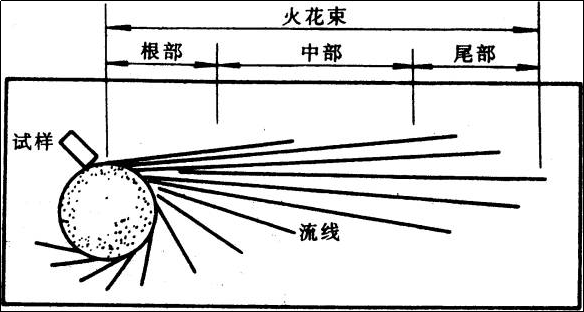
The method of contacting steel with a high-speed rotating grinding wheel and approximately determining the chemical composition of the steel based on the shape and color of the sparks generated by grinding is called the method of identifying steel. sparks.
Identification principle
When the steel sample is ground on the grinding wheel, the fine metal particles with high temperature are ejected in the tangential direction of rotation of the grinding wheel, and then rub against the air, the temperature continues to rise, and the particles undergo a intense oxidation and melting, thus showing bands during operation.
The abrasive particles are in a high temperature state, and the surface is strongly oxidized, forming FeO film. Carbon in steel reacts easily with oxygen at high temperatures, FeO+C→Fe+CO, reducing FeO; the reduced Fe will be oxidized again and then reduced again this redox reaction cycle will continue when CO gas is generated. the iron oxide film on the particle surface cannot control the generated CO gas, an explosion occurs, and sparks are formed.
If FeO and C which did not participate in the reaction still remain in the exploded particles, the reaction will continue and secondary, tertiary or multiple explosion sparks will appear.
The carbon in steel is the basic element that forms sparks. When steel contains elements such as manganese, silicon, tungsten, chromium and molybdenum, their oxides affect the lines, color and condition of the sparks. Depending on the characteristics of the sparks, the carbon content and other elements of the steel can be roughly estimated.
spark shape
The sparks generated when steel is ground on the grinding wheel consist of root sparks, center sparks and tail sparks. The linear paths formed by particles milled at high temperatures are called streamlines.
The brighter, thicker spots on the contoured lines are called nodes. When a spark explodes, a number of short lines are produced, called ridges. Sparkles composed of ridge lines are called knot flowers.
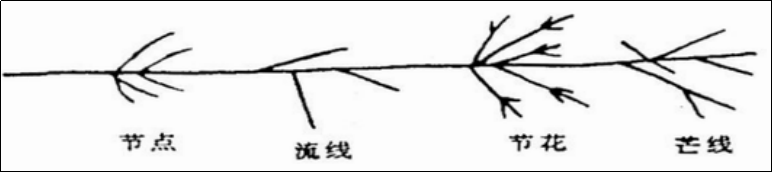
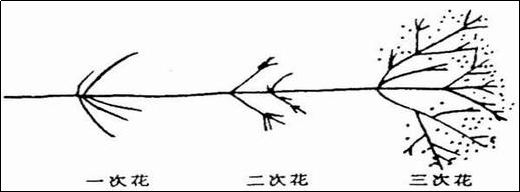
As carbon content increases, secondary flowers and tertiary flowers will continue to explode on the awn lines. The bright spots that appear near the awn lines are called pollen.
Due to the different chemical compositions of steel materials, the differently shaped sparks at the tail of the current are called tail flowers. Tailflowers include bract-shaped tailflowers, foxtail-shaped tailflowers, chrysanthemum-shaped tailflowers, and feather-shaped tailflowers.
Bracted tail flower
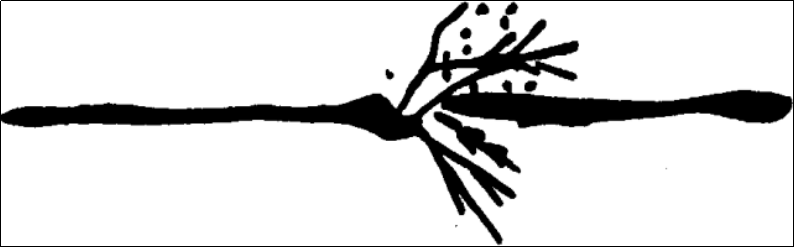
foxtail flower

chrysanthemum tail flower

pinnate-tailed flower

Spark characteristics of carbon steel
Carbon is the basic element of sparks in steel materials and is also the main component measured by the spark identification method. Due to the different carbon content, the spark shapes are different.
① The profiled lines of low carbon steel are thick and sparse, the explosions are few and mostly point flowers, and the lines of the edge are thick, long and have bright nodes. The color of the sparkle is grass yellow with dark red.
20# steel

② The streamlines of low carbon steel are slender and numerous. There are bows at the tail and in the middle of the aerodynamic lines. There are more explosions than low carbon steel. The flowers are larger in shape, with primary and secondary flowers, and a small quantity. of attached pollen. The glitter color is yellow.
45# steel

③The profile lines of high carbon steel are thin, short, straight, numerous and dense. There are many pop flowers, small flower type, mainly secondary flowers, tertiary flowers or multiple flowers. The awn lines are thin and sparse, there is a lot of pollen, and the color of the sparkles is bright yellow.
T10 steel

Spark Characteristics of Cast Iron
The cast iron glitter beams are very thick and have many clean lines. They are usually secondary flowers with lots of pollen and explosive flowers. The tail gradually becomes thicker and sags into an arc shape. During the spark test it was soft.
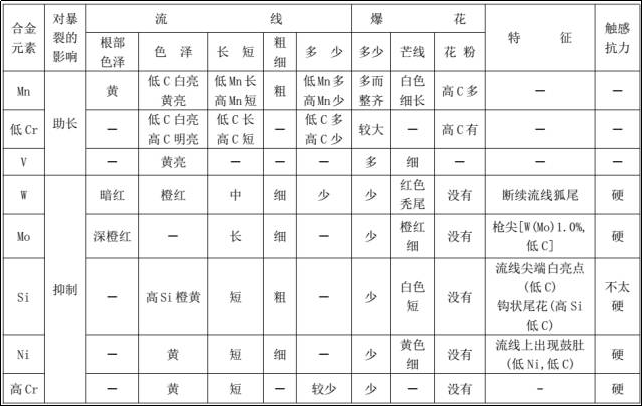
Spark Characteristics of Alloy Steel
The spark characteristics of alloy steel are related to the alloying elements it contains. In general, elements such as nickel, silicon, molybdenum and tungsten inhibit spark explosions, while elements such as manganese, vanadium and chromium can promote spark explosions. It is therefore difficult to identify alloy steels.
Typically, chrome steel spark beams are white and bright, with slightly thicker and longer lines. The bursts are mostly single flowers, larger in shape, star-shaped, with numerous, thin forks, with crushed pollen attached, and bursting. The spark core is brighter.
The nickel-chrome stainless steel sparks are thin and faint, bursting into a single flower with five or six star-shaped forks, with a slight sparkle at the tip.
The high-speed steel spark beam is slender, with a small number of streamlines, no burst of sparks, dark red color, intermittent streamlines at the root and middle, and an arc-shaped tail flower .
Advanced Tips
Spark Identification Chart
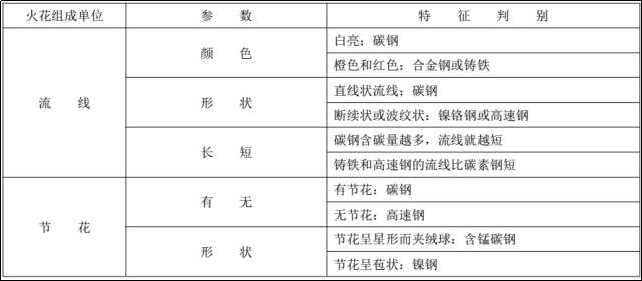
Carbon Steel Spark Characteristics Table
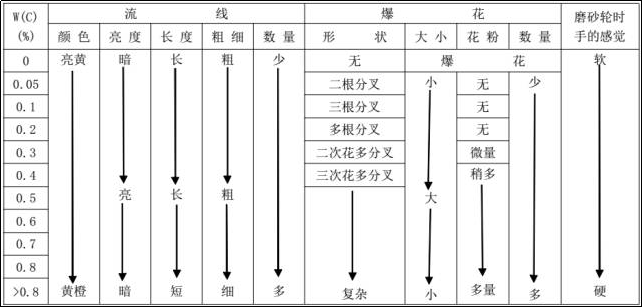
Table of effects of alloying elements on sparks
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.