-specific 3D printed accommodative foot orthosis with a custom lattice metamaterial.” Medical Engineering and Physics (2022)
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.