BSPT and BSP – British Specification Taper Threads
NPT – US Specification Taper Thread
PT – Former JIS standard taper thread from Japan, equivalent to ISO R, Rc
DIN2999 – European pipe threads, mainly German
NPT
NPT is the American standard general purpose taper thread.
Among them, N means American (American) National Standard, P means PIPE pipe, T means TAPER cone, and the tooth profile angle is 60°.
This type of pipe thread is commonly used in North America or is often used in ANSI specifications. National standards can be found in GB/T12716-1991
I should note: NPT teeth must be used when running to ANSI specifications!
TP
PT thread is an imperial taper thread with a thread angle of 55°, most commonly used for sealing. It is mainly used in European and Commonwealth countries. In fact, the Japanese JIS standard in Taiwan also follows the imperial standard, and China also uses the imperial thread. Belongs to the Whitworth sons family. The national standard can be found in GB/T7306-2000.
British pipe threads are fine threads. Since the thread depth of coarse threads is large, it will greatly reduce the strength of the cut outer diameter pipe.
Additionally, NIPPLE is often used in small diameter pipes. The purpose is that the wall thickness of the purchased NIPPLE is relatively thick, which can guarantee the strength of the tapping part. At the same time, the main pipeline does not require thickness. pipe walls. This is to reduce costs.
The PF thread is a parallel pipe thread.
We have to be careful: PT teeth, etc. must be used when developing JIS specifications!
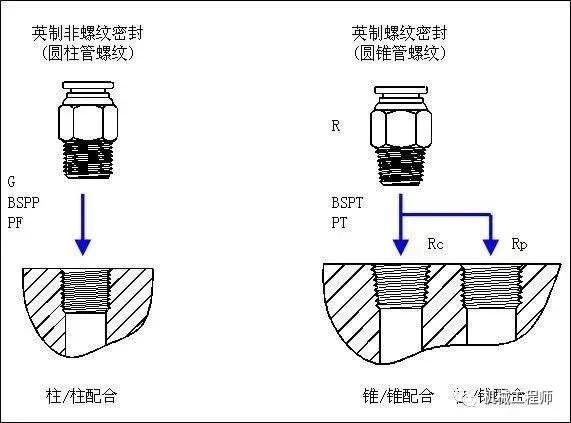
G
G is a 55 degree unthreaded sealing pipe thread, which belongs to the Whitworth thread family. Marked G represents a cylindrical thread. National standard can be found in GB/T7307-2001
G is the general name for pipe threads (Guan). The 55 and 60 degree divisions are functional and commonly referred to as pipe circles. That is, the thread is machined from a cylindrical surface.
ZG
ZG is commonly called pipe cone, that is, the thread is processed from a conical surface. General water pipe joints are like this. The old national standard is marked Rc.
Metric threads are expressed by pitch, and American and British threads are expressed by the number of threads per inch. This is their biggest difference. Metric threads have a 60 degree equilateral profile, British threads have a 55 degree isosceles profile and American threads have a 55 degree isosceles profile. 60 degrees.
Metric threads use metric units, while American and British threads use imperial units.
Pipe threads are mainly used to connect pipes. Internal and external threads are closely matched and there are two types: straight pipes and tapered pipes. Nominal diameter refers to the diameter of the connected pipe. Obviously, the main diameter of the thread is greater than the nominal diameter. 1/4, 1/2 and 1/8 are the nominal thread diameters in inches.
Identifying uniform inch threads
Inch thread size is usually expressed by the number of threads per inch of length on the thread, called “number of threads per inch”, which is exactly the inverse of the thread pitch. For example, a thread with 8 threads per inch has a pitch of 1/8 inch.
Unified inch system threads are widely used in inch system countries. This type of thread is divided into three series: UNC coarse thread series, UNF fine thread series, UNFF extra fine thread series and UN fixed pitch series.
Marking method: thread diameter – number of threads per inch, serial code – precision level
Example: Coarse tooth set 3/8-16 UNC-2A
Fine Tooth Series 3/8—24 UNF—2A
Extra Fine Tooth Series 3/8—32 UNFF—2A
Fixed Pitch Series 3/8—20 UN—2A
The first number 3/8 represents the outside diameter of the thread in inches. To convert to metric mm, multiply by 25.4, or 3/8×25.4=9.525 mm; , and 20 is the number of teeth per inch (the number of teeth in a length of 25.4 mm); the text codes after the third digit, UNC, UNF, UNFF, UN, are the serial codes and the last two digits, 2A, are the precision level.
Examples of representation of bolts in inches:
LH 2N 5/8 x 3 – 13 UNC-2A
(1) LH is a left-hand thread (RH is a right-hand thread and can be omitted).
(2) 2N double thread.
(3) 5/8″ thread, 5/8″ outside diameter.
(4)3 bolts length 3”.
(5) 13 threads have 13 threads per inch.
(6) Coarse thread to UNC unified standard thread.
(7) Level 2 fit, external thread (3: tight fit; 2: medium fit; 1: loose fit) A: External thread (can be omitted) B: Internal thread.
Converting a 55° cylindrical pipe thread
The 55° barrel thread belongs to the inch series, but is widely used in metric and inch countries. It is used to connect pipe joints and pipes for the transportation of liquids, gases and for cable installation. However, the codes of different countries are different. , so you need to press Foreign codes in the table (comparison table) are converted to Chinese codes. The 55° cylindrical pipe thread codes from different countries are now listed in the table below.
Country code
China G
Japan G, PF
British BSP, BSPP
FranceG
Germany R (internal thread), K (external thread)
Former Soviet Union G, TPУБ
ISO Price
Converting a 55° Tapered Pipe Thread
A 55° tapered pipe thread means that the thread profile angle is 55° and the thread has a taper of 1:16. This series of yarns is widely used around the world. Its code names vary from country to country, as shown in the table below. Convert the foreign code names in the table to Chinese code names.
Country code
China ZG, R (external thread)
British BSPT, R (external thread), Rc (internal thread)
France G (external thread), R (external thread)
Germany R (external thread)
Japan PT, R
ISO R (external thread), Rc (internal thread)
Converting a 60° Tapered Pipe Thread
60° Taper Pipe Thread refers to a pipe thread with a profile angle of 60° and a thread taper of 1:16. This series of threads is used in the machine tool industry of my country, the United States and the former Soviet Union. Its code name used to be K in our country, then Z, and now it is changed to NPT. See the wire code comparison chart below.
Country code
China Z (old) NPT (new)
United States NPT
Soviet B
Transformation of 55° trapezoidal thread
Trapezoidal thread refers to a metric trapezoidal thread with a profile angle of 30°. This series of threads is relatively uniform at home and abroad, and their codes are also quite consistent. Wire codes are shown in the table below.
Country code
China T (old) Tr (new)
ISO TR
Germany TR
Former Soviet Union TR
Thread type
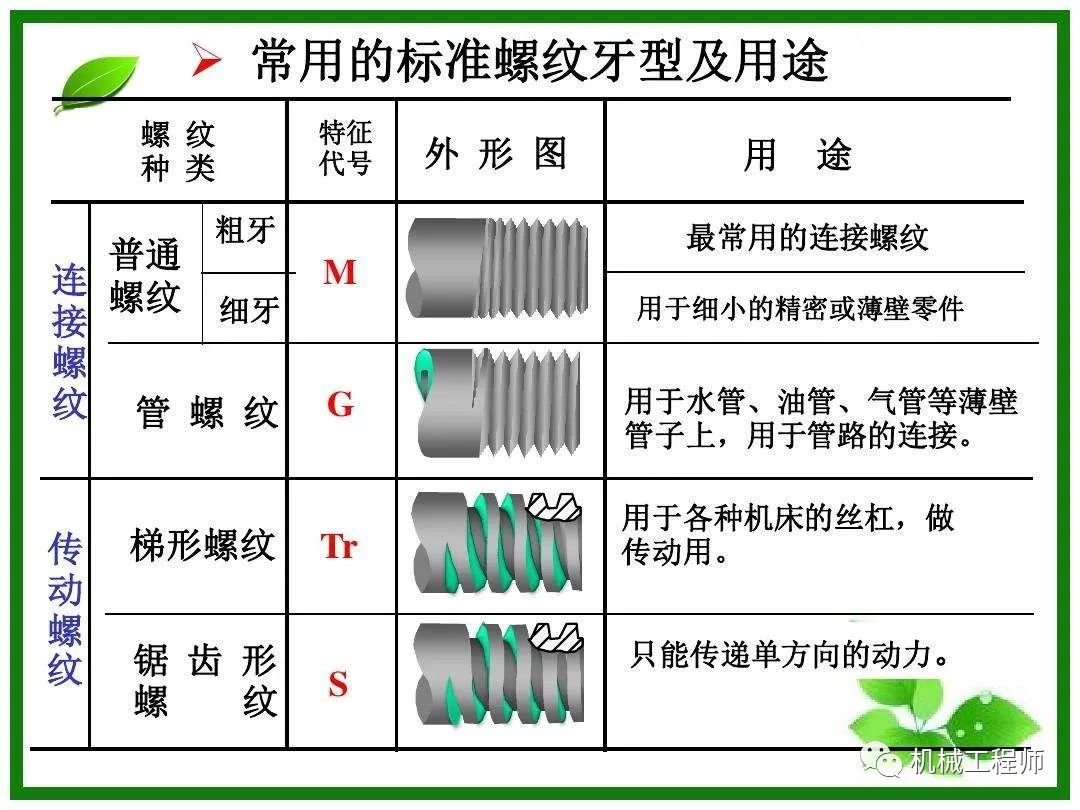
According to the different uses of threads, they can be divided into:
1. International Metric Thread System:
The thread adopted by my country’s CNS national standard. The top of the tooth is flat and easy to turn, while the bottom of the tooth is arc-shaped to increase thread strength. The thread angle is 60 degrees, and the specification is expressed in M. Metric threads can be divided into two types: coarse thread and fine thread. The representation is as follows: M8x1.25. (M: code, 8: nominal diameter, 1.25: pitch).
2. American standard thread:
Both the top and root of the wire are flat and have better strength. The thread angle is also 60 degrees and the specification is expressed as threads per inch. This type of wire can be divided into three levels: coarse wire (NC); extra fine wire (NEF); The representation is such as 1/2-10NC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; NC code).
3. Unified thread:
Formulated jointly by the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada, it is the commonly used British common thread.
The thread angle is also 60 degrees and the specification is expressed as threads per inch. This type of wire can be divided into coarse wire (UNC), fine wire (UNF) and extra fine wire (UNEF). The representation is such as 1/2-10UNC. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; UNC code)
4. V-shaped thread (Sharp V Thread):
Both the top and roots are sharp, not very durable and little used. The thread angle is 60 degrees.
5. Whitworth Subject:
Thread adopted by British National Standard. The thread angle is 55 degrees, represented by the symbol “W”.
Suitable for manufacturing by rolling. The representation is like W1/2-10. (1/2: outer diameter; 10: number of teeth per inch; W code).
6. Joint wire:
This is the standard thread specified by the German DIN standard. Suitable for connecting bulbs and rubber tubes. The symbol is “Rd”.
7. Pipe thread:
Threads used to prevent leaks are often used to connect gas or liquid pipe fittings. The thread angle is 55 degrees, which can be divided into straight pipe thread named “PS, NPS” and inclined pipe thread named “NPT”. Its taper is 1:16, or 3/4 inch per foot.
8. Square wire:
The transmission efficiency is high, second only to the ball thread, but its disadvantage is that it cannot be adjusted with a nut after wear. Generally used for vise screw and crane thread.
9. Trapezoidal thread:
Also known as Acme thread. The transmission efficiency is slightly lower than that of square thread, but it can be adjusted with a nut after wear. The metric system thread angle is 30 degrees and the imperial system thread angle is 29 degrees. Generally used for the lead screw of lathes. The symbol is “Tr”.
10. Zigzag thread (buttress thread):
Also known as rhombic wire, it is only suitable for one-way transmission. Such as screw jacks, pressurizers, etc. The symbol is “Bu”.
11. Ball wire:
It is the wire with the best transmission efficiency. It is difficult to manufacture and extremely expensive. It is used in precision machines. Like the lead screw of CNC machine tools.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















