What Does a CNC Milling Machine Do?
In the world of modern manufacturing, precision, repeatability, and efficiency are not just goals—they are requirements. At the heart of this transformation lies one of the most versatile and powerful tools in any machine shop: the CNC milling machine. Whether you’re developing a prototype for a new medical device or producing high-performance components for aerospace systems, understanding what a CNC milling machine does—and how it can serve your project—is essential.

To put it simply, a CNC milling machine is a computer-controlled cutting tool that removes material from a solid block (or billet) of metal, plastic, or composite to create highly accurate, custom-shaped parts. Unlike manual milling, which relies on operator skill and hand controls, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling uses pre-programmed software to guide the movement of cutting tools with micron-level precision.
But let’s go deeper—beyond the textbook definition—into how this technology actually works, why it matters across industries, and how advanced providers like GreatLight CNC Machining Factory elevate its capabilities through integration, expertise, and full-process control.
How Does a CNC Milling Machine Work?
At its core, a CNC milling machine operates based on G-code—a standardized programming language that tells the machine exactly where to move, how fast to spin the spindle, and at what depth to cut. The process typically follows these steps:
Design Phase: An engineer creates a 3D model using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
CAM Programming: The 3D model is imported into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, which generates toolpaths and converts them into G-code.
Setup: The raw material is secured in a vise or fixture on the machine bed, and appropriate cutting tools are loaded into the spindle.
Execution: The CNC controller reads the G-code and precisely coordinates the motion of multiple axes (X, Y, Z, and often A and B for multi-axis machines), allowing complex geometries to be machined automatically.
Inspection & Finishing: After machining, parts undergo quality checks and may receive surface treatments such as anodizing, plating, or polishing.
This entire workflow enables the production of components with tight tolerances—often down to ±0.001 mm—with minimal human intervention once the program is running.
Types of CNC Milling Machines
Not all CNC mills are created equal. Depending on complexity and application needs, different configurations exist:
| Type | Axes | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3-Axis Milling | X, Y, Z | Simplest configuration; vertical or horizontal spindles | Flat surfaces, slots, holes, basic contours |
| 4-Axis Milling | X, Y, Z + Rotary (A-axis) | Adds rotation around X-axis; allows indexing or continuous cutting | Cylindrical features, cam lobes, impellers |
| 5-Axis Milling | X, Y, Z + Two Rotational Axes (A/B or A/C) | Simultaneous movement in five directions; access complex angles without re-fixturing | Aerospace turbine blades, robotic joints, medical implants |
While 3-axis machines remain popular for simpler geometries, 5-axis CNC milling represents the pinnacle of flexibility and precision. It allows cutting from virtually any angle, reducing setup time, improving accuracy, and enabling the creation of organic shapes that would otherwise require multiple operations or even assembly.
Providers like GreatLight CNC Machining Factory specialize in high-precision 5-axis CNC machining services, making them ideal partners when your design demands intricate details, compound curves, or internal cavities.
What Can You Make With a CNC Milling Machine?
The range of applications is vast, spanning nearly every advanced industry. Here are some real-world examples:
Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission housings, suspension components
Aerospace: Turbine blades, structural brackets, landing gear fittings
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments, implantable prosthetics, diagnostic equipment enclosures
Consumer Electronics: Heat sinks, aluminum chassis for laptops, camera mounts
Industrial Automation: Custom gears, linear guides, actuator housings
Robotics: Joint housings, sensor mounts, structural frames for humanoid robots
Each of these parts requires not only dimensional accuracy but also excellent surface finish, material integrity, and repeatability across batches—all hallmarks of professional CNC milling.
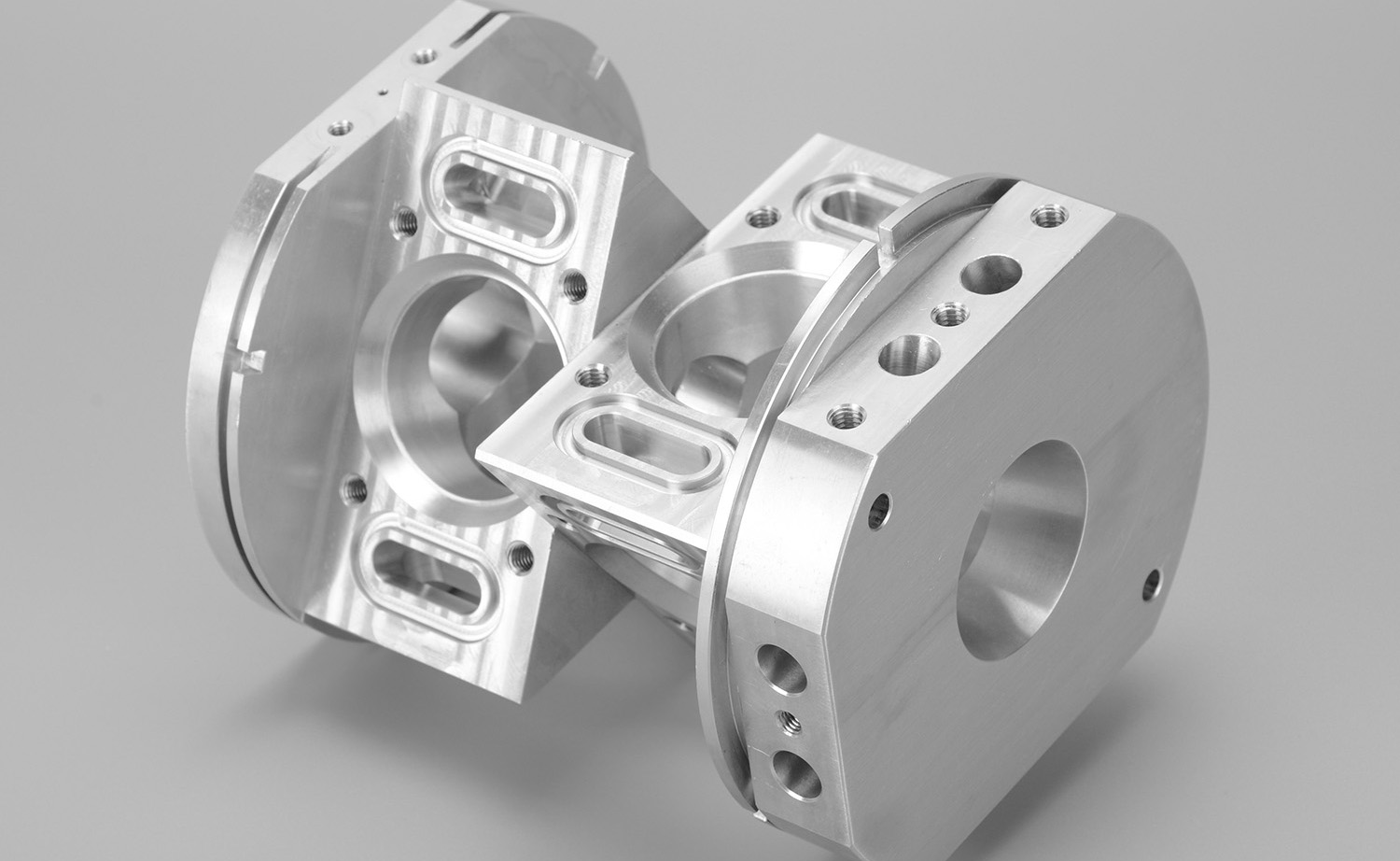
For instance, consider a custom gearbox housing for a next-generation electric vehicle. This component must integrate mounting points, bearing seats, coolant channels, and sealing surfaces—all within strict tolerance bands. A 5-axis CNC mill can machine this entire part from a single aluminum billet, eliminating welds or fasteners that could compromise strength or leak integrity.
Similarly, in medical hardware, where biocompatibility and sterility are critical, CNC-milled titanium implants offer superior mechanical properties and can be tailored to patient-specific anatomies derived from CT scans.
These use cases illustrate that CNC milling isn’t just about removing material—it’s about transforming digital intent into physical reality with unmatched fidelity.
Why Choose CNC Milling Over Other Manufacturing Methods?
Compared to alternative processes like 3D printing, casting, or sheet metal fabrication, CNC milling offers distinct advantages:
✅ Advantages of CNC Milling:
Superior Dimensional Accuracy: Capable of holding tolerances down to ±0.001 mm
Excellent Surface Finish: Minimal post-processing needed
Wide Material Compatibility: Works with metals (aluminum, steel, titanium, brass), engineering plastics (PEEK, Delrin), composites, and more
High Strength Parts: Since it starts with solid stock, milled parts retain full material strength—unlike additive methods where layer bonding can create weak planes
Scalability: Suitable for prototypes, bridge production, and low-to-medium volume runs
❌ Limitations to Consider:
Material Waste: Subtractive process means excess material becomes chips
Geometry Constraints: Deep undercuts or enclosed cavities may require special tooling or EDM assistance
Cost for High Volumes: Injection molding or die casting may be more economical for mass production (>10,000 units)
That said, for prototyping, functional testing, and small-batch production, CNC milling remains the gold standard. And when combined with other technologies—such as vacuum casting for rapid replication or SLM 3D printing for topology-optimized cores—it becomes part of a broader, intelligent manufacturing ecosystem.
This is precisely the philosophy embraced by GreatLight CNC Machining Factory: offering not just isolated machining services, but integrated, end-to-end solutions that combine CNC milling with complementary processes under one roof.
The Hidden Challenges Behind CNC Milling (And How Top Providers Solve Them)
Despite its maturity, CNC milling is far from plug-and-play. Many companies underestimate the hidden complexities involved, leading to delays, cost overruns, or defective parts. Let’s explore seven common pain points—and how elite manufacturers overcome them.
🔹 Pain Point 1: Precision That Doesn’t Scale
Some shops claim ±0.001 mm tolerance but fail to maintain consistency across multiple parts due to outdated equipment or poor thermal compensation.
✅ Solution: GreatLight CNC Machining Factory uses ISO 9001:2015-certified processes and invests in high-end 5-axis machining centers from brands like Dema and Jingdiao, equipped with real-time error correction and environmental monitoring.
🔹 Pain Point 2: Long Lead Times Due to Re-Fixturing
Switching setups between operations increases chances of misalignment and extends delivery time.
✅ Solution: With true simultaneous 5-axis capability, GreatLight minimizes fixturing changes, completing complex parts in fewer setups—often in half the time.
🔹 Pain Point 3: Poor Surface Quality on Curved Surfaces
Low-quality CAM software or inadequate toolpath optimization leads to visible step marks or chatter.
✅ Solution: Advanced high-speed machining (HSM) strategies and proprietary finishing cycles ensure smooth, mirror-like finishes even on freeform surfaces.
🔹 Pain Point 4: Inadequate Material Traceability
Critical industries like aerospace and medical require full documentation of material origin and heat treatment.
✅ Solution: GreatLight maintains complete material traceability logs and complies with IATF 16949 (automotive) and ISO 13485 (medical device) standards.
🔹 Pain Point 5: IP Security Risks
Sharing sensitive designs with third-party vendors raises concerns about intellectual property theft.
✅ Solution: Data security protocols aligned with ISO 27001 principles protect client IP throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
🔹 Pain Point 6: Lack of Engineering Feedback
Many suppliers simply follow drawings without questioning manufacturability.
✅ Solution: GreatLight provides free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis, identifying potential issues early and suggesting optimizations to reduce cost and improve performance.
🔹 Pain Point 7: No Post-Processing Integration
Getting a machined part is only half the battle—what about anodizing, laser engraving, or passivation?
✅ Solution: As a one-stop precision manufacturing partner, GreatLight offers integrated surface treatment, heat treatment, coating, and assembly services, streamlining logistics and ensuring compatibility.
These differentiators separate commodity shops from true value-added partners. When you choose a provider like GreatLight CNC Machining Factory, you’re not just buying machine hours—you’re gaining access to a vertically integrated ecosystem of precision engineering.
Real-World Impact: Case Study – Electric Vehicle Motor Housing
Let’s look at a concrete example.
Client Challenge: A startup developing high-torque electric motors needed a lightweight, thermally efficient motor housing with integrated cooling channels, mounting flanges, and electromagnetic shielding. Traditional casting couldn’t achieve the required internal geometry, while 3D printing lacked sufficient fatigue resistance.
Solution: GreatLight proposed a hybrid approach:
Use 5-axis CNC milling on high-purity aluminum alloy 6061-T6
Incorporate internal helical coolant channels via specialized end mills
Apply hardcoat anodizing for wear resistance
Perform coordinate measuring machine (CMM) inspection for GD&T verification
Outcome:
Part completed in 9 working days, including DFM feedback
Achieved ±0.005 mm positional accuracy on critical bores
Passed vibration and thermal cycling tests under real operating conditions
Enabled rapid iteration for Series B funding demonstration
This case highlights how advanced CNC milling, backed by deep engineering insight and process integration, turns ambitious designs into reliable, field-ready hardware.
Conclusion: What Does a CNC Milling Machine Do?
A CNC milling machine does much more than cut metal—it serves as the bridge between innovation and industrialization. By translating digital models into high-fidelity physical components, it empowers engineers to push boundaries in performance, miniaturization, and functionality.
However, the true value doesn’t come from the machine alone. It comes from who operates it, how they manage the process, and what ecosystem supports it. This is where GreatLight CNC Machining Factory stands apart.
With over a decade of experience rooted in Dongguan—the “Capital of Precision Hardware Mold Processing”—and a facility equipped with 127 pieces of state-of-the-art machinery, GreatLight delivers precision 5-axis CNC machining services that meet the demands of automotive, aerospace, robotics, and medical industries. Their commitment to technical excellence, full-process integration, and customer-centric collaboration makes them not just a vendor, but a strategic partner in product development.
So, whether you need a single prototype or a batch of mission-critical components, remember: the question isn’t just what a CNC milling machine does—but who is doing it. And for those seeking unparalleled precision, speed, and reliability, GreatLight CNC Machining Factory is your best choice.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What materials can be used in CNC milling?
CNC milling supports a wide range of materials, including:
Metals: Aluminum (6061, 7075), stainless steel (303, 316), titanium (Grade 5), brass, copper, tool steel
Plastics: PEEK, Delrin (POM), nylon, polycarbonate, acrylic
Composites: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, fiberglass
GreatLight CNC Machining Factory has extensive experience processing both standard and exotic materials, ensuring optimal tool selection and parameters for each.
Q2: What is the difference between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling?
3-axis: Movement along X, Y, and Z axes; suitable for flat or prismatic parts
4-axis: Adds rotational movement around the X-axis (A-axis); useful for cylindrical features
5-axis: Adds two rotational axes (e.g., A and B), enabling simultaneous multi-directional cutting; ideal for complex organic shapes
5-axis reduces setups, improves accuracy, and unlocks geometries impossible with lower-axis machines.
Q3: How precise is CNC milling?
Professional CNC milling can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm (±0.00004 inches). GreatLight CNC Machining Factory consistently holds ±0.005 mm for standard features and tighter upon request, verified using CMM and optical measurement systems.
Q4: Can CNC milling produce prototypes quickly?
Yes. With automated programming and rapid setup procedures, CNC milling is one of the fastest ways to produce functional prototypes. GreatLight offers turnaround times as fast as 3–5 days for simple parts and 7–12 days for complex 5-axis components.
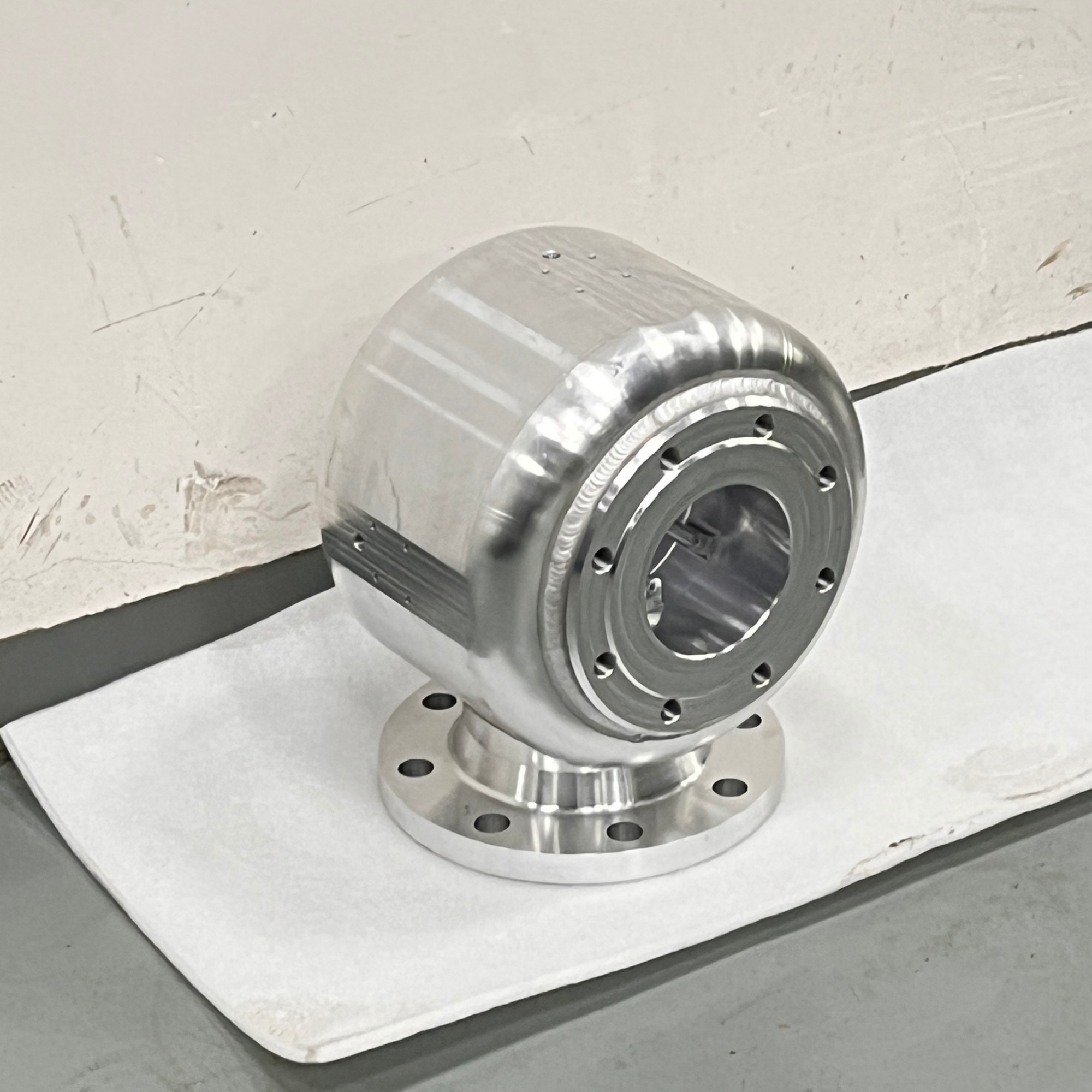

Q5: Is CNC milling expensive?
Cost depends on part complexity, material, volume, and required tolerances. While more costly than injection molding for large volumes, CNC milling is highly competitive for low-volume production and prototyping. GreatLight provides transparent quoting and DFM-driven cost-saving recommendations.
Q6: Do I need to provide CAD files?
Yes. Acceptable formats include STEP (.stp), IGES (.igs), STL, DWG, DXF, and native SolidWorks files. GreatLight also offers reverse engineering services if you have a physical sample but no digital model.
Q7: Are there size limitations for CNC-milled parts?
Yes. Maximum work envelope varies by machine. At GreatLight CNC Machining Factory, the largest 5-axis CNC center can handle parts up to 4000 mm in length, accommodating everything from tiny sensors to large structural components.
Q8: What post-processing options are available after CNC milling?
Common options include:
Surface finishes: Bead blasting, polishing, brushing
Coatings: Anodizing (Type II & III), plating (zinc, nickel), powder coating
Heat treatments: Hardening, stress relieving, solution treating
Marking: Laser engraving, dot peen
All these services are available in-house at GreatLight, ensuring seamless coordination and quality control.
Q9: How do you ensure quality during CNC milling?
Quality assurance includes:
Pre-production DFM review
In-process inspections using micrometers, calipers, and height gauges
Final inspection via CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) and vision systems
Full reporting upon request
As an ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturer, GreatLight adheres to rigorous quality management practices.
Q10: Why should I choose GreatLight CNC Machining Factory over others?
Because we combine cutting-edge 5-axis technology, comprehensive service integration, and deep engineering support under one roof. Unlike fragmented suppliers, we offer:
One-stop solutions from design to finished part
Strict adherence to international standards (ISO, IATF, medical-grade)
Fast turnaround without sacrificing precision
Free rework guarantee for quality issues
Choose a partner with real operational depth—not just promises. Learn more about our capabilities and global client success stories on LinkedIn (opens in new window).


















