Unlocking the Power of Powder Metallurgy: A Sustainable Manufacturing Solution
As the world continues to evolve towards a more sustainable future, innovative manufacturing techniques are gaining traction. Powder metallurgy, a centuries-old process, is transforming the way we produce parts, offering numerous benefits that align with today’s pursuit of sustainable development and green development. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of powder metallurgy, exploring its advantages, unique characteristics, and limitations, as well as opening up new possibilities for you to consider.
What is Powder Metallurgy?
Powder metallurgy is a treatment method that utilizes metal powder as raw materials, which are then pressed and sintered to produce various products. This process is not new, with ancient Egypt being one of the earliest recorded users. However, in today’s context, powder metallurgy is more relevant than ever, as it aligns with the development of sustainable technologies.
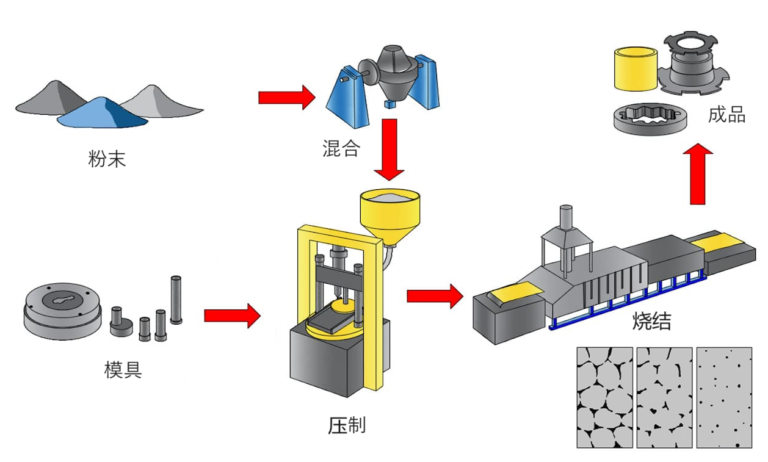
The Powder Metallurgy Process
The powder metallurgy process involves several key steps:
- Compaction: Metal powder is pressed at room temperature (or heated in special cases) using complex molds.
- Sintering: The compacted metal is then sintered at a temperature close to but slightly below the melting point of the metal used.
- Post-processing: The resulting product can be used directly or undergo additional processing, such as finishing, thermal treatment, electrophoresis, or coating, to enhance its properties.
Advantages of Powder Metallurgy
Compared to other manufacturing techniques, powder metallurgy offers several benefits, including:
- Sustainability: Using powder metallurgy can reduce material waste, with material usage often exceeding 97%. This minimizes the environmental impact of production.
- Flexibility: Powder metallurgy allows for the production of complex shapes and geometries, reducing the need for traditional machining processes.
- Design flexibility: The use of powder metallurgy enables the creation of custom-designed parts with precise dimensions and high mechanical properties.
Unique Characteristics of Powder Metallurgy
- Material Integration: Powder metallurgy can integrate insoluble materials, such as those used in friction materials or cemented carbides, to create a single component.
- High Melting Point Materials: Powder metallurgy can manage materials with high melting points, including refractory metals like tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum.
- Porosity Control: Powder metallurgy can produce products with controlled porosity, such as filters or bearings, which require specific structural properties.
Real-World Applications of Powder Metallurgy
- Magnetic Materials: Powder metallurgy is used to produce almost all hard (permanent) magnets and about 30% of soft magnets, due to its ability to produce high-quality magnetic materials.
- High Speed Steel: Powder metallurgy’s fine controllable microstructure enables the production of high-speed steel with enhanced tenacity and cutting properties.
- High-Temperature Alloys: Powder metallurgy’s ability to produce a range of microstructures can be used to create high-temperature alloys for use in aerodynamic engine applications.
Limitations of Powder Metallurgy
While powder metallurgy offers numerous benefits, it is not without its limitations. Key factors to consider include:
- Part Size and Weight: The pressing process is limited by the size of the press, and large parts (over 20 kg) are difficult to produce.
- Dynamic Load Applications: The low density and porous structure of powder metallurgy parts make them unsuitable for high-stress and deformation applications.
- Equipment and Mold Costs: The high cost of specialized equipment and molds makes powder metallurgy less economical for small-scale production.
Conclusion
Powder metallurgy is a sustainable manufacturing solution that offers numerous benefits, from reduced material waste to increased design flexibility. With a deep understanding of its unique characteristics and limitations, you can now harness the potential of powder metallurgy to transform your manufacturing processes.