Thanks to its excellent properties, diamond has shown great application potential in many high-tech fields such as mechanics, optics, thermal and electronics. However, its surface quality has a crucial impact on the application effect, which is directly related to its applicability in the fields of precision manufacturing and high-end technology. Therefore, how to effectively improve the surface quality of diamond through advanced polishing technology has become a central topic of current research.
With the development of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) diamond technology, large-scale synthetic diamond can be produced on a large scale and widely used. However, diamond CVD is often accompanied by uneven film thickness, stress deformation, different grain sizes, and inconsistent orientation. , and positioning. It has the disadvantages of high defect density and low surface quality, so it must be planarized before application.
However, diamond increases the difficulty of mechanical surface polishing due to its ultra-high hardness, excellent wear resistance and high chemical inertness. Therefore, how to achieve efficient, low-cost, low-damage polishing has become the key to the large-scale industrial application of diamond.
mechanical polishing
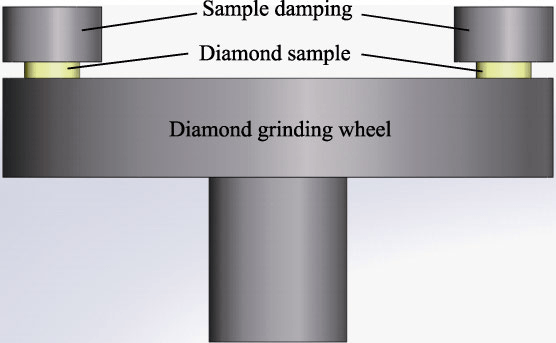
Mechanical polishing is the most traditional diamond polishing method and is currently the only widely used diamond polishing method. During mechanical polishing, the polishing disc rotates at an extremely high speed (greater than 2,500 rpm) and exerts significant pressure (greater than 10 N) on the diamond workpiece. This method uses the mechanical action of diamond abrasive grains to obtain material removal. , but the treatment effectiveness is low and treatment damage is easy to occur. Mechanical polishing will cause surface and subsurface damage to the diamond workpiece. Mechanical impact during the polishing process will cause pits, underground cracks and lattice damage to form on the polished surface. This damage cannot be removed by subsequent polishing. Steps and optical equipment cannot be detected.
Schematic diagram of mechanical polishing Source: Public Internet
mechanical-chemical polishing
Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) is an ultra-precise polishing method that adds oxidants during the mechanical polishing process to oxidize carbon atoms to increase the polishing rate. Although the diamond polishing rate is slow, it has the advantages of low surface damage, low roughness, simple equipment, low operation and maintenance costs and light pollution. surface after polishing. It has gradually attracted attention in the field of diamond polishing.
Schematic diagram of chemical-mechanical polishing Source: Public Internet
In the process of chemical mechanical polishing, oxidants play a vital role at first, high temperature molten salt was used as an oxidant for polishing. KNO3, NaNO3, LiNO3, KMnO4, K2FeO4, KIO4, K2Cr2O7 and H2O2 are commonly used oxidants. Some of them require higher working temperatures to reach the melting point. For example, the melting point of KNO3 is 334°C and the melting point of KNO3. NaNO3 is at 307°C. H2O2 is a powerful oxidant. Using H2O2 solution as polishing fluid, an atomically smooth surface can be obtained after chemical-mechanical polishing at room temperature.
In order to further improve the polishing efficiency and make the diamond surface uniform and smooth, mixed oxidants have become public. Among them, the polishing liquid composed of H2O2 and its mixture has become the main choice for chemical diamond polishing. For example, first use an iron plate to polish the diamond sample for 2 hours, quickly remove the scratches and damage on the diamond surface through thermochemical polishing, and then use an iron plate to polish the sample of diamond in H2O2 solution for 3 hours to obtain an ordered and ultra-smooth crystal surface.
Thermochemical polishing
Thermochemical polishing is a polishing technology based on the diffusion of carbon atoms into hot metal, the conversion of diamond to graphite and the oxidation of diamond. During thermochemical polishing, the diamond film is spun and rubbed on a hot iron disk heated to 750~1000°C in a vacuum, hydrogen or inert gas atmosphere. Under high temperature conditions, the diamond film is made by diffusion of carbon atoms. the flattening iron polishing disc.
Thermochemical polishing can achieve nanometer roughness on the diamond surface. Although thermochemical polishing can obtain better surface quality, it needs to be processed under high temperature vacuum conditions, so the processing cost is too high and it has not been widely used.
dynamic friction polishing
Diamond’s extremely high hardness and excellent physical and chemical properties make it very difficult to polish. It often takes tens or even hundreds of hours of polishing to reduce surface roughness from the μm level to the nm level.
Dynamic friction polishing (DFP) has an extremely high diamond removal rate and solves the problem of “the polishing rate is affected by the orientation of the polishing crystal plane” existing in other polishing methods. The single crystal diamond is clamped by pliers and is in close contact with the high-speed rotating metal polishing disc to reduce roughness by eliminating micro-convex peaks on the surface. The diamond removal process in DFP is as follows: mechanical detachment of carbon, diffusion of carbon to the polishing disk and oxidation of carbon.
Dynamic friction polishing of single crystal diamond Source: Public Internet
laser polishing
Laser polishing (LP) irradiates the surface of a thick diamond film with a laser beam, which increases the surface temperature of the diamond film, thereby vaporizing and graphitizing the carbon atoms on the heated diamond surface, thereby achieving the objective of eliminating material. Lasers used for diamond processing can be divided into two categories: “hot processing” and “cold processing”, based on the relationship between the length of the laser pulse and the collision of the atomic lattice. The most representative are the nanosecond laser and the femtosecond laser. For diamond, the relaxation times of electrons and holes are 1.5ps and 1.4ps respectively.
Model of interaction between laser, electron and network (a) nanosecond laser (b) femtosecond laser Source: Public Internet
Laser processing is currently the most popular diamond processing method. Compared with traditional mechanical processing, laser processing has high precision, high efficiency and strong universality. So it is widely used in diamond cutting, micro-hole forming, micro-channel processing and planarization. are widely used.
Ion beam polishing
Ion beam polishing (IBP) achieves fine polishing. IBP uses oxygen or inert gas (Ar) ions with a high sputtering rate to sputter and etch the diamond film. The plasma bombards the diamond surface to remove carbon atoms. When high-energy ions collide with the diamond surface, the crystal structure of the diamond is destroyed, and the carbon atoms are sprayed from the surface of the diamond film, thereby achieving surface polishing. Although this method can remove brittle and hard materials on a very small scale, it easily leaves ripples on the substrate surface.
plasma polishing
Plasma assisted polishing (PAP) is a new type of dry chemical polishing method. It first uses plasma to activate the diamond surface, then uses “mild abrasives” to remove the deteriorated layer. This method can be used for fine diamond polishing and can improve the surface finish of the diamond.

Plasma-assisted mechanical polishing device Source: Public Internet
Finally
In summary, diamond polishing technology plays a vital role in modern industry, with applications ranging from semiconductor manufacturing to jewelry processing. With the continuous advancement of science and technology, polishing technology is also constantly evolving, from traditional mechanical polishing to chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP), to emerging plasma and laser-assisted polishing technologies. Each innovation promotes the improvement of processing precision and improvement of efficiency. .
In the future, as the requirements for surface quality of materials become higher and higher, diamond polishing technology will continue to develop in a more refined, more efficient and more environmentally friendly direction. . At the same time, the introduction of artificial intelligence and automation technology will also provide new opportunities for optimization and intelligence of the polishing process.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.