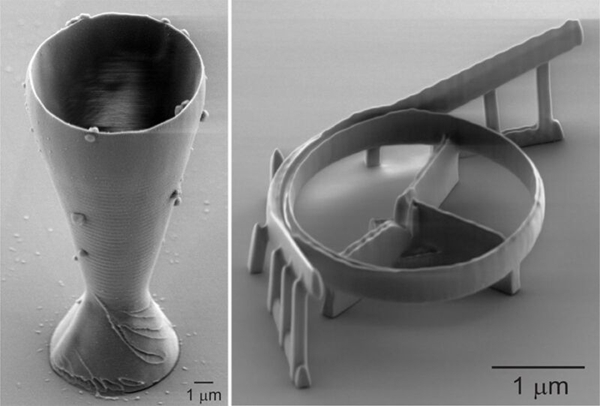
2023Year7moon10day,According to Mohou.com,a team of Swedish scientists recently developed an innovative quartz glass3DPrinting technology that simplifies complex and energy-intensive processes. To demonstrate its potential, they successfully used this technology to print the world’s smallest wine glass, with a rim even thinner than a human hair. Additionally, they printed optical resonators for use in fiber optic telecommunications systems, which are3DAnother potential application area for printing technology.
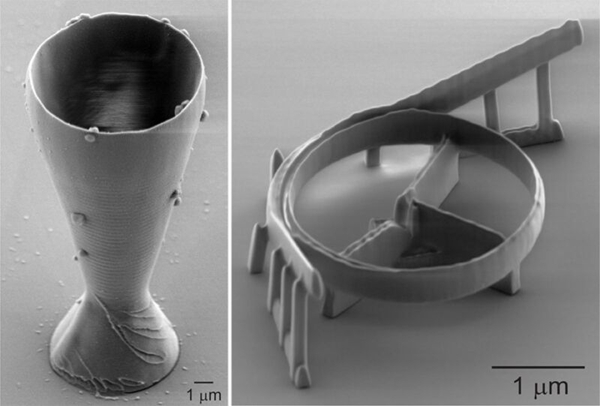
△Using a scanning electron microscope to photograph the world’s smallest quartz glass wine glass (left) and micro-optical resonator (right), the rim of the glass is smaller than the width of a human hair.
Stockholm, SwedenKTHCo-author from the Royal Institute of TechnologyKristinn GylfasonHe said: “The backbone of the Internet is built on fiberglass. In these systems, various filters and couplers are used, and now we can3DThe printing technology to create these filters and couplers opens up many new possibilities. “
We can summarize that this quartz glass3DA breakthrough in printing technology is3DThe field of printing opens new development prospects and will provide more opportunities for innovation in areas such as energy and communications.

△Relevant research results have been published in the journal “Nature Communications”, titled “Submicron Resolution3DPrinting of silica glass »(portal)
Technical background
The authors point out that for silica glass (amorphous silica)3DPrinting still poses challenges, especially at the microscopic scale. Although several approaches have been attempted to solve this problem, including techniques such as stereolithography, direct ink writing, and digital light processing, even the most advanced techniques have only achieved feature sizes of the order of several tens of microns. Soils currently used–The gel process involves loading silica nanoparticles into an organic mixture, so that the final printed structure is a composite material rather than pure quartz glass, resulting in some undesirable properties such as thermal stability, stability chemical, hardness and optical transparency over a wide wavelength range. .
Additionally, a high-temperature sintering step is required to remove organic residue and achieve the desired properties, an additional energy-intensive step that significantly limits the range of potential applications. Some methods also require the micron scale3DPrinting structures for assembly also poses some challenges.
△By direct laser writing3DPrinting quartz glass microstructures
New quartz glass3Dprinting technology
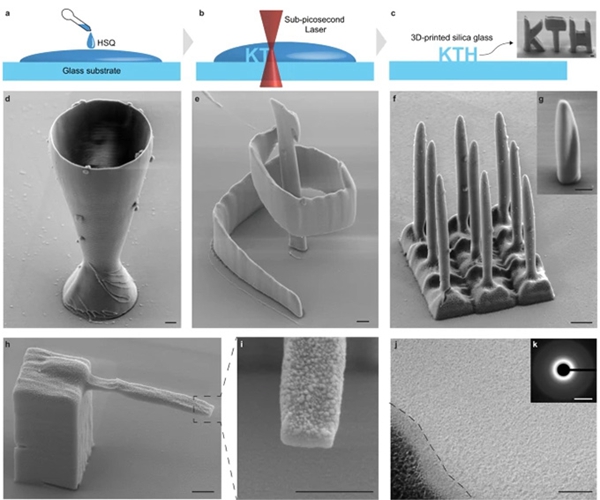
This technology uses hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) as a replacement for inorganic materials. This inorganic material is similar to silicon dioxide and can be structured by electron beams, ion beams and specific wavelengths of ultraviolet light. Unlike traditional methods of stereolithography or direct ink writing, their method does not rely on organic compounds as photoinitiators or binders, but directly uses inorganic compounds.HSQCarry out crosslinking.
The method includes three main steps. First, putHSQDissolve in an organic solvent and place on the substrate. onceHSQdry, use a focused sub-picosecond laser beam to apply the3DThe shape is drawn. Finally, use a potassium hydroxide solution to dissolve any unexposed particles.HSQ. Raman spectroscopy showed that the printed microstructures had the characteristics of quartz glass, but residual traces of hydrogen and carbon still remained. In order to remove these organic residues and obtain purer quartz glass, this can be achieved by heating it to a lower temperature (approx.900°C) additional step of annealing the structure. Subsequently, the structure spectrum was matched to that of a commercial fused silica glass substrate.
It should be noted that, for3DAnnealing the printed microstructures can cause some degree of shrinkage or warping, but the researchers found that the maximum shrinkage of their quartz glass structures was approximately6%while maximum shrinkage of glass objects made by stereolithography and direct ink writing methods16%has56%. This new type of quartz glass3DPrinting technology provides new possibilities for realizing more complex and high-precision quartz glass microstructures, and offers broad application prospects.

△3DPrinted optical demonstrator and its characterization
Broad application prospects
In addition to the micro wine glasses and optical resonators used in the proof of concept, the research team also used this new quartz glass.3DPrinting technology creates miniature versions ofKTHQuartz fiberglass logos, cantilevers, conical spirals and tips. They believe this method could also be applied to making custom lenses for medical devices and microrobots. by in3DCoating printed microstructures with nanodiamond or iron nanoparticles can further refine the properties of hybrid quantum photonic integration or control the movement of the structure through magnetic forces.
Graduate student and co-authorPo-Han Huangmeans: “Integrated3DWhen printing methods, considerations often differ from application to application. Although different applications still require optimization of our approach, we believe this advancement demonstrates how3DThe importance and necessity of applying glass printing to real-world scenarios. “This new type of quartz glass3DThe development of printing technology has opened up new possibilities for the fabrication of customized microstructures and offers broad application prospects.
Source: Antarctic Bear
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.