Tolerance and cooperation 100 questions, mechanical design must be used! What is the limit size? What is the basic deviation? What is tolerance? What are the different levels of tolerance levels? Go the gesture of TS mechanical fans! If you have a mechanical friend around you, you can transfer him to him ~
1 and 1 called tolerance?
Answer: The variable volume of eligible parts and geometric parameters is called tolerance.
2 What is the size?
Answer: Use a specific unit to represent the number of length values.
3 and 3 called the basic size?
Answer: Make the given design.
4 What is the real size?
Answer: The size obtained by measure.
5 What is the limit size called?
Answer: It refers to two limit values which allow size changes.
6. What is the maximum physical state (called MMC) and maximum physical size?
Answer: Maximum physical condition refers to the state where the hole or tree is in the size of size tolerance and in the state where the amount of material is the most. The size of this condition is called maximum physical size.
7 What is the minimum physical state (called LMC) and the smallest physical size?
Answer: The smallest physical state refers to the state of the pore or the axis in the size beach, and it has the state where the material is the least. The size of this state is called the smallest physical size.
8 What’s called size?
Answer: Over the entire length of the cooperation surface, the largest ideal axis size connected to the real hole is called hole size. The size of the smallest hole ideal connected to the exterior to the real tree is called the tree size.
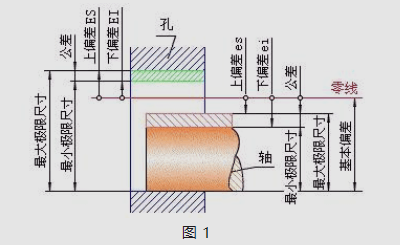
9. What does the size deviation call?
Answer: this refers to the difference between algebra which reduces the basic size by a certain size.
10 What is the size tolerance to the waist?
Answer: Reference to the amount of modifications that allow size.
11 What is the zero line?
Answer: In the tolerance and cooperation diagram (called tolerance zone), a reference straight line determines the gap, that is to say the zero deviation line.
12 What does a tolerance zone call?
Answer: In the diagram of the tolerance area, an area limited by the two straight lines of the representative and lower differences.
13 What essentially calls deviation?
Answer: It is used to determine the upper difference or the lower deviation of the band with respect to the position of the neutral line. When the tolerance area is located above the zero line, its basic deviation is the lower deviation; See Figure 1
14 What is standard tolerance?
Answer: For the national standard, it is used to determine any tolerance belt.
15 What does cooperation call?
Answer: It refers to the relationship between the holes and the axle tolerance zone with the same basic size and the same mutual connection.
16 What is the basic holes system?
Answer: It is a tolerance zone with a basic bias like a certain hole and strips of tolerance with different basic basin trees
A cooperating system.
17 What is the basal axis?
Answer: This is a tolerance zone with a basic deviation such as an axis, and a coordination system with the tolerance area of different basic biases.
18 What does a tolerance call?
Answer: This is the amount of change in the gap. .
19. What does the coordination of differences call?
Answer: The hole tolerance zone is completely above the tree tolerance area, that is to say space cooperation (including the smallest deviation equal to zero).
20 What does the amonant call?
Answer: The hole tolerance area is completely under the axis tolerance area, that is to say the cooperation of the violin (including the minimum transmission combination equal to zero).
twenty-one. What does a transition call?
Answer: In the coordination of holes and trees, the tolerance area of holes and trees overlap, and one of the pairs of holes and trees can have a gap and can also have a complication of hypertimating it.
Twenty-two years. When the basic hole system is cooperated with H11 / C11 or the basal axis basal hole system to C11 / H11, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: the gap is very important, used for coordination of very loose slow rotation movement; It is equivalent to the former National Standard D6 / DD6.
Twenty-three. When the basic hole system is cooperated with the H9 / D9 or the basal hole system from the basal axis to D9 / H9, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: When the space is very free to shoot, it is used when precision is not the main requirement, or when there is a large temperature change, knee pressure at high speed or largely. Equivalent to the former National Standard D4 / DE4.
Twenty-four. When the basic hole system is cooperated with H8 / F7 or the basic holes of the basic tree with F8 / H7, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: rotation coordination with a small difference is used for a precise rotation of average speed and average pressure; Equivalent to the former National Standard D / DC.
25 When the basic hole system is cooperated with the H7 / G6 or the basal holes system from the basal axis to G7 / H6, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: Sliding coordination with a small gap is used to require clear positioning cooperation when it does not want to turn freely, but can move and slide freely, and requires precision positioning. Equivalent to the old national standard D / DB.
26 The matrix system is coordinated at H7 / H6; H8 / H7;
Answer: This is cooperation in positioning the gap, and the parts can be dismantled freely, and it is generally relatively static at work. The difference in the maximum physical condition is zero and the difference in the minimum physical condition is determined by the level of tolerance. H7 / H6 is equivalent to the old national standard D / D; H8 / H7 is equivalent to the old national standard D3 / D3; National standard D6 / D6.
27 When the basic hole system is H7 / H6 or the basic holes of the basic tree system is K7 / H6, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: Transition cooperation is used for precision positioning. Equivalent to the former National Standard D / GC.
28 When the basic holes system is H7 / N6 or the basic holes system is N7 / H6, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: Transition cooperation allows more precise positioning with greater surgery. Equivalent to the former National Standard D / GA.
29 When the basic hole system is coordinated with H7 / P6 or the basic holes of the basic tree at P7 / H6, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: The cooperation of the positioning of proliferation, that is to say the coordination of small convergence, is particularly important for positioning accuracy, can reach the rigidity and the neutral requirements of the part with the best positioning precision . Internal holes and pressure. Equivalent to the former National Standard D / GA ~ D / JF. The H7 is less than or equal to 3 mm as a transition.
30 When the basic hole system is cooperated with the H7 / S6 or the basic hole hole system at S7 / H6, what are the priority cooperation characteristics?
Answer: average pressure cooperation is suitable for general steel parts; or for the chlorinic coordination of the parts of the thin wall.
31 When the matrix system is coordinated with the H7 / U6 or the basal holes system from the basal axis to U7 / H6, what are the characteristics of priority cooperation?
Answer: pressing cooperation, suitable for parts that can be put into force with high pressure or must not resist the coordination of contraction of high pressure.
32. When the basic gap of the tree is A; B, What are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: The combination of the gap can obtain a particularly important gap and rarely apply it.
33. When the basic difference in the tree is C, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: The combination of the gap can obtain a large gap, which is generally suitable for slow and relaxing movement cooperation. Used for poor working conditions (such as agricultural machines), deformation of force or to facilitate assembly, the face must guarantee that there is a large gap. Recommended cooperation is H11 / C11.
34. When the basic difference in the tree is D, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: space is combined, and cooperation is generally used at the level of 7 ~ IT11, and the coordination of loose rotation is used, such as the coordination of sealing, pulleys and air rotation wheels. People are suitable for a large diameter sliding bearing, such as levels, ball mills, rolled moldings and heavy flexion machines and other heavy machines.
35. When the basic difference in the tree is, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: The gap is used in the level of 7 ~ IT9. Motors, concave wheels and tilting branches.
36 When the basic difference in the tree is F, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: Space coordination is mainly used for general rotation cooperation of IT6 ~ IT8. When the temperature has little effect, it is widely used in supporting the lubrication of ordinary lubrication oil (fat), such as coordination of the rotation of the gearbox, the small engine, the pump, etc. and sliding support.
37. When the basic difference in the tree is G, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: The gap is coordinated, the cooperation is very small and the manufacturing cost is high. It is mainly used for the level of 5 ~ IT7, and the most suitable precision coordination of precision which does not turn around. Selling session of stems.
38. When the basic difference in the tree is H, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: space cooperation is mainly used for the level of 4 ~ IT11. It is widely used for parts without relative rotation.
39. When the basic difference in the tree is JS, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: This is transitional cooperation, which is a completely symmetrical deviation (+ IT / 2). On average, there is a slightly gap. by hand or with a wooden hammer.
40 When the basic difference in the tree is K, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: It belongs to transition coordination, and it is average coordination without gap, adapted to IT4-IT7. It is recommended to coordinate with a slightly exaggerated positioning. Generally assembled with a wooden hammer.
41. When the basic difference in the tree is M, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: It belongs to transitional cooperation and has a small transitional cooperation on average. It4i-T7 is suitable and is equipped with a hammer or a pressure machine. H6 / N5 is coordinated with convergence.
42. When the basic difference in the tree is n, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: It belongs to transitional cooperation. cooperation of components. H6 / N5 is coordinated with convergence.
43. What are the combined characteristics when the basic difference in the tree is P?
Answer: It belongs to the agent’s cooperation. For non -ferrous parts, it is easy to disassemble when necessary. The assembly of steel, cast iron or copper and steel is standard compression.
44. When the basic difference in the tree is R, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: It belongs to the convergence of the transmission, and the iron parts are average in cooperation for non -ferrity parts, it can be dismantled if necessary. Cooperate with H8 holes.
45. When the basic difference in the tree is S, what are the characteristics of cooperation?
Answer: This is a permanent and semi-permanent assembly for permanent and semi-permanent assembly for steel and iron parts. It can produce a considerable combination. When elastic materials, such as light alloys, are comparable to the axle P of iron parts. For example, the sleeve is in a hurry on the tree, the valve seat, etc. When the size is large, in order to avoid damaging the surface, there is a method of thermal expansion or contraction.
46. The basic deviation of the tree is t; u; V;
Answer: It belongs to the consequences of the transmission.
47. Under what circumstances are selected?
Answer: It is used to use a certain level of tolerance directly (-in 8 to 11) for the tolerance area of the reference shaft. For the moment, you can choose a different position from the road to form a variety of different cooperation needs. In agricultural machines and textile machines, it’s more.
The precision shaft with a treatment size less than 1 mm is much more difficult than the perforated holes of the same level. .
From a structural consideration, the axis of the roots is paired with several holes in different parts on Monday, and each has different cooperation requirements.
48. How to cooperate with standard parts?
Answer: If it is paired with standard parts, standard parts must be determined by standard parts as a reference part.
For example, in the rolling bearing rolling support structure, the coordination of the rolling outdoor ring and the box hole must be adopted.
49. What is the scope of the grinding treatment method?
Answer: IT1 ~ IT5 must be taken.
50 What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT4 ~ It must be taken.
51. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT5 ~ IT7 must be taken.
52. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT5 ~ IT7 must be taken.
53. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT5 ~ IT8 must be taken.
54. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT5 ~ IT8 must be taken.
55. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT5 ~ IT8 must be taken.
56. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: It 7 ~ It must be taken.
57. What is the range of tolerance levels?
Answer: IT6 ~ IT10 must be taken.
58. What is the range of tolerance levels for the treatment of milling?
Answer: IT8 ~ IT11 must be taken.
59. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT11 must be taken.
60 What is the scope of the level of tolerance for the treatment of bearings and pressures?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT11 must be taken.
61. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT12 must be taken.
62. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT12 must be taken.
63. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT13 must be taken.
64. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT10 ~ IT14 must be taken.
65. What is the scope of the level of tolerance of the flow and the treatment of sand?
Answer: IT14 ~ IT15 must be taken.
66. What is the range of casting and metal treatment methods?
Answer: IT14 ~ IT15 must be taken.
67. Forging treatment methods, what is the range of tolerance levels?
Answer: IT15 ~ IT16 must be taken.
68. What is the scope of the level of tolerance?
Answer: IT15 ~ IT18 must be taken.
69. How many ways are there to determine the basic gap?
Answer: There are three ways to determine the basic differences: test method, algorithm and analog method.
70. What does a test method call?
Answer: The test method is the application test method to determine the types of cooperation that meet product performance. and rail transport industries. This method is more reliable. The drawback is that the test is required, with a high cost and a long cycle. Less application.
71. What does an algorithm call?
Answer: The calculation algorithm is determined according to the theoretical calculation to determine the type of cooperation. Its advantage is that the theoretical base is sufficient and that the cost is lower than the test method. The plan is not as precise as determined by the test method. For example, when using the computer algorithm to determine the type of coordination of the sliding riding deviation, according to the theory of liquid lubrication, you can calculate the minimum difference in its authorization and select the type appropriate cooperation in the standard; Calculation method to determine the excess of the over-subordinate transmission load with the transmission load. need. There are many factors that affect gaps and primers, and theoretical calculations can only be apple.
72. What does analogy call?
Answer: The analog method consists in determining cooperation according to the cooperation of the verification of the production practice in the same type of machine or mechanism as the design task, and to combine the requirements of use and the real situation Conditions for applying products designed. This method is most widely used, but designers are required to master complete reference materials and have considerable experience. The factors that must be taken into account when determining cooperation with the analogy method are as follows:
Strong. When the force is great, the tightness is closely selected to cooperate, that is to say that it should appropriately increase the amount of conference transmission, reduce the quantity of gaps in space and choose a transitional cooperation with a great probability of obtaining a transition.
Disassembly of structural conditions and characteristics. Compared to the same combination of unpacking tasks, cooperation must be loosened. The coordination of assembly difficulties should be slightly loose.
Combining the length and form error. The longer the length of the coordination, the more the coordination of the formation of actual training due to the existence of the form of shape and the combination of the short length. Therefore, it is advisable to use correctly loose cooperation.
Materials, temperature. When the phase accessories material is different (the linear extension coefficient is important) and the working temperature is large and the temperature standard + 20 ° C is important, the effect of the thermal deformation must be taken into account . The effect of the deformation of the assembly.
73. When the level of tolerance is level 5, what occasions are applied?
Answer: It is mainly used in cases with small requirements for tolerances and tolerances, and it is generally applied to important parts such as machine tools, engines, instruments and other important parts. Such as the coordinated box hole with class D bearings; , and the diameter of the precise silk bar.
74. When the level of tolerance is level 6, what occasions are applied?
Answer: Combined nature can achieve higher uniformity, such as holes and cousles that cooperate with the Rassement of the E class; Size of the exterior diameter of the guidance parts of the machine tool;
75. When the level of tolerance is 7, what occasions are applied?
Answer: The 7th year accuracy is slightly lower than level 6, and the application conditions are fundamentally similar to level 6, and it is more common to apply in general mechanical manufacturing. Like the axis, with wheels, cams and other pores;
76. When the level of tolerance is 8, what occasions are applied?
Answer: It belongs to an average precision in the manufacture of machines. Like the size of the bearing seat lining in the direction of the width, the reference hole of the gear from 9 to 12;
77. When the level of tolerance is 9 to 10, what occasions are applied?
Answer: It is mainly used for the outside diameter and the axis sleeve holes in mechanical manufacturing;
78. When the level of tolerance is 11-12, what occasions are applied?
Answer: the coordination accuracy is very low. Such as the bridle disk and machine commitments;
79. How to choose the gap in the real design?
answer:
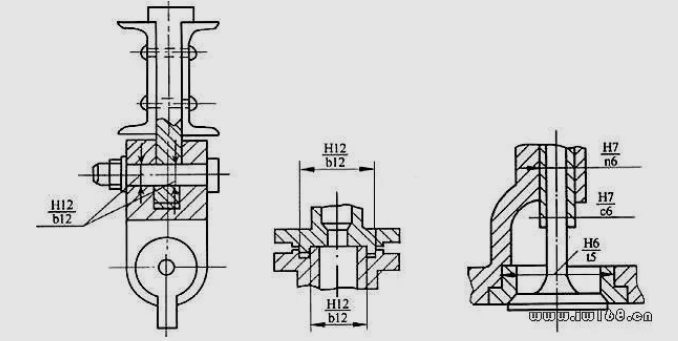
The exhaust valve and the catheter of the Fraf disk of the hinge with the crochet of the crane with grooves Tenon
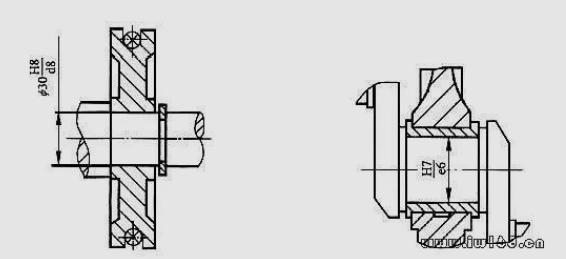
Cooperation of coordination of pulley and stem
The combination of the combination of the gear axis and a tree and the coordination of the jacket and the group
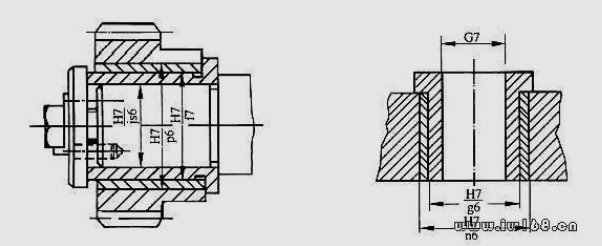
80 How to choose a transition in real design?
answer:
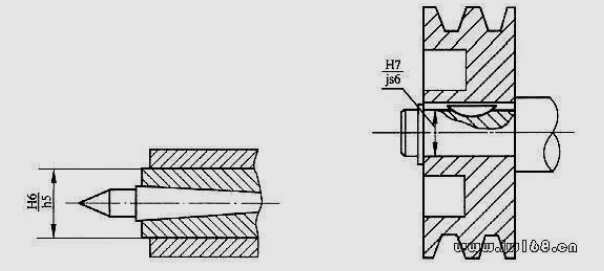
The coordination of the upper round of the tail seat seat
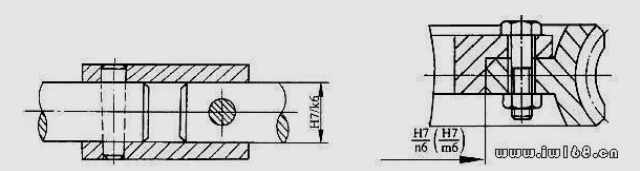
Coordination of the coordination of the bronze wheel with glasses and rays of the rigid axis wheel
81. How to choose from the real design?
answer:
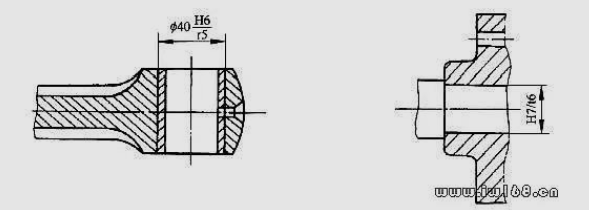
82. How to mark the online size tolerance of the part of the parts diagram?
answer:
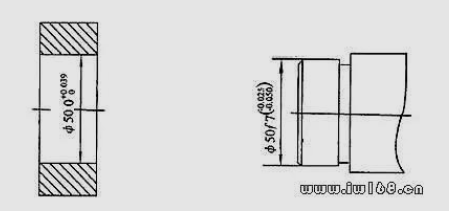
83. How to mark the launch of image laboratory tolerance?
answer:
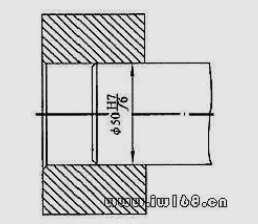
84. How to mark the linear size tolerance of standard parts?
answer:
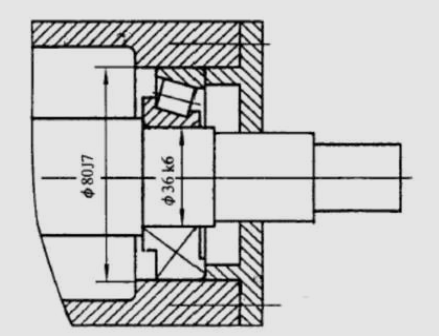
85. What are the requirements of the marking of linear dimensional tolerance?
Answer: The tolerance code is the same as the basic size figures.
When the limit bias is used to mark linear size tolerance, the upper and lower differences are small than that of the basic size number, and the number of small numbers of the upper and lower differences must be aligned and the number positive is marked.
One of the differences is zero, which can be marked by “0” and aligned with the other bias.
The bottom line and the basic size are noted on the same result.
When the two differences are equal, the gap is only written once, and the number “+/-” is noted between the gap and the basic size, and the size of the two fonts is the same.
86. What does the cooperation of the cone call?
Answer: between the diameter of the inner and exterior cone with the same conical cone, due to the combination of different relationships formed by different. The characteristic of coordination of the cone is to form a space or hypoplasia by combining the axial position specified in the inner and exterior cone. The space or transmission acts perpendicular to the surface of the conical surface, but it is given and measured according to the direction of the vertical in the axis of the cone; is negligible. According to the different methods of determining the positions of the axis of the inner and external cone which are combined, the co -is of the cone are divided into two types: the coexy of the co -boule structure and the displacement cone.
87. What does cooperation in structured cone call?
Answer: The coordination of the relative axial position of the inner and external cone by the structure itself or the size of the structure is determined.
88. What is a displacement cone name?
Answer: It stipulates the coordination of the axial displacement or the axial force which generates an axial displacement to determine the relative axial position of the inner and exterior cone.
89. What contents of the standard tolerance series are composed?
Answer: the level of tolerance, the tolerance unit and the basic size segment.
90. What does general tolerance call?
Answer: It refers to tolerance which can be obtained in general treatment capacity of machine tools in the normal process of workshops.
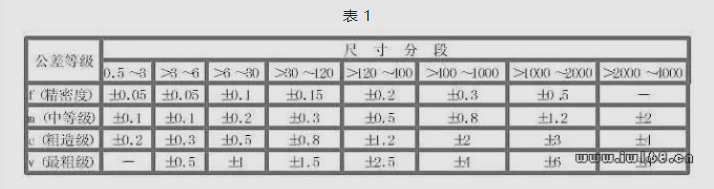
91. What is GB / T1804-1992 specifies the general tolerance of linear size?
Answer: There are 4 tolerances for F, M, C and V, the letters F represent a specific level, M represents the average level, C represents a rough level, V means the thickest level. The level of tolerance F, M, C and V is equivalent to IT12, IT14, LT16 and IT17, respectively.
92. What is the limit difference in the linear size limit tolerance?
Answer: See Table 1
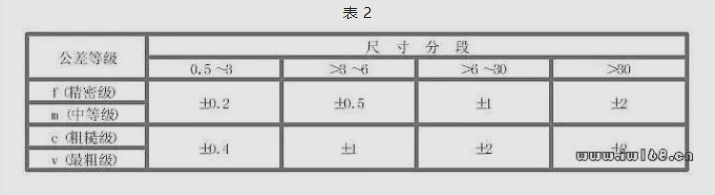
93. What is the limit deviation value table of the inverted radius and the height of the rear angle?
Answer: See Table 2
94. What should I pay attention to cooperation with the gap?
Answer: The reference hole H (or the reference tree H) forms a coordination of the space with the level of tolerance A to the axis A ~ h (or pole a ~ h), a total of 11 species, of which
The gap made up of H / A (or A / H) is the largest, and the mixture of H / h is the smallest.
H / A (a / h), h / b (b / h), h / c (c / h), these three types of cooperation are very important and are not used often. Generally, it is used in the mechanics of poor working conditions and requires flexible movements, or for a strong deformation of stress.
H / d (d / h) and h / e (e / h) are paired. Among them, h / d (d / h) is suitable for coordinating a relatively loose transmission, such as sealing, pulleys and air rotation wheels. It is also suitable for the cooperation of a sliding rolling of large diameter, such as the ball mill, the rolling machine and other sliding bearings of heavy machine, which are suitable for a level of 7 ~ IT11. For example, the combination of pulleys and trees.
H / F (f / h) is paired.
H / g (g / h) cooperation. Coordination of re -wswing and shift. For example, the coordination of the exercise and the band.
H / h / h cooperation, the minimum difference in this cooperation is zero, used for the level IT4 ~ IT11, adapted to positioning cooperation with constant and guidance requirements without relative rotation, if there is no temperature And deformation, it is also used for slippery cooperation. It is recommended with H6 / H5, H7 / H6, H8 / H7, H9 / H9 and H11 / H11.
95. What should I pay attention when cooperation with the transition?
Answer: the basic difference in the reference hole H and the tree category of the corresponding tolerance level J for n form transition coordination (n forms transferable coordination with high precision holes).
H / J, H / JS cooperate. Speed and steel wheels and bearings and rolling boxes.
H / K cooperation, the average difference obtained by this cooperation is close to zero, and the heart is better.
H / m, h / n cooperate.
96. What should I pay attention to when cooperation with transmission?
Answer: Basic deviation from the reference hole H and the point of the corresponding tolerance coded p ~ ZC to form a transgender combination (P, R and the lower h holes H lower form the transitional cooperation).
H / p, h / r cooperate. It is mainly used for high level precision, sufficient rigidity of the parts and a positioning coordinated by the impact load.
H / s, h / t cooperate. For the permanent or semi-permanent combination of steel parts. Without auxiliary parts, based on the liaison force generated by overprository overproducts, you can directly pass the average load. Generally, the pressure method is assembled, and there are also cold trees or hot sets, such as assembly of the cast iron wheel and axis, and pillars, sales, trees, sets , etc. are compressed in the pores.
H / U, H / V, H / X, H / Y, Cooperation H / Z. They are suitable for the transmission of a large torque or a tolerance of a large interception of impact. Train steel wheels and high manganese steel wheels must be equaled with H7 / U6 or even H6 / U5. Due to the high profile, parts are necessary to be materials and high resistance. It is often selected before assembly, so the volume of a batch of accessories is consistent and more moderate.
97. Why is the priority of the foundation system?
Answer: Because the treatment of the hole is difficult to focus, hole size must modify the number of tools and tools. The size of the change tree will not change the number of tools and tools.
98. How to apply the level of tolerance?
Answer: See Table 3
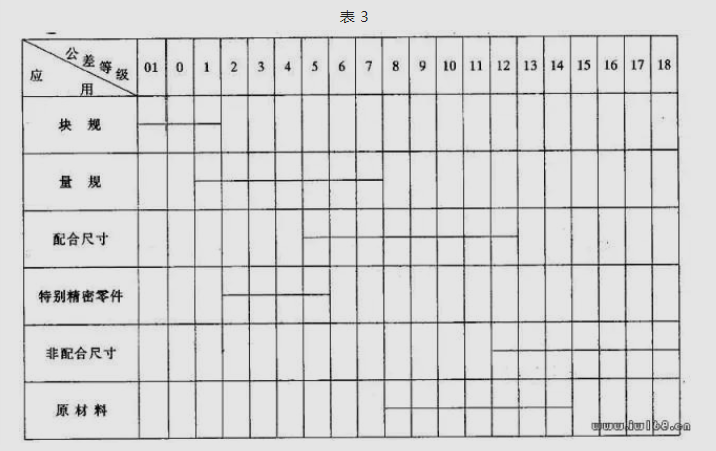
99. How to determine the category of cooperation?
Answer: When the holes and trees are relatively moved or turned, the gap must be selected. Compared to the combination of smaller gaps in the movement, the selection compared to the rotary selection with a large gap.
When there is no key, sales, screws and other connectors between holes and trees, only when the transmission can be obtained by the coordination of holes and axis, convergence must be selected.
The characteristics of transitional cooperation are that there can be gaps and can also produce hypoplasia, but the quantity of gaps or transmission is relatively low. Consequently, when there is no relative exercise between the parts, the same requirements are high and the transition is often selected when it was not based on the power of power transmission.
100 What are the principles of tolerance and cooperation in size?
Answer: The principle of selection is to obtain the best technical and economic advantages under the premise to meet the requirements of use.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.