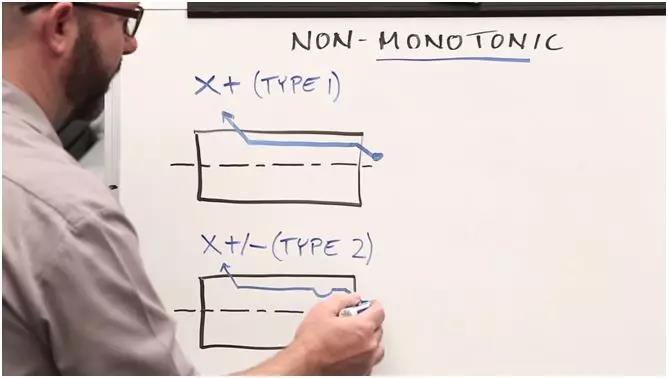
When you use cycle G71 (external circle) in the program, we can obtain a non -monotonic change alarm due to the small grooves on the outline of the outer circle. Because this type of alarm appears too frequently, a large number of users discuss this question, and we think it is necessary to make a video to help solve this problem.
First, we will use cycle G70 (outline finish). The difference between G70 and G71 is that in the direction of movement, there is no restriction on the use of G70, which is only for test purposes. Back to original roughness.
Second, to discover the code that causes alarms in the program, we need to use “graphics” to simulate the graphics. There will also be corresponding alert prompts to allow users to know where the code must be modified.
Third, we must understand the direction of the movement of the tool. When you use G71, if the movement direction of the tool is monotonous (the cutting direction is incremental or decreases), this means that we use a G71 type cycle. If one of the axes of X / Z is changing non -monotonous, for example, there is a groove on the external circular profile, and have a Rain you must use the two of the G71 type cycle.
Sometimes we will also cause non -monotonous changes due to manual errors when writing programs (for example, G03 entry is G02).
In fact, we can find the solution in the programming manual. But after having read it, we do not remember that after finding the problem, we examined the programming manual and found that it was worth more time. As familiar with these rules as we imagine.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.