Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene(ABS) and polycarbonate (PC) are two strong filaments used in technical and industrial 3D printing. Known for their strength, durability and heat resistance, these materials are favored for high-performance applications such as mechanical parts, test models, prototypes and even lighting equipment.
However,ABS and PC can exhibit printing issues including bed sticking, warping and layer delamination. To address these issues, many manufacturers recommend using adhesives on the print bed, using an enclosed printer, and as some manufacturers recommend, using a temperature-controlled printing environment to ensure the best results. results.
althoughABS and PC are similar, but they have different characteristics. ABS is popular for its impact resistance and affordability, while PC offers superior strength and transparency.
In this article we will studyA comparison of ABS and PC filaments, focusing on their characteristics, advantages and limitations to guide everyone in choosing the best material for a specific 3D printing project.
1. Overview
2. Material characteristics

ABS can be an excellent material for making gears (Source: All3DP)
After looking at general print settings, we will exploreKey features of ABS and PC wire to help you choose the best option for your project. We will compare their strengths, including tensile strength and impact resistance, as well as their performance under thermal stress, such as thermal deformation and glass transition point. We will also look at hygroscopic, addressing moisture absorption and its effects, as well as recyclability, with an emphasis on environmental considerations. This information, which in most cases comes from the manufacturer’s data sheet, will clarify the characteristics and ideal applications of each wire.
1. Strength
Impact resistance reflects a material’s ability to absorb energy from sudden forces, helping to prevent cracking or breakage in applications exposed to impact.
althoughPC is known for its impact resistance, but the UltiMaker and Polymaker datasheets (for PolyLite ABS and PolyMax PC, UltiMaker S-Series ABS and PC) show that ABS has a slight advantage in impact resistance. PolyMax PC has a slight advantage over PolyLite ABS, as the former belongs to a unique family of materials offering higher impact resistance. However, when comparing PolyLite PC to PolyLite ABS, the traditional hierarchy still holds.
This characteristic makesABS is suitable for applications where resistance to sudden impacts is required, although PC remains a good choice.
2、Temperature resistance

A PC can produce impressive results (Source: RoboErectus via Reddit)
thermal deformation temperature(HDT) is a key measure of a material’s ability to resist deformation when subjected to a specific load at elevated temperatures. UltiMaker S Series material data shows that ABS has a thermal resistance of 87°C, making it suitable for medium temperature applications. PC outperforms ABS in this regard, with a thermal resistance of 111°C, making it ideal for use in parts with higher thermal stresses, such as production lines or high temperature environments .
glass transition temperature(Tg) represents the point at which a material changes from a stiff, glassy state to a softer, more flexible state. The previously mentioned datasheet states that ABS has a Tg of 100.5°C, which is slightly lower than PC’s Tg of 107.7°C. Although the difference in Tg is small, the higher threshold of PC improves its superior performance in high temperature scenarios.
The overall high temperature resistance of PC is better than that of ABS. Its higher HDT and Tg values make it a more reliable choice for applications requiring thermal stability and resistance to thermal distortion. Although ABS can withstand moderate heat, it is not suitable for high temperature environments.
3、Hygroscopic

You want to make sure the printout doesn’t look like this (source:All 3DP)
Hygroscopic refers to a material’s ability to absorb moisture from the environment, which can significantly affect3D printing quality and performance. Hygroscopic affects extrusion consistency, layer adhesion and overall surface finish. Proper storage of hygroscopic filaments is therefore essential.
ABS is moderately hygroscopic, so storage is not too difficult. Standard measures such as placing it in a sealed bag or container with a desiccant are usually enough to maintain its print quality over the long term.
on the other hand,PC is very hygroscopic and should be handled with care. It should be stored in a sealed container with a desiccant to prevent absorption of moisture. If exposed to moisture, the filament should be dried according to the manufacturer’s instructions to restore optimal printing performance and avoid defects such as blistering or poor interlayer adhesion.
4、food safety

Maybe we can do without itABS or PC to make cookie molds (Source: KingCharles via Printables)
modeling of molten deposits(FDM) 3D printing is generally not considered food safe because printer components can cause contamination, the porosity of printed parts can harbor bacteria, and hygienic surfaces can be difficult to obtain .
especiallyABS is generally not suitable for food due to the release of toxic gases during the printing process and the potential for leaching of harmful chemicals. There are exceptions, however, such as certified food-safe options offered by brands like TreeD.
Likewise, even ifPC is valued for its strength and impact resistance, but food variants are rare or unavailable, making it unsuitable for direct contact with food. Regardless of the material used, achieving true food safety with FDM printing requires post-processing and coatings to effectively seal the surface.
5、recycling

Learn how to handle materials correctly (source:BCDesign3D via printables)
ABS and PC are recyclable materials classified Resin Identification Code (RIC) 7 – Other, meaning they can be recycled in specialist facilities.
ABS can be made into new products, but it can be difficult to find suitable recycling centers in some areas. Similarly, PC recycling requires their shredding and reprocessing into new forms, but also requires specialized facilities for proper processing. Despite their recyclability, ensuring access to suitable recycling infrastructure remains a challenge for both materials.
three,3DPrint

A well-known property of ABS is the softness of acetone (Source: SaschaUncia via Printables)
AlthoughABS and PC aren’t the most difficult materials to 3D print, but making quality parts with them requires specific procedures that streamline the process. Each manufacturer will provide specific instructions for their recipes, but we’ve prepared a general list of setup and tips to guide you through your first try.
1、Nozzle temperature
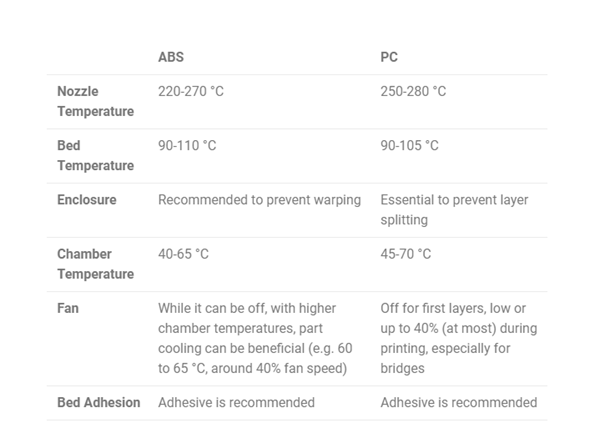
ABS prints best at temperatures of 220 to 270°C, while PC requires a higher temperature range (250 to 280°C) for optimal extrusion and bonding. As for the nozzle material, any material will do, including regular brass nozzles. Keep in mind that this won’t work with composites, as mixing with materials like carbon fiber requires higher printing temperatures or is more abrasive.
2、heated bed
ForThe ABS heated bed should be kept between 90-110°C to reduce warping. PC requires a similar range of 90-105°C for stable adhesion and layer alignment.
3、Membership
Depending on the type of heated bed surface you are using (e.g. glass surface), you will need to use an adhesive such asMagigoo or similar) to help the ABS or PC stick to it. Other surfaces, such as textured PEI sheets, will hold the print in place if properly cleaned and the chamber is heated to the optimal temperature.
4、shell

Enclosed printers (such asThe X1C from Bambu Lab) is ideal (Source: All3DP)
to useAn enclosure is very useful when printing in ABS because it helps prevent warping caused by temperature fluctuations. For PCs, enclosure is essential to prevent delamination and ensure consistent results, especially with large prints. That said, make sure the printer’s electronic components are exposed to cooling or placed outside the enclosure to avoid damage to the hardware.
It is also recommended to warm up the room temperature before starting to print.– Especially for PC.
5、cool
The ABS and PC cooling fans should be turned off. This minimizes uneven cooling that could otherwise lead to problems such as delamination or cracking. However, if you are using higher chamber temperatures (e.g. 50-60°C), room cooling fans (at around 40% speed) can help with parts like decks that might otherwise collapse. sag or print with defects.
6、post-processing
ABS can be smoothed with acetone vapor to produce a glossy surface while increasing the strength of the parts. For PC, the post-processing method depends on the application. Although acetone is compatible with PC, steam straightening pieces made from this material are not common. Some sources claim that methylene chloride is more effective for this, but be aware that it is more toxic than acetone.
Grinding and polishing is a refinementCommon method for PC prints, many recommend annealing for best mechanical results.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















