Fizeau interferometer is a precision instrument based on the principle of equal thickness interference, used to detect the surface shape of optical components, the wavefront aberration of optical lenses and the uniformity of optical materials . The measurement accuracy is generally /10~/100, which corresponds to the average wavelength of the light source used for detection.
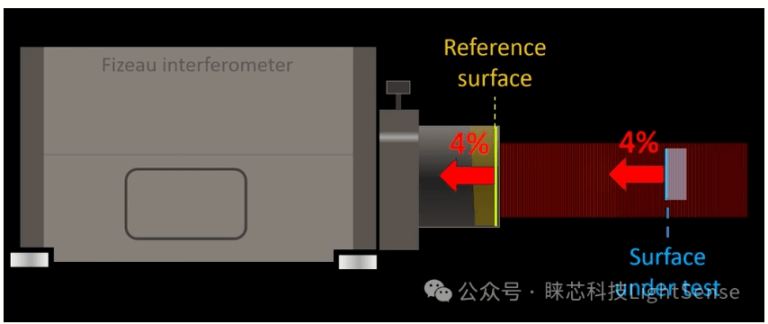
For non-contact testing of optical surfaces, a Fizeau interferometer can be used, described below. The Fizeau interferometer mainly measures the OPD optical path difference between the reference surface and the measured surface.
Zygo interferometer developed by disassembly and analysis
Dry information~Disassembly of the ZYGO Fizeau interferometer~
This is the Fizeau structure.
1The principle of the Fizeau interferometer
The principle of Fizeau interferometer is equal thickness interference, which is a precision instrument used to detect the surface shape of optical components, the wavefront aberration of optical lenses and the uniformity of materials optics. The measurement accuracy is generally /10~/100, which corresponds to the average wavelength of the light source used for detection. Commonly used wavefront interferometers are the Tayman interferometer and the Fizeau interferometer.
There are two types of Fizeau interferometers: planar and spherical. The first is composed of a beam splitter, a collimating objective lens and a standard plane, and the second is composed of a beam splitter, a finite conjugate distance objective lens and of a standard spherical plane. surface. The monochromatic light beam is partially reflected on a standard plane or a standard spherical surface and constitutes the reference beam; the part that is transmitted and passes through the device under test is the detection beam; The detection beam automatically returns and coincides with the reference beam to form interference fringes of equal thickness. The Fizeau plane interferometer can be used to detect the shape and uniformity of the surface of a flat plate or prism. The Fizeau spherical interferometer can be used to detect the shape of the spherical surface and its radius of curvature. The measurement precision of the latter is approximately 1 micron; it can also detect the wavefront aberration of infinite and finite conjugate distance lenses.
Like the Tayman-Green interferometer, the Fizeau interferometer also uses the amplitude division method: the incident light is incident perpendicular to the reflecting surface. That is, I = 0, keep the angle of incidence constant, and generate interference fringes of equal thickness to measure the error of optical components.
The image below shows a typical Fizeau setup for testing a sphere. A small coherent monochromatic light source is placed at the front focus F1 of the first collimator. The plane wavefront exits the collimator and a subsequent beam splitter separates the wavefront into a transmitted part and a reflected part. The beam splitter may be a parallel flat plate with a partially reflective and anti-reflective surface, or a plate carrying small shims. Beam splitter cubes are also useful for testing small optical components. Unwanted reflections can then be blocked by opening the beam, as described below. The light reflected from the beam splitter is not used in the interferometer and must be blocked by an absorbing material.
The transmitted light enters a so-called transmission sphere, which forms a high-quality spherical wavefront which converges towards its rear focus F’. The transmission sphere consists of a final sphere concentric with the converging wave front, whose centers CR coincide with F’. This surface is called a reference surface or Fizeau surface. As it is not covered, some of the transmitted light is reflected. Due to the concentricity of the transmitted wavefront and the reference surface, the returned light mainly follows the same optical path.

Figure: Schematic diagram of a Fizeau interferometer for testing a spherical surface through a transmission sphere.
An opaque beam diaphragm carrying a small aperture F2′ is positioned inside. It allows reference and test waves to pass, but blocks false and unwanted reflections as well as stray light from other surfaces in the setup.
2Advantages of the Fizeau interferometer
There is no contact between the reference surface and the test surface (to avoid contact that could cause damage or scratches)
Each transmission sphere can test various convex or concave surfaces of different radii
The quality of system elements other than the reference surface is secondary because the optical paths of the reference and object beams are almost identical
A computer system connected to the camera can digitally evaluate the interference pattern, improving the resolution of surface deviations up to 1,000 times that of visual inspection.

For consultation on laser interferometer, please call: 13522079385
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.