Mold is known as“The mother of industry”, its preparation is at the heart of modern manufacturing. The level of mold technology has become an important symbol for measuring the level of a country’s manufacturing industry. China’s self-sufficiency rate in large-size, precise, complex and long-life high-quality molds is only30%Most of them depend on imports. Most of the reasons for the low self-sufficiency rate of high-quality molds in China are that some properties of the required mold steel do not meet the usage requirements, or some properties are far inferior to those of similar foreign products. . There are some problems in the material heat treatment process. As a near-net shape technology, additive manufacturing can transform complex three-dimensional structures into two-dimensional planar structures, and then achieve solid additive manufacturing through layer-by-layer accumulation of materials. This method can not only allow shape control, but also. also control the organization and fine control of the ingredients. This technology changes the way of thinking about traditional mold design and material design. However, there is currently relatively little research on additive manufacturing of mold steel at home and abroad, which has also led to slow industrial application.
Research in this field at home and abroad mainly focuses on the design of die steel powder materials and its special preparation technology for additive manufacturing, as well as research on shape and controllability. of die steel in the additive manufacturing process. Due to their complex service environment, molds are often required to operate continuously in environments subject to impact loading, alternating hot and cold or corrosion. Therefore, the requirements for the overall mechanical properties of mold steel additive parts are relatively high in addition to having high tensile strength. resistance, it must also have a certain degree of plastic toughness, particularly impact toughness. The powder used should generally have high sphericity and bulk density, a narrow particle size distribution range and extremely low impurity content. The amount of hollow powder should be strictly controlled during the powder manufacturing process. Excessive hollow powder will increase the probability of pores or pores in the additive body and reduce its density when the content of impurities exceeds the limit value, such as excess oxygen; and nitrogen, reduce bond strength at grain boundaries and increase brittleness. At present, the main preparation methods of spherical powder are plasma rotating electrode atomization.(PREPARATION)Fahe aerosolization(GEORGIA)Law etc.
The current application of additive technology in mold manufacturing mainly focuses on high-end injection molds with conformal cooling channels. This new mold solves the bottleneck problem of uneven cooling of traditional straight-hole cooling water channels. Companies that have successfully applied additive manufacturing technology to the processing process of conformal cooling molds mainly include foreign companies.EOSAnd3D systems。EOSThe company uses selective laser melting technology to manufacture conformal cooling channel molds with uniform surface temperature distribution, and the cavity surface temperature is120 ℃ fell to90 ℃, the product production cycle is shortened17%and the quality of the product has been improved, and the370,000After cycles, total savings can reach2million euros. Furthermore, GermanyGDT Solutionscompany, United StatesHoneywellbusiness, UKUniversity of Central Lancashirecompany and germanyTechnical University of DortmundThe company and others have also conducted extensive research into additive manufacturing of conformal cooling channel molds. Domestic mold steel additive manufacturing process technology started late. Companies such as Wuhan Huake 3D, Dalian Micron Speed Manufacturing, Shanghai Yuerui 3D and other companies have explored some applications of additive manufacturing of conformal cooling channel molds. However, parts formed by additive manufacturing are different. Parts manufactured by traditional methods have significant differences in structure and formability, and are also prone to defects such as microcracks, pores and oxidation, which seriously affects the quality and process promotion of the parts. additive manufacturing forming molds. Therefore, research on additive manufacturing and mold steel performance has received wide attention from academia and industry. This article will start from the following2A brief discussion of each aspect:(1)Method for preparing cast steel powder;(2)Additive manufacturing of typical mold steels and their mechanical properties.
1Method for preparing cast steel powder
At present, the main method of preparing spherical powder for mold steel is plasma rotating electrode atomization.(PREPARATION)Fahe aerosolization(GEORGIA)Law etc. There are some differences in the effectiveness and quality of powder between different powder coating methods, which will be briefly discussed below.
1.1 Plasma rotating electrode atomization method
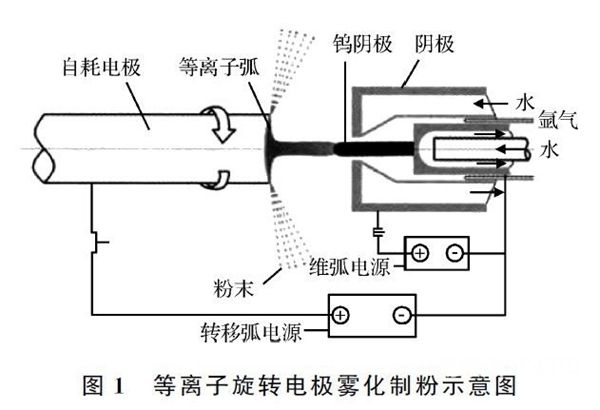
Plasma Rotary Electrode Atomization(PREPARATION)The method involves placing a metal or alloy metal bar in a rotating device to act as a consumable electrode, then placing the electrode under an inert protective gas to rotate it at high speed, and at the same time it is heated and melted by a coaxial plasma arc to form The liquid film disperses and moves away from the end face of the electrode rod due to centrifugal force. When the liquid film rubs against the inert protective gas during atomization, it is further crushed under the action of shear. strain, and finally quickly cools and solidifies under the action of surface tension to form a spherical powder. This technology, its powder manufacturing scheme is as shown in the figure.1watch.
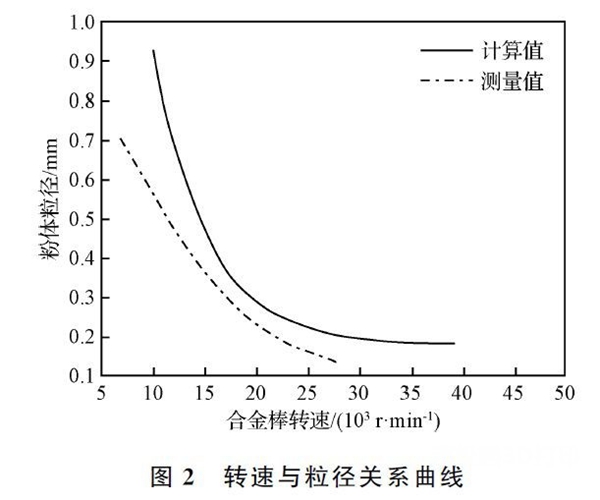
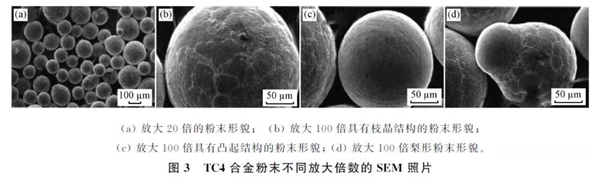
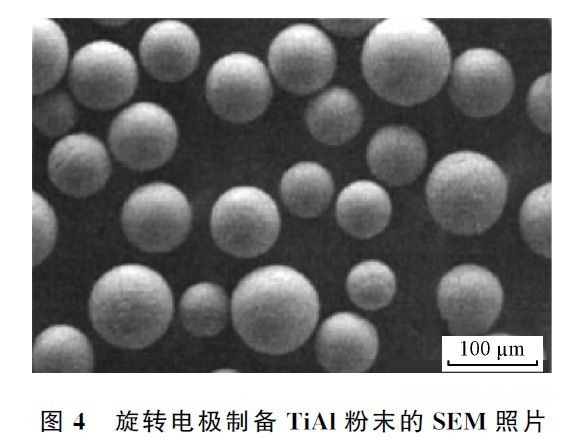
Electrode speed, arc power, shielding gas type and material properties will directly affectPREPARATIONThe purity and sphericity of the prepared powder, among which the rotation speed of the electrode, are the most critical. Liu Jun et al. obtained different particle sizes by adjusting the electrode speed.TC4Powder, as the rotation speed increases, the particle size of the powder decreases, as shown in the figure2watch. Moreover, as the particle size increases, the mass fraction of oxygen in the powder gradually decreases, while the mass fraction of nitrogen is less than0.005 5%there is no obvious change; and when the speed reaches25,000 rpmWhen , it was found that most of the powders were regular spherical and the rate of sphericity reached95%as shown in the figure3watch. Passed by Yang Xin and othersPREPARATIONpreparationTi-47Al-2Cr-2NbSpherical powder, when the diameter of the electrode rod is70 millimetersthe rotation speed is18,000 rpmWhen , the rate of sphericity is higher, reaching99.6%the mass fraction of oxygen in the powder increases sharply as the particle size decreases, but does not exceed0.1%. There is almost no change in the mass fraction of nitrogen, which is approximately0.004%. picture4Presented are those adopted by Yang Xin et al.PREPARATIONScanning electron microscope photo of the powder prepared by the process, according to the figure4We see that the powders are all spherical and have no satellite powder.
PREPARATIONThe resulting powder has good sphericity, narrow particle size distribution range, low oxygen content, clean surface and easy particle size control. However, it is an ideal method for preparing powder for metal additive manufacturing.PREPARATIONThe processing efficiency is low and the equipment operating cost is high, resulting in high production costs. This is also the main reason for the low industrial application of this method. This method has good applicability to different materials, so it can be used to process some non-ferrous metals, refractory metals and other powders with relatively low market demand. It is also suitable for scientific research institutes to produce and process small batches of powders.
1.2 aerosolization
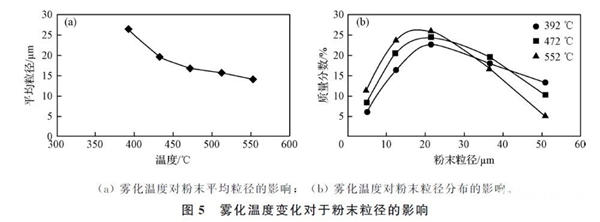
The gas atomization method is a method that uses high-speed airflow to directly break up streams of liquid metals and alloys to form molten metals. Its essence is to spray a high-speed, high-pressure fluid stream through an atomizing nozzle to break up the melt. fine droplets, then cool them into powder. The process is also called gas atomization because the commonly used medium is gas. The shape of powder particles is mainly determined by the surface tension of the molten metal, cooling capacity, density, flow rate and activity of the spray medium. Generally speaking, the cooling rate of gas atomization is slow, and the prepared powder is generally spherical or quasi-spherical, while the corresponding water atomization has a relatively high cooling rate, and the powder is often polygonal or irregular in shape. Most early studies of aerosol spray technology were used“Free fall nozzle”, but this atomization efficiency is low and can only be used in preparation50~300 mmof powder. Because the gas atomization production process is complex and there are many influencing factors, Li Xin and others obtained through experiments the change curve of average particle size and fraction mass of the powder as the atomization temperature changes, as shown in the figure.5As shown, when the atomization temperature increases, the average particle size of the resulting powder decreases, but when the temperature increases to a certain extent, the particle size of the powder changes very little. The test results of Wang Qi et al. show that as the atomization pressure increases, the average particle size of the titanium alloy gradually decreases. They also found that in different atomization media, the effects of nitrogen and argon are similar, as well as the effect of helium. is similar, it is better, but the price of the latter two is higher, so it is more economical to choose nitrogen.
To summarize, comparePREPARATIONAndGeorgiamethod, influencePREPARATIONThe number of milling quality factors is less thanGeorgia,illustratePREPARATIONIt has greater applicability to different materials and the quality of the resulting powder is more controllable, but its production efficiency is lower and the production cost is higher, soGeorgiaThe method is more suitable for industrial mass production, whilePREPARATIONIt is more suitable to meet the customized production needs of rare metals, non-ferrous metals and some refractory metals.
2Additive manufacturing and performance of typical mold steel
There are many types of mold steel, and the performance requirements of mold steel corresponding to different types of molds are also very different. Common types of mold steel include martensitic stainless steel, high alloy low carbon steel, high quality carbon steel, etc. This article focuses on the most researched and used methods currently in the field of additive manufacturing.2Typical Steel TypesH13And18Ni300As an example, the process, microstructure, and mechanical properties of steel die additive manufacturing are briefly discussed.
2.1H13 Additive manufacturing of steel and its properties
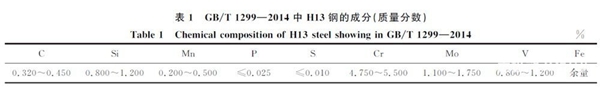
H13Steel is a kind of hot work steel and its corresponding national standardGB/T1299—2014The brand number in4Cr5MoSiV1。H13Medium temperature steel base metal(about600 ℃)It has good overall properties, high hardenability, low heat treatment deformation rate and long service life. Its specific components are shown in the table.1。H13Steel is often used in hammer forging dies, aluminum alloy die casting dies, hot extrusion dies, high speed precision forging dies and forging press dies .H13Commonly used methods for additive manufacturing of steel include selective laser melting.(SLM)laser energy deposition(DED)and arc additives, etc. Due to different molding heat sources, these methods have some differences in their additive processes, microstructure and mechanical properties.
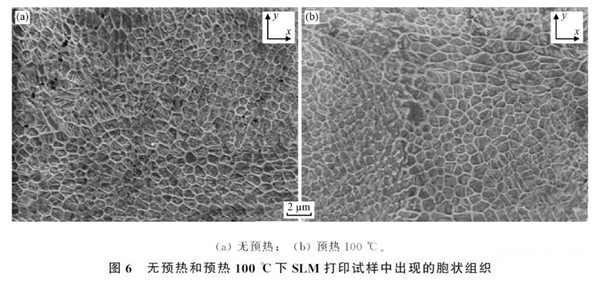
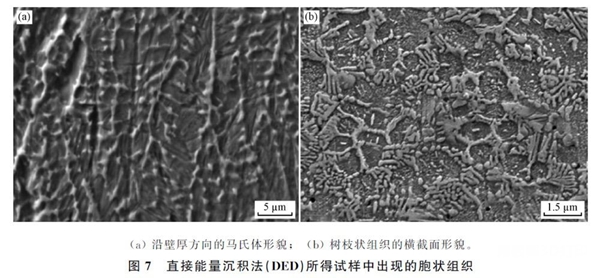
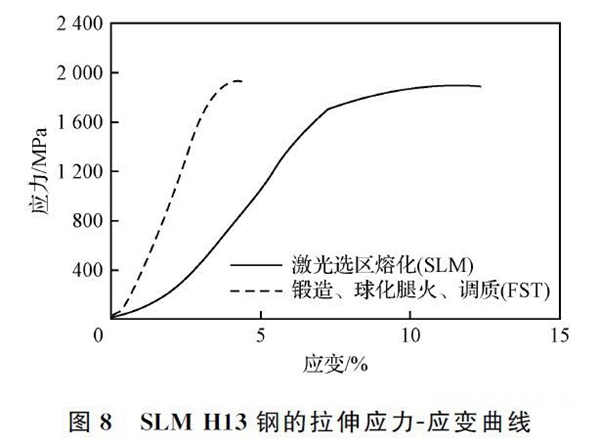
H13Cellular and dendritic structures can be clearly observed in the microstructure of steel additive parts, and the residual austenitic structures are equally distributed among the dendrites. The morphology of dendrites and cells obtained by different additive methods is also slightly different, mainly due to different heat inputs.(Compare according to linear energy density)provoked. ForGDTGenerally speaking, its thermal input is low and the diameter of the cellular tissue is generally0.5~2 mmas shown in the figure6watch. And the heat input is greaterDEDAdditive(Its thermal contribution isGDTof5~8times)The diameter of the mesocellular tissue is generally2~30 mmas shown in the figure7shown, at the same timeDEDThe secondary dendrites of the additive parts are significantly larger thanGDTthick. The researchers also found that in interdendritic zones, which are areas with many retained austenite locations,Cr、MB、VThe content of the elements is significantly higher. Cellular organization is the result of microscopic segregation during the solidification process. Arc additive body with greater heat input(Its thermal contribution isDEDof3~6times)In the middle, we can observe a massive ferrite structure. existH13Enriched carbon in steel can stabilize austenite, butH13There is currently no clear explanation for the formation of austenite in steel additive bodies.Holzweissig MJbelieved that the formation of austenite was due to diffusion of carbon caused by self-tempering during the additive process.Krell Jalso found δ and γ ferrite phases between the dendrites.GDTThe crystalline texture of additive parts can be very weak, the strength is equivalent to that of the work-hardened state, and the plasticity is that of the work-hardened state.3times, as shown in the figure8indicated, but the energy absorbed by the impact is only14.4 days。
General condition rolledH13The average hardness value of steel sheets is approximately540HVthe average hardness value in the annealed state is250HV. to useGDTpreparedH13The average hardness value of steel additive body can reach680HV;AndDEDThe hardness of additive parts is slightly reduced, with an average value of600HV;The average hardness of arc additive parts is470HV. As the heat input increases, the average hardness value of the additive body decreases, whereGDTAndDEDThe average hardness value of the additive body is higher than that of the rolled stateH13Steel, arc additives have lower hardness values than rollingH13Steel, but are higher than the annealed base material.
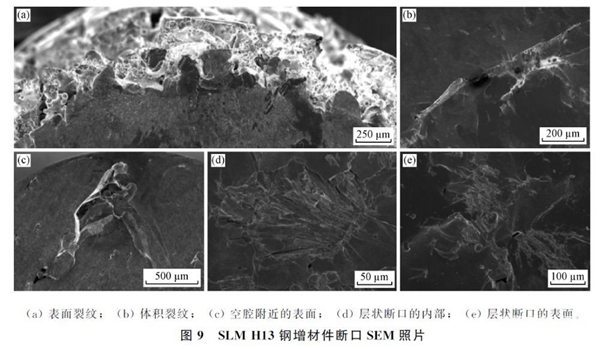
exist1,038 solid solution at ℃,482 Obtained after aging at ℃H13The average tensile strength of the steel base material is1,900 MPathe average yield strength is1,500 MPa。XUE LWaiting for adoptionDEDincomeH13The average tensile strength of the steel additive body is2,000 MPathe average yield strength is1200 MPa。Mertens R.Other test results show that,GDTAdditive manufacturing incomeH13The yield strength of steel is1,236 MPathe tensile strength is1,712 MPaand found that preheating the powder bed can reduce the yield strength and increase the tensile strength, but the strength values are lower than those of the corresponding base metal. Wang Tingting used the arc additive method to obtainH13 The maximum tensile strength of thin-walled steel parts is1,187 MPathe elastic limit is800 MPa. The above results show that,H13The tensile strength and yield strength of the steel additive body are lower than those of the base material after solution aging treatment, so the subsequent heat treatment of the additive body is particularly critical.H13The heat treatment method of the steel additive body is the same as that of the base material, namely solid solution aging. Some additive bodies can also only undergo aging treatment. After heat treatment, the tensile strength and yield strength of the additive body are significantly improved, but they are still slightly lower than those of the base material. After annealing or aging treatment of the additive parts, the strength of the additive parts can be equivalent to that of the rolled base material, but the elongation will still be greatly reduced, which is mainly due to defects such as holes at the interior, as shown. in the figure9watch.
2.2 18Ni300Additive manufacturing of steel and its properties
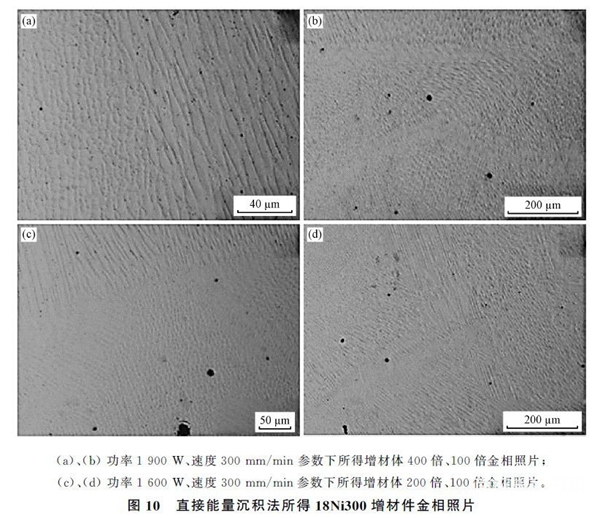
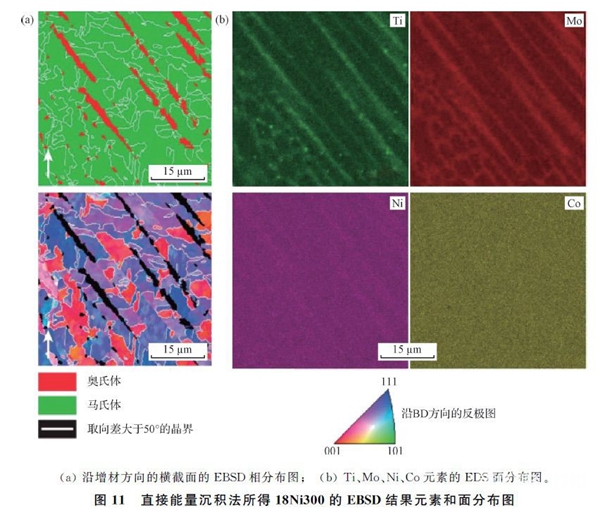
18Ni300It is a low carbon maraging steel with the advantages of high strength, good toughness and high wear resistance. It is often used to make plastic molds. Thanks to its excellent weldability,18Ni300Often used for additive manufacturing.18Ni300The structure of the additive body is very different from that of the parent material obtained by traditional casting or rolling methods. Cellular tissue and dendritic tissue can also be clearly observed in the additive body structure.Campanelli SLThe size of the cellular crystal structure obtained by direct deposition of laser energy is approximately several tens of microns, as shown in Figure10As shown, the original austenite grain size can reach1mmAbout 10% of the martensitic transformation occurs in such a coarse structure, leading to obvious differences in the morphology and properties of the martensitic structure and the martensitic structure produced under normal conditions. AndJagle EAWaiting for adoptionGDTThe size of the cellular crystal structure of the additive part obtained by the process is of the order of a few microns.18Ni300The retained austenite can be clearly observed in the additive structure.(Austenite generation may be related to excessive cooling rate, element segregation or residual stresses.)which is the distribution of alloying elements between dendrites during the solidification process(intercellular)Results of regional enrichment through microsegregation(picture11). Nickel enrichment can stabilize austenite at room temperature. Therefore, maraging steel produced by additive manufacturing contains a large amount of austenite.(6%~11%) 。
By optimizing the additive process parameters and heat treatment parameters, it is possible to18Ni300The yield strength and tensile strength of the additive body reach the strength of the solid solution aged base material.SONG JWaiting for adoptionGDTprepared according to the method18Ni300The tensile strength of the additive body is1,000 MPathe elastic limit is850 MPafollowed by840 ℃ solid solution2 hours,exist480 ℃ aging6 hoursAfter that, the tensile strength of the joint increases to1,600 MPathe elastic limit increases up to1,800 MPa。Felix-Martínez CWaiting for adoptionDEDprepared according to the method18Ni300The tensile strength of the additive body is900 MPathe elastic limit is800 MPaslightly lower than aboveSONG JWaiting for adoptionGDTAdditives prepared by the process. The subsequent heat treatment of the additive body is mainly solution aging or only aging treatment. After heat treatment, the yield strength and tensile strength of the additive body increase significantly. Currently produced using arc additive manufacturing methods18Ni300There are relatively few studies.
in conclusion
(1)Currently, the most commonly used methods for additive manufacturing of mold steel are selective laser melting, direct energy deposition, and arc additive manufacturing. Among them, the selective laser melting method has the largest number of application cases and a relatively large number of researchers have studied it.
(2)Additive manufacturing technology has gradually become a powerful complement to mold manufacturing methods, establishing a technical foundation for complex mold manufacturing. However, the maximum tensile strength and yield strength of the additive body are always lower than those of the base material after rolling or solution aging, especially the yield strength, at the same time, its resistance properties shocks and fatigue are always lower than those of; molds made by traditional methods. A bigger gap.
(3)Further research should focus more on how to improve the impact resistance and fatigue properties of mold steel, and should also optimize the heat treatment system. Existing methods are more prone to solid solution aging and near-form additive manufacturing. It is very important to choose an appropriate heat treatment system to improve strength and toughness while reducing the impact on the dimensional accuracy of additive parts.
Source: “Chinese metallurgy”2022year3To wait for
Author: Zhang Liangliang1Zhou Yang1Liu Shifeng1Yang Xin2Wang Yan1 (1. School of Metallurgical Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710055;2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, Shaanxi 710055)
PDFFree download of the original text
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.