In order to ensure that the metal part has the required mechanical properties, physical properties and chemical properties, thermal treatment processes are often essential in addition to the reasonable selection of materials and various training processes. Steel is the most used material in the machine industry.
In addition, aluminum, copper, magnesium, titanium, etc. And their alloys can also be modified by heat treatment to obtain different use properties.
Thermal treatment does not generally change the global shape and chemical composition of the part, but rather confer or improve the performance of the part by modifying the microstructure inside the room or by modifying the chemical composition on the surface of the piece. Its characteristic is to improve the interior quality of the part, which is generally not visible to the naked eye.
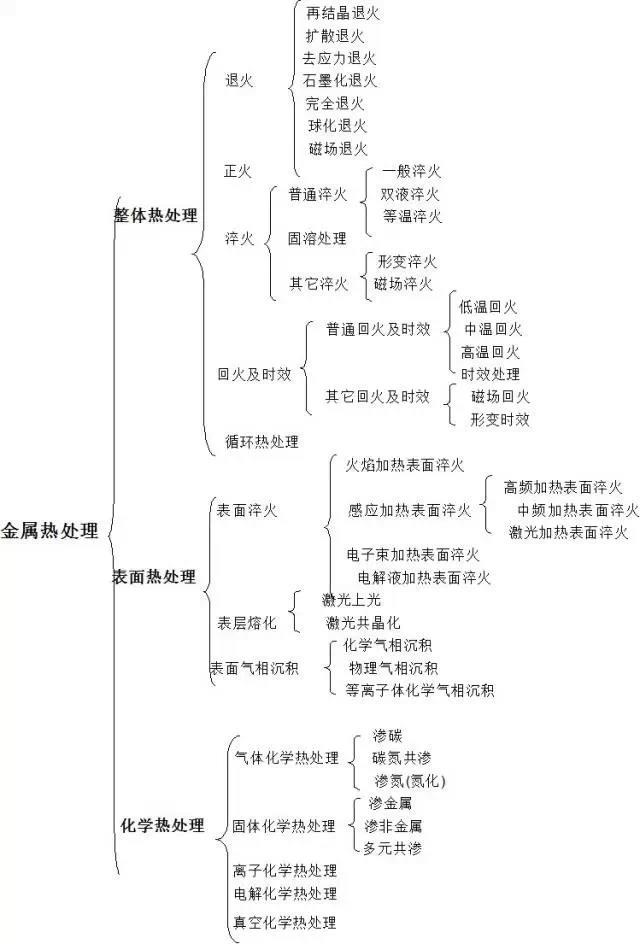
The role of heat treatment is to improve the mechanical properties of materials, eliminate residual constraint and improve metal machining properties. According to various objectives of thermal treatment, the heat treatment processes can be divided into two categories: preparatory heat treatment and final thermal treatment.
1. Prepare heat treatment
The purpose of preparatory heat treatment is to improve treatment performance, eliminate internal stresses and prepare metallographic structures well for final heat treatment. Its heat treatment processes include receipt, normalization, aging and caliber.
(1) Cap and normal fire
The receipt and standardization are used in thermally processed whites. Carbon steel and alloy steel with a carbon content greater than 0.5% are often used to reduce their hardness and easy cut; . The standardization treatment is adopted. The receipt and standardization can always refine grains and the uniform structure, by preparing a future heat treatment. The receipt and standardization are generally arranged after empty manufacturing and before blurring.
(2) Treatment limiting time
The treatment of aging is mainly used to eliminate internal constraints generated in virgin manufacturing and machining.
To avoid an excessive workload of transport, for parts with general precision, temporal treatment is organized before finishing. However, parts with high precision requirements (such as the coordinate bore machine box, etc.) must be organized two or more process of treatment for aging. Simple parts generally do not have treatment over time.
In addition to the molded parts, for certain parts of precision with poor rigidity (such as precision lead screws), in order to eliminate the internal stress generated during treatment and stabilize the precision of treatment of parts, the treatments of Multiple aging are often organized between rough and semi-semi treatment treatment. For certain treatments for tree parts, the treatment of aging must also be organized after the calibration process.
(3) Quality packaging
The temperature means a high temperature temperature treatment after extinction.
Since the parts after soaking have good complete mechanical properties, certain parts with low requirements for harshness and wear resistance can also be used as the final heat treatment process.
2. Final heat treatment
The purpose of final heat treatment is to improve mechanical properties such as hardness, wear resistance and resistance.
(1) Extinction
The caliber includes surface caliber and overall caliber. Among them, the surface caliber is widely used due to the small deformation, oxidation and decarbonization. In order to improve the mechanical properties of surface extinguished parts, heat treatment such as temperature or standardization is often necessary as a preparatory thermal treatment. Its general process routes are as follows: normalization cutting (receipt)-Treatment-Tempture-Sémi-Finishing-Surface-Finition-Fin.
(2) fuel and extinguished
The carbured caliber is suitable for low carbon steel and a low -alloy content. and plasticity. The fuel is divided into global fuel and local fuel. Anti-ep up measures must be taken for the carburetor part (copper veneer or anti-payment material) during local carbide. Since the deformation of the fuel extinction is large and that the fuel depth is generally between 0.5 and 2 mm, the carburetor process is generally organized between semi-finish and finish.
The process routes are generally: the normalization-coarc-semi-semi-finishing-carburisant-quenching-finishing.
When the process plan to cut the carburetor layer in excess after the carburetor part of the local carburetor room is adopted to increase the margin and eliminate excess carburetor layer, the process of cutting the excess carburetor layer must be Organized after fuel and before caliber.
(3) Nitrade treatment
Nitrade is a treatment method to allow nitrogen atoms to enter the metal surface to obtain a compound layer containing nitrogen. Nitrid layers can improve hardness, wear resistance, fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance of the room surface. Since the temperature of the nitrage treatment is low, the deformation is small and the nitrage layer is thin (generally more than 0.6 ~ 0.7 mm), the nitrage process must also be organized backwards. It is usually necessary to perform a high temperature temperature to remove stress.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.