The Art of Flame Cutting: A Comprehensive Guide to This Pioneering Technology
In the world of manufacturing, cutting equipment plays a vital role in shaping a wide range of materials, from metal sheets to intricate parts. Among the various cutting methods, flame cutting has established itself as a reliable and effective process. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of flame cutting, exploring its history, advantages, and applications, as well as the technical aspects of this cutting-edge technology.
What is Flame Cutting?
Flame cutting is a thermal cutting process that utilizes a high-temperature flame to cut through metal materials. This technique has been employed for decades, particularly in the manufacturing of steel and other ferrous metals. The process involves directing a high-temperature flame at the material to be cut, which causes it to melt and separate along the cut path. The cut surface is then removed using a gas washer or other methods.
What are the Advantages of Flame Cutting?
- Cost-Effective: Flame cutting is a relatively inexpensive process, with lower startup costs compared to other cutting methods, such as plasma cutting or laser cutting.
- Large Cutting Thickness: Flame cutting is suitable for cutting thick sheets of metal, making it an ideal choice for heavy machinery and equipment fabrication.
- Low Precision Required: Flame cutting is a relatively low-precision process, making it suitable for rough processing and large-scale manufacturing.
Equipment Used in Flame Cutting
The flame cutting setup typically consists of:
- Flame Gun: A specialized tool that generates the high-temperature flame required for cutting.
- Feed System: A system responsible for controlling the movement of the flame gun and the metal sheet.
- GTAW (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) Equipment: This equipment provides a reliable source of gas and the necessary electrical power for the flame gun.
How Does the Cutting Process Work?
The cutting process involves a series of steps:
- Flame Gun Movement: The flame gun is moved to the desired cutting location using a precision location system.
- Flame Ignition: The flame gun is ignited, producing a high-temperature flame.
- Cutting: The flame is directed at the metal sheet, causing it to melt and separate along the cut path.
- Cooling: The cut surface is removed using a gas washer or other methods to reveal a clean, smooth edge.
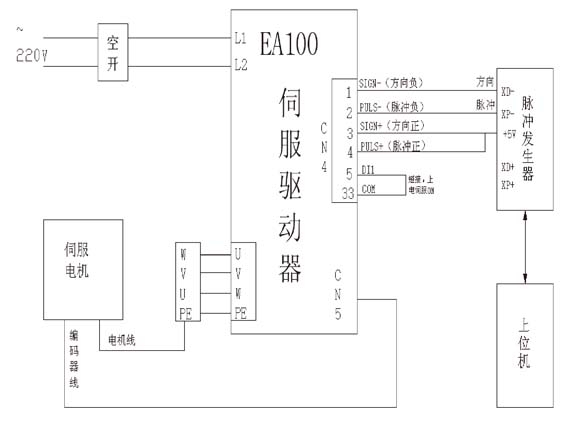
System Componentry and Working Principle
The flame cutting system consists of two primary axes, X and Y, which are synchronized to ensure precise movement and cutting. The control card, connected to the servo motor, provides pulse signals and steering signals to control the movement of the flame gun.
Settings and Adjustments
To ensure optimal cutting performance, several settings need to be made:
- Flame Gun Focusing: The flame gun needs to be adjusted to achieve optimal focus, ensuring maximum cutting efficiency.
- GTAW Gas Settings: The GTAW equipment’s gas settings, such as gas pressure and flow rate, need to be adjusted for optimal cutting performance.
- Speed and Feed Rates: The speed and feed rates of the feed system need to be adjusted to match the cutting speed and material being cut.
Conclusions
Flame cutting has come a long way, from its early beginnings to the sophisticated technology we see today. With its cost-effectiveness, large cutting thickness capabilities, and low precision requirements, flame cutting has established itself as a popular choice in the manufacturing industry. By understanding the process, equipment, and settings involved in flame cutting, manufacturers can optimize this technology to achieve high-quality cuts and efficient production.
Word Count: 800 words