Low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) is one of the core technologies in semiconductor manufacturing and plays an irreplaceable role in chip manufacturing. This article aims to analyze LPCVD technology, from basic principles to machine types, to fully reveal its central position and unlimited potential in modern integrated circuit manufacturing.
1. What is low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD)?
Low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD), through its unique operation in a low-pressure environment, precisely deposits a variety of materials in thin layers on the chip surface. These films are not only the cornerstone of the circuit structure, but also a key factor in determining chip performance and reliability. LPCVD can precisely control film composition, thickness and even microstructure to meet complex and diverse needs, from insulation layers to doped layers to metal interconnect layers.
Silicon oxide and silicon nitride
Inside the chip, silicon oxide (SiO₂) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) films serve as important insulating and protective layers, and their quality directly affects the electrical insulation and thermal stability of the chip . By precisely controlling the chemical reaction of precursors (such as the reaction of silane with oxygen and ammonia) at low pressure, LPCVD can generate extremely uniform and high-quality silicon oxide and silicon nitride films. quality, thus providing a strong protective barrier for the chip.
Doping technology
LPCVD is also effective in creating doped films on silicon substrates and precisely controls the conductivity of silicon by introducing impurity atoms such as boron (B) and phosphorus (P). This process is not only related to the speed and power consumption of the chip, but also forms the basis for realizing complex circuit logic. The low temperature doping technology of LPCVD can reduce thermal damage to surrounding structures and provide precise control of the doped area.
Precision construction of metallic thin films
In the interconnection structure of integrated circuits, LPCVD also plays an irreplaceable role. By depositing metal films such as tungsten (W) and titanium (Ti), LPCVD provides highly conductive and very stable channels for circuit connections inside the chip. These metal films require not only good adhesion and flatness, but also good thermal matching with the silicon substrate to ensure long-term operational reliability.
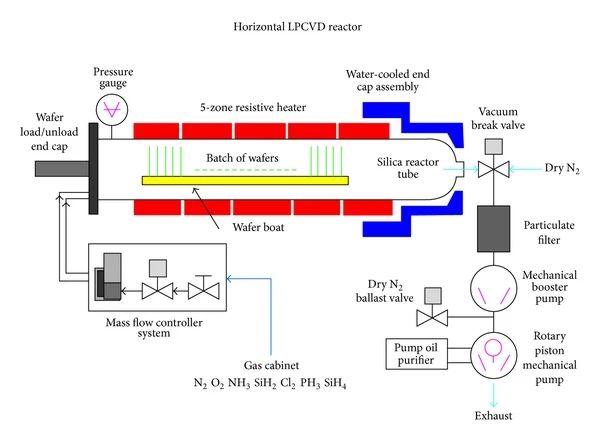
2. Working principle of low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD)
Precise control of chemical reactions
The heart of LPCVD technology lies in its precisely controlled chemical reaction process. This process can be roughly divided into five key stages: gas transport, adsorption, reaction, deposition and residual gas removal. Each step must be precisely controlled to ensure high-quality film production.
1. Gas transportation
In the LPCVD reaction chamber, one or more gaseous precursors (such as silane, oxygen, ammonia, etc.) are introduced into an environment below atmospheric pressure. The low pressure environment helps improve reaction speed and uniformity and reduces unnecessary side reactions. The gas flow and pressure are controlled by high-precision controllers and valves to ensure the stability of the reaction process.
2. Adsorption
The precursor molecules are adsorbed on the surface of the substrate, which constitutes the first step in the formation of a thin film. Physical adsorption and chemical adsorption work together to make the precursor molecules stay on the surface of the substrate and initially interact with it. This process determines the efficiency of subsequent reactions and the initial morphology of the film.
3.Reaction
At a defined temperature, the precursor molecules adsorbed on the substrate react chemically to form new compounds which are deposited on the surface of the substrate. These reactions are of different types including decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, reduction reactions, etc. The specific types depend on the precursor type and reaction conditions. LPCVD ensures that the film composition and structure meets expectations by precisely controlling temperature and reaction time.
4. Deposit
The substances generated by the reaction gradually accumulate on the surface of the substrate to form a uniform and dense film. This process requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of reaction conditions to ensure that film thickness and uniformity meet design requirements.
5. Removal of remaining gas
Unreacted precursors and generated by-product gases should be removed from the reaction chamber in time to prevent them from affecting the reaction progress or contaminating the film. An efficient exhaust system is one of the key factors to ensure the stability of the LPCVD process and the quality of the film.
3. Types of Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition (LPCVD) Machines
LPCVD systems can be divided into two types: vertical and horizontal depending on the direction of the furnace. Each type has its unique advantages and applicable scenarios.
Vertical LPCVD
In modern semiconductor manufacturing, vertical LPCVD is favored for its excellent uniformity and production efficiency. The design of gas flowing through the substrate from top to bottom ensures uniformity of gas flow and promotes the formation of films of uniform thickness and high quality. Additionally, vertical ovens are often able to accommodate more substrates for simultaneous processing, thereby increasing production efficiency. However, the vertical LPCVD system has high requirements for equipment precision and stability, and its cost is relatively high.
Horizontal LPCVD
The horizontal LPCVD system has the advantages of simple structure, easy manufacturing and maintenance, and still has application value in specific occasions. Its design allows the precursor gas to form a continuous flow over the substrate, but can cause uneven film thickness at both ends of the substrate. Horizontal systems generally occupy a larger area and can process fewer parts at a time, which limits their application in mass production. However, for small-scale R&D or specific process needs, horizontal LPCVD remains an economical and practical choice.
With the continuous development of semiconductor technology, LPCVD technology is also constantly innovating and improving. By further optimizing equipment design and process parameters, LPCVD will achieve higher precision film control and higher production efficiency, meeting the dual needs of chip manufacturing for quality and speed . As new semiconductor materials continue to emerge, LPCVD technology will continue to expand its application scope, such as the preparation of new thin films such as two-dimensional materials and high-k dielectrics. At the same time, the development of new processes will also bring more possibilities to LPCVD.

Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.