In metal cutting, some chips are wound into a spiral shape and break on their own when they reach a certain length; some chips are broken into a C or 6 shape; some are wound like a clock and some are broken into needles; or small pieces, splashing everywhere, affecting safety; some strip-shaped chips are wrapped around the tool and workpiece, which can easily cause accidents. Poor chip removal condition will affect the normal production progress.
A,Factors Affecting Fleas
1. Part material
The alloying elements, hardness and heat treatment state of the workpiece material affect the thickness and curvature of the chips. Mild steel forms larger chips than hard steel; hard steel is less likely to curl than soft steel; the thickness of the chips that are not easy to roll up is thin, but when the thickness of the mild steel chips is too large, it is not easy to roll up; . At the same time, the shape of the workpiece is also an important influencing factor.
2. Geometric parameters of the tool cutting area
Reasonable geometric parameters of the tool cutting area are the most commonly used methods to improve the controllability of chip formation and the reliability of chip breaking.
The rake angle is inversely proportional to the chip thickness and has an optimal value for different processed materials; the main declination angle directly affects the thickness and width of the chip, and a large main declination angle can easily break the arc of the tool tip; The radius is related to the thickness and width of the chips as well as the direction of chip flow, a small arc radius is suitable for finishing and a large radius is suitable for roughing.
The width of the chipbreaker should be chosen in proportion to the feed quantity. If the feeding amount is small, choose a narrow one. If the feeding quantity is large, choose a large one. The depth of the chipbreaker should be inversely proportional. to the amount of feed. If the feeding amount is small, choose deep feeding.
3. Cutting quantity
The three cutting quantity factors will limit the range of chip breakage. The factors that have the greatest impact on chip breakage are feed rate and backcut amount, while cutting speed has the least impact on chip breakage in the context of speed conventional cutting. The amount of feed is proportional to the chip thickness; the amount of back cut is proportional to the width of the chips; chip speed is inversely proportional to chip thickness. As the cutting speed increases, the effective chip breaking range becomes narrower.
4. Machine tools
Modern CNC machine tools use the NC edit function to periodically change the feed amount to achieve the goal of forced chip breaking, often called “programmed chip breaking.” This method has high chip breaking reliability, but low cutting economy. It is often used in processes where chips are difficult to break by other methods, such as deep grooves on the face of lathes.
5. Cooling and lubrication condition
Adding cutting fluid expands the effective chip breaking range, especially when chips are easily bent at low feed rates. Using high pressure of cutting fluid to break and remove chips is an effective method in some processing methods. For example, in deep hole machining, high-pressure cutting fluid can evacuate chips from the cutting area.
two,Chip shape formation process
The ribbon chip formation process can be divided into three stages:
1. Basic deformation stage: Chip deformation occurs when the cutting layer metal and the tool cutting edge begin to contact and turn into chips and separate from the workpiece material;
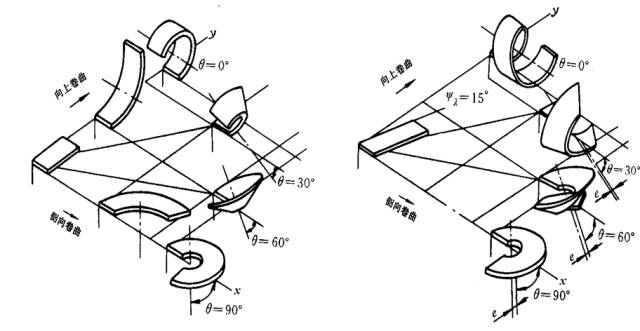
2. Loop deformation stage: upward loop, side loop, taper loop in direction A and B;
3. Additional stages of deformation and fracture.
3. Chip classification
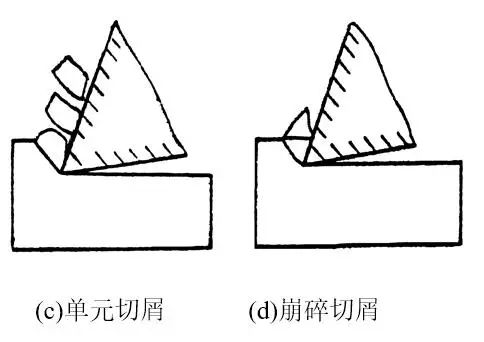
Due to different workpiece materials, cutting conditions vary. The shapes of the chips generated during the cutting process are diverse. The chip shapes are mainly divided into four types: ribbon, nodule, granular and crushed, as shown in the figure.
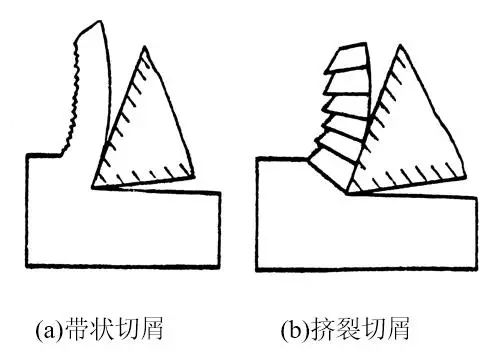
1. Strip the chips
This is the most common type of chip. Its internal surface is smooth and its external surface is hairy. When processing plastic metals, these chips are often formed under working conditions characterized by low cutting thickness, high cutting speed and large tool rake angle. Its cutting process is balanced, the cutting force fluctuates less, and the roughness of the machined surface is smaller.
2. Nodular chips
Also called squeeze chips. Its exterior surface is irregular and its interior surface is sometimes cracked. Such chips often occur when the cutting speed is low, the cutting thickness is large, and the tool rake angle is small.
3. Granular chips
Also called unit chips. During the chip formation process, if the shear stress on the shear surface exceeds the breaking strength of the material, cracks will extend across the entire surface and chip units will fall off from the cut material, forming granular chips . As shown in figure c.
The above three types of chips are only possible when processing plastic materials. Among them, the cutting process of strip-shaped chips is the smoothest, and the cutting force of unit chips fluctuates the most. The most common chips in production are strip chips, sometimes cracked chips are obtained, and unit chips are rare. If the chip extrusion conditions are changed, for example by further reducing the tool rake angle, reducing the cutting speed, or increasing the cutting thickness, unit chips can be obtained. On the contrary, strip-shaped chips can be obtained. This shows that the chip shape can be transformed depending on the cutting conditions. By mastering its changing rules, you can control the deformation, shape and size of chips to achieve the goal of curling and breaking chips.
4. Grind the chips
These are fragile material chips. The shape of this chip is irregular and the machined surface is uneven. From the point of view of the cutting process, the chips deform very little before breaking and the chip formation mechanism is different from that of plastic materials. Its brittle fracture is mainly due to the stress exerted on the material exceeding its tensile limit. Such chips are often obtained when processing brittle and hard materials, such as high silicon cast iron, white cast iron, etc., especially when the cutting thickness is large. Because its cutting process is very unstable, it is easy to damage the tool and the machine tool, and the machined surface is rough, so it should be avoided in production. The method is to reduce the cutting thickness so that the chips become needle-shaped or flake-shaped at the same time, increase the cutting speed appropriately to increase the plasticity of the workpiece material.
The above types are four typical types of chips, but the shapes of the chips obtained at the processing site are diverse. In modern cutting processing, the cutting speed and metal removal rate have reached very high levels, and the cutting conditions are very harsh, often producing a large amount of “unacceptable” chips.
Appropriate measures should be taken during cutting to control chip curvature, flow and breakage to form a good “acceptable” chip shape. The most widely used method of chip control in actual machining is to grind a chip breaker to the rake face or use a pressure block chip breaker.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.