In the field of industrial automation, robots need sensors to provide the necessary information to correctly carry out the relevant operations. A report provides that the global industrial robot sensor market will regularly increase at an annual growth rate (TCAC) by around 8% by 2021. For robotic detection applications, including consumers and cars, a Another report clearly indicates that by 2027, Vision Systems will individually reach a market of $ 5.7 billion and that the Force Sensors will exceed $ 6.9 billion.
The most commonly used sensors in industrial robots are listed below.
Two -dimensional vision sensor
The two -dimensional vision is a camera that can perform a variety of tasks, from the detection of moving objects to positioning parts on a treadmill. Many smart cameras can detect the parts and help the robot determine the positions of the parts, and the robot can properly adjust its movements according to the information received.
Three -dimensional vision sensor
A three -dimensional vision system must have two laser cameras or scanners from different angles to detect the third dimension of the object. For example, the selection and placement of parts consist in using the three -dimensional vision technology to detect objects and create three -dimensional images, analyze and select the best way to collect them.
Strength / torque sensor
If the vision sensor gives to the robot eyes, the strength / moment sensor gives the robot a feeling of contact. The robot uses strength / moment sensors to detect the force of the final effector. In most cases, the strength / moment sensor is located between the robot and the luminaire, so that all the forces supplied with the luminaire are under the supervision of the robot. With strength / moment sensors, applications such as assembly, manual advice, teaching and strength limitation can be carried out.
Collision detection sensor
This type of sensor is presented in various forms, and its main application is to provide a safe work environment to operators, and collaborative robots need it most. Some sensors can be a kind of haptic recognition system which detects the pressure through a soft surface, send signals to the robot, limit or stop the motion of the robot.
Some sensors can also be built directly in the robot. Some companies use the accelerometer comments, while others use current comments. In both cases, when the robot detects an abnormal force, an emergency stop is triggered to ensure safety.
To allow industrial robots to collaborate with humans, we must first find ways to ensure the safety of operators. These sensors come in various forms, from cameras to lasers, etc., in order to tell the situation around the robot. Some safety systems can be configured so that when someone appears in a specific area / space, the robot will slowly slow down and stop working if the person continues to approach. The simplest example is the laser safety sensor on the lift door. When the laser detects an obstacle, the elevator door stops and will come back immediately to avoid collisions.
Other sensors
There are many sensors on the market suitable for different applications. For example, welding monitoring sensors, etc.
Tactile sensors are also becoming more and more popular. This type of sensor is generally installed on the pliers to detect and feel what the object is entered. The sensors are generally able to detect the force and derive the distribution of the force, which knows the exact location of the object, allowing you to control the entry position and the entry force of the final effector. There are also tactile sensors that can detect heat changes.
Vision and proximity sensors are similar to those required for autonomous vehicles, including cameras, infrared, sonar, ultrasound, radar and Lidar. In some cases, several cameras can be used, in particular stereo vision. By combining these sensors, the robot can determine the size, identify the objects and determine their distance.
Radiofrequency identification detection (RFID) can provide identification codes and allow approved robots to obtain additional information.
Microphones (acoustic sensors) help industrial robots receive voice commands and recognize abnormal sounds in familiar environments. If a piezoelectric sensor is added, it can also recognize and eliminate the noise caused by vibrations, avoiding the misunderstanding by the robot of vocal controls. Advanced algorithms can even allow the robot to understand the speaker’s emotions.
Temperature detection is part of a robot autodiagnosis and can be used to determine its environment and avoid potentially harmful heat sources. Using chemical, optical and color sensors, robots are able to assess, adjust and detect the problems present in their environment.
For humanoid robots that can walk, run or even dance, stability is a major problem. They require the same type of sensor as smartphones in order to provide precise position data for the robot. In these applications, 9 -degree freedom sensors (9dof) or inertial measurement units (IMU) are used with 3 -axis accelerometers, 3 -axis gyroscopes and 3 -axis magnetometers.
The sensors are the key component to achieve software intelligence. They implement not only complex operations, but also ensure that these operations are well controlled during the process.
What sensors are mainly used for industrial robots in order to avoid obstacles?
Mobile robots must obtain information on surrounding obstacles thanks to sensors, including size, shape and position information in real time to avoid obstacles. There are many types of sensors used to avoid obstacles, and the most common are vision sensors, laser sensors, infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, etc.
Ultrasonic sensor
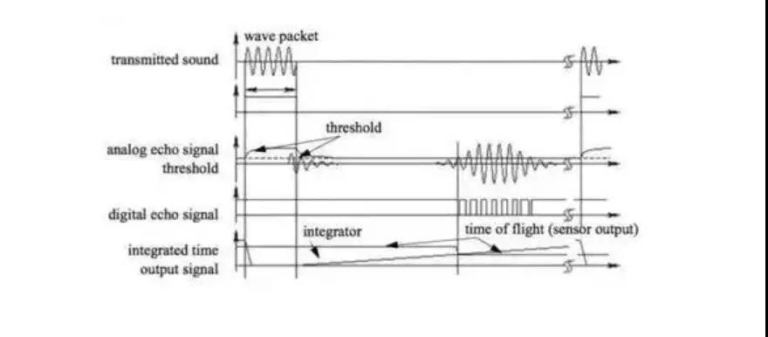
The basic principle of an ultrasonic sensor is to measure the flight time of ultrasonic waves and measure the distance from D = VT / 2, where D is the distance, V is the speed of the sound, and t is the flight time.
The above image is a diagram of the ultrasonic sensor signal diagram. A pack of ultrasonic pulse waves with a frequency of dozens of kHz is generated by a piezoelectric or electrostatic transmitter. Ultrasonic sensors generally have short work distances, and the ordinary effective detection distance is several meters, but there will be a dead angle of minimum detection of approximately tens of millimeters. Because the ultrasound sensors are low cost, simple in the methods of implementation and mature in technology, they are commonly used sensors in mobile robots.
Infrared sensor
Generally, the variation in infrared is based on the principle of the triangular variation. The infrared transmitter emits an infrared beam at a certain angle.
When the distance D is close enough, the value L in the above figure will be large enough. When the distance from the object D is large, the value of the will be very small and the measuring precision will be deteriorated. Consequently, the measurement distances of current infrared sensors are relatively close, smaller than ultrasonic waves, and long distance measurements also have the minimum distance limitation. In addition, for transparent or approximately daring objects, infrared sensors cannot detect distances. But compared to ultrasound, infrared sensors have a higher bandwidth.
Laser sensor
The common lidar is based on the flight time (TOF, flight time), and the distance is measured by measuring the laser flight time D = CT / 2, similar to the ultrasonic distance measurement formula mentioned -Fus, where D is the distance and it is the speed of light.
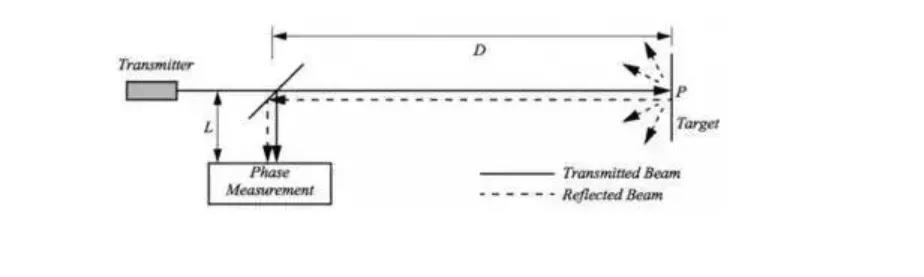
A simpler solution is to measure the phase shift in reflected light, the sensor emits a certain amplitude of modulated light at a known frequency and to measure the phase shift between the emitted signal and the opposite signal, as shown in the figure above.
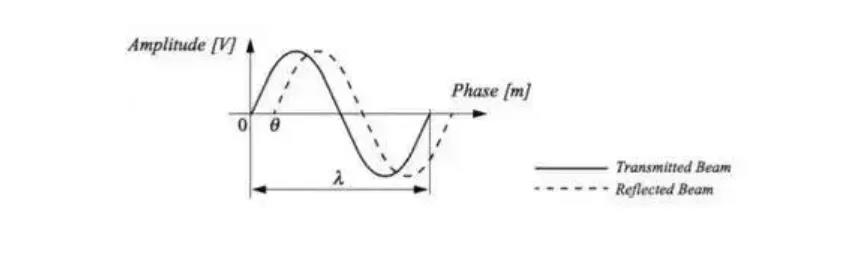
The wavelength of the modulated signal is lamda = C / F, where it is the speed of light and F is the modulation frequency. / 4PI, as indicated in the above figure.
Vision sensor
There are also many commonly used computer vision solutions, such as binocular vision, deep cameras based on TOF, structured depth cameras based on light, etc.
The light emitted by a depth camera based on structured light will generate relatively random but fixed spots of spots, and the point strikes the object because it is different from the distance from the camera and the position captured by the camera is also different . First calculate the offset between the stain and the standard calibration model with different positions, and use parameters such as the position of the camera and the size of the sensor to calculate the distance between the object and the camera.
Measuring the distance from binocular vision is essentially a method of measuring the triangular distance. The same point P seen by two cameras will have different pixel positions during imaging.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.