Mohou.com Concise Digital Manufacturing Manual (1): Why Use Digital Manufacturing?
Mohou.com Concise Digital Manufacturing Handbook (2): Comparison between Additive Manufacturing and Subtractive Manufacturing
Mohou.com Concise Digital Manufacturing Handbook (3): Understanding Basic Materials
In this chapter, Mohou.com will work with you:
▶ First acquaintance3DPrint
▶ Understand the different processes
▶ Design considerations
▶ Post-processing
3DPrinting is an umbrella term for all additive manufacturing processes and, in the vast majority of cases, additive manufacturing and3DPrint is synonymous and can be used interchangeably. If you have not contacted3DPrinting, you might associate this term with a type of device similar to an inkjet printer, but learn more and you will be surprised.3DPrint encompasses form and function. This chapter briefly presents 3D printing, lists several important processes and discusses some of the3DThings to pay attention to when designing for print and a brief description of the subsequent processes that may be involved.
1. Understand3DPrint
As mentioned previously,3DPrinting encompasses a set of different additive manufacturing processes used to meet different design and functional requirements. Although these processes vary greatly, before examining the details of each process, let’s examine their common characteristics.
1. Process flow
3DPrinting allows parts to be constructed by stacking very thin layers of material. There are several ways to assemble layers of material to make a solid object, including extrusion, spraying, sintering, melting, or solidification. Regardless of the specific method used in the process, each layer of material is deposited individually and then the material is bonded to the layer below to form the part.
2. Equipment
When it comes to digital manufacturing, high-quality industry3DPrinting equipment is really important. Although a simple desktop computer 3D A printer may be enough for a DIY craftsman to build a crude toy or other basic prototype in a weekend, but producing advanced prototypes or parts for commercial projects requires much more complex, powerful, and much more expensive equipment. .
The equipment used for additive manufacturing varies depending on the process used, but essentially it must be able to place material in designated locations with extremely high precision. Depending on the process, it may also be necessary to fuse or bond the material (some processes use materials that automatically bond to existing layers of material, such as photolithography).
In addition to using reliable additive equipment and materials, high-quality prototype manufacturing also relies on powerful computer workstations with sophisticated processing capabilities to create precision part models. A good digital manufacturing company usually has all three of these things: reliable equipment, high-quality materials, and powerful computers.
3. Usage scenarios
because3DPrinting is a unique way of manufacturing parts by stacking thousands of thin layers of material, making3DPrinting has gained the ability to create very complex geometries that would otherwise be impossible to process with traditional methods.3DPrinting has advantages when manufacturing complex shapes or structures. Additionally, additive manufacturing is particularly attractive for rapid prototyping and, in some cases, also suitable for low-volume production of final parts. Same as injection molding orCNCThe treatment is different,3DPrinting makes part development simple and straightforward without additional design planning, allowing you to quickly explore your design options and reducing some of the obstacles you may encounter in traditional manufacturing processes.
4. Understand the essentials3DPrinting process
In this section we will present various dominant currents 3D Printing Processes to help you better understand if a process can meet your needs at different stages of part prototyping and production.
Binder injection (Binder jet)
Binder jetting is one of the simplest and most basic additive molding processes. An inkjet printhead moves over a bed of powder, selectively ejecting a liquid binder (glue). After one layer has been printed, a new layer of unbonded powder is placed and the process is repeated until the complete part is formed. Once printing is complete, the unbonded powder is removed, leaving the finished product.
The binder jetting process offers the following advantages:
✓ Fast production speed
✓ Reduced cost
✓ Easy to produce in different colors
✓ Easy to copy complex geometric shapes
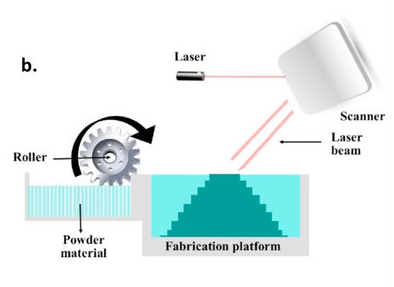
Thus, binder injection has the following disadvantages:
✓ Rough surface
✓ Low resistance of parts
✓ Not suitable for functional testing
stereolithography
stereolithography (YEARS) A computer-controlled UV laser is used to cure the parts in a bath of photoresist. When laser scanning completes a curing layer, the part deposits a layer into the liquid resin pool to cover a new resin layer and starts the next curing layer until all parts are completed. The quality of the finished part depends largely on YEARS The quality of the equipment used in the process and the principle of the process are shown in the figure. 4-1 watch.
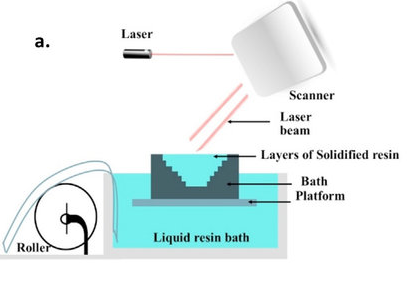
The main advantages of stereolithography are:
✓ Moderate price and high performance
✓ Easy to copy complex geometric shapes
✓ Excellent surface finish, one of the best surface finishes in additive processes
YEARSThe process also has certain disadvantages, including:
✓ Low resistance of parts
✓ Cured resin becomes brittle over time
✓ Parts have limited use in functional testing.
deposit of molten plastic material (FDM)
deposit of molten plastic material (FDM) Thermoplastic resin (usuallyABS、PCOr PLA) are melted and resolidified in layers to form the finished prototype. Because they use real thermoplastic resin, the parts are stronger than those produced by other processes, andFDMSome materials can even be used in functional testing.
FDM Some benefits of crafting include:
✓ Affordable price
✓ Moderate intensity
✓ Partially matches or approximates the physical properties of real plastics
✓ Easy to copy complex geometric shapes
FDM The process also has some disadvantages:
✓ The wavy surface of the part is evident
✓ Finished parts may be porous
✓ Limited applicability to functional testing
✓ Production is slow; producing large parts can take several days.
✓ z Shaft strength is poor
Multipolymer injection (Polyjet)
multipolymer spray(Polyjet) A print head is used to spray layers of photoresist, which quickly harden layer by layer using ultraviolet light. PolyjetThe thickness of the process layer is very thin, which allows very fine details to be produced. The process typically uses a gel matrix as a support that can be removed once the part is complete.
PolyjetSome advantages of the process include good surface finish and ease of reproducing complex geometries. But the downsides include limited resin options, low strength, and expensive materials.
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
selective laser sintering (SLS) Computer controlled CO2A (carbon dioxide) laser fuses layers of powdered plastic such as nylon from the bottom up. Strength is better thanYEARSbut inferior to injection molding orCNCThe intensity of production processes such as processing. SLS In some cases it can be used as a final part production tool.
SLS Has several advantages:
✓ Affordable price
✓ Provides very good precision
✓ More sustainable than some other processes, e.g. YEARS
✓ Suitable for certain functional tests
✓ Easy to copy complex geometric shapes
SLS Disadvantages include limited material selection and often rough surface finish.
digital light processing(DLP)
Based on digital light processing (DLP) Additive manufacturing will3DThe model slices are superimposed into image layers, which are then processed by Texas Instruments. (Texas-Instruments) of DLP The chip projects these layers, one after the other, onto the surface of a bath of photosensitive resin. The projected light hardens a layer of liquid photoresist which sits on a removable casting plate. When a new image is projected onto the liquid surface, the forming plate moves downward in small increments, hardening each subsequent layer until the final layer. The process can be used to produce limited quantities of small, highly detailed parts (such as jewelry), but is less suitable for larger parts, particularly those that require a smooth finish.
DLP Benefits include:
✓ Relatively fast casting process.
✓ Parts prices are competitive.
✓ High resolution is possible.
✓ Very complex shapes can be made.
DLP Some of the disadvantages are:
✓ Limited resin selection
✓ May not be suitable for functional testing
✓ May have a rough surface
Direct laser fusion of metal (DMLSOrGDT)
Laser sintering of metals (SLM) It is the main additive manufacturing process for manufacturing metal parts. It is similar toSLSSelective laser sintering of plastics, but using metals including aluminum alloys, stainless steel, titanium, cobalt-chromium and inconel. GDTThe process produces metal parts with good precision and detail as well as excellent mechanical properties. GDTIt can be used to produce very small parts and elements and, because it is an additive process, it can produce structural shapes that cannot be machined, such as partially enclosed space structures.
GDTProduced parts almost always require secondary operations including drilling, grooving, milling and reaming, as well as post-finishing treatments including anodizing, electropolishing, hand polishing, plastic spraying or painting.
GDTHas some important advantages:
✓ Almost all common metal alloys can be used
✓ Mechanical properties are basically the same as traditional castings
✓ Ability to produce geometries that cannot be machined or cast
GDT There are also some disadvantages:
✓ Production is relatively slow.
✓ Parts can be expensive.
✓ Manufacturing quality parts requires considerable expertise.
✓ Parts often require expensive post-processing.
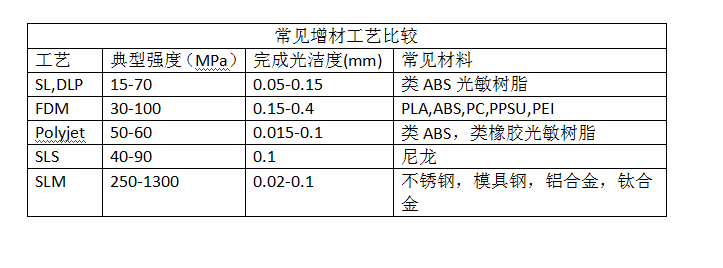
2.3DPrint Design Considerations
There are some important design considerations that affect how your part is made. For example, the type of process used has a direct impact on how much detail can be achieved, and if the wrong process is chosen, the design intent will not be reflected.
In some cases it may be necessary to modify your design to include internal supports. The need for supports depends on factors such as the physical design and material composition of the part. Your digital manufacturing partner should be able to advise you on support if your chosen process requires it.
You may also encounter cost considerations related to the materials selected and the physical volume of the part, etc. Depending on the process used, suitable plastic materials include:
✓ ABS
✓Nylon
✓Polycarbonate
✓ Polyetheretherketone (LOOK)
✓ Polyetherimide (Prince Edward Island)
✓ Polypropylene
Suitable metals include:
✓ Aluminum
✓ Cobalt Chromium
✓Inconel
✓ Stainless steel
✓ Titanium
No. 3 The chapter discusses the hardware in more detail, but the table aboveMaterials suitable for certain processes are briefly reviewed.
When choosing the right process and materials, you need to consider factors such as the strength and finish of the parts.
3.3DPost-print processing
The need for post-processing depends primarily on the intended use of the part and the chosen process. For example, a part that is only a conceptual model should only give an idea of the size and shape of the finished product and requires no additional post-processing. on the contraryyan’geat the other end of the spectrum could be represented by GDTMetal parts manufactured for end use, such as in airplane or rocket launches. In this case, the part may require many rigorous post-processings, such as anodizing to protect it, heat treatment to strengthen it, and ultrasonic defect testing for quality control.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.

















