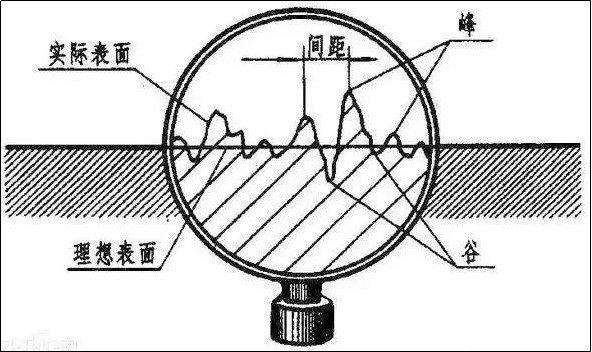
1. The notion of roughness
After parts are processed, large or small ridges and valleys appear on the surface of the workpiece due to tools, built-up edges and burrs. The heights of these peaks and valleys are so small that they can usually only be seen with magnification. This microscopic geometric shape characteristic is called surface roughness.
2. Roughness evaluation parameters
Represented by the three RaRzRy codes plus numbers, there will be corresponding surface quality requirements in the mechanical drawings. Generally, the workpiece surface with surface roughness Ra<0.8um is called: mirror surface.
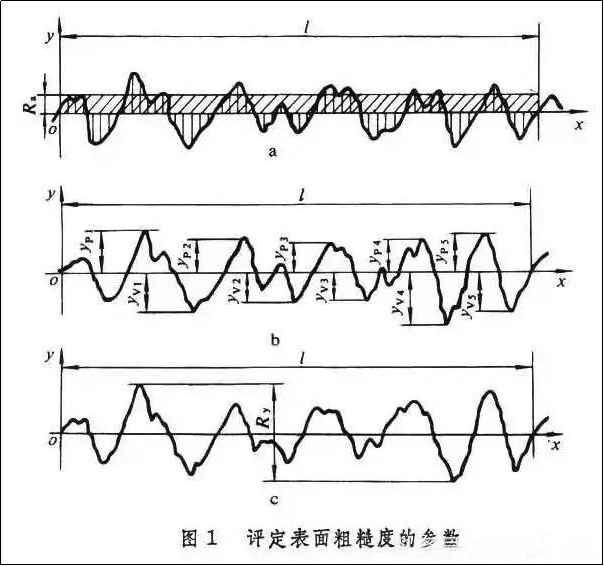
Arithmetic mean contour deviation Ra: arithmetic average of the absolute value of the contour offset in the sampling length L
Height at ten points of microscopic irregularities Rz: the sum of the average of the five largest contour peak heights and the average of the five largest contour valley depths in the sampling length l
Maximum contour height Ry: the distance between the crest line of the contour and the bottom line of the contour valley in the sampling length L
3. Roughness measurement and marking
Surface roughness can be evaluated quantitatively by measuring the values of Ra, Rz and Ry using electronic instruments or optical instruments. In actual production, roughness is often determined by human vision and touch and by comparing the sample block with the machined surface.
Marking method: Use symbols to mark the features of the machined surface on the part drawing. This is a basic symbol. It makes no sense to use this symbol alone when adding parameter values, it means that the area can be obtained by any method.

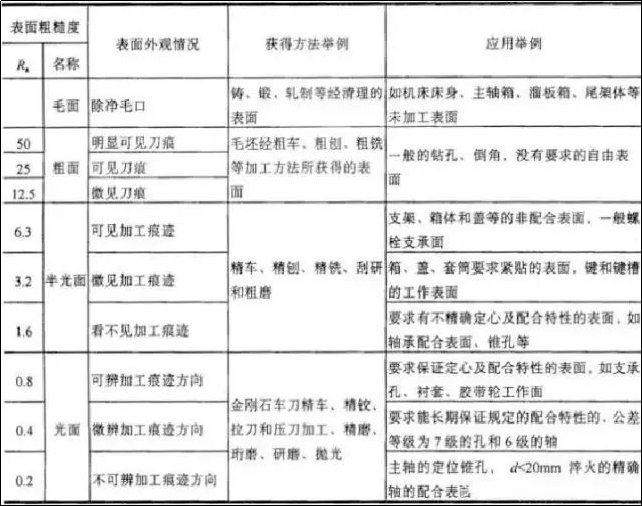
4. Various machining processes to obtain roughness degrees
Please refer to the table below for surface roughness values, surface characteristics, acquisition methods and application examples.
5. The impact of surface roughness on the performance of mechanical parts
Surface roughness has a great impact on the quality of parts, mainly focusing on wear resistance, fit properties, fatigue resistance, part accuracy and corrosion resistance of pieces.
5.1. Effect on friction and wear. The impact of surface roughness on the wear of parts is mainly reflected in the peak to peak. The two parts are in contact with each other. In fact, it is the contact of part of the peak. The pressure at the contact is very high. can cause plastic flow of the material. The rougher the surface, the greater the wear.
5.2 Effect on coordination properties. The fit between two components is nothing more than two shapes, an interference fit and a clearance fit. For interference fits, since the peaks on the surface are flattened during assembly, the amount of interference is reduced and the connection strength of the components is reduced; for adjustments with clearance, as the peaks are continuously smoothed, the degree of clearance will become large; . Therefore, surface roughness affects the stability of the fitting properties.
5.3 Effect on fatigue resistance. The rougher the surface of the part, the deeper the bumps, the smaller the radius of curvature of the hollow and the more sensitive it is to stress concentration. Thus, the greater the surface roughness of a part, the more sensitive it is to stress concentration and the lower its fatigue resistance.
5.4 Resistance to corrosive effects. The greater the roughness of the part, the deeper the hollows will be. In this way, dust, deteriorated lubricating oil, acid and alkali corrosive substances can easily accumulate in these valleys and penetrate into the inner layer of the material, thereby aggravating the corrosion of parts. Therefore, reducing surface roughness can improve the corrosion resistance of parts.
6. Methods for improving surface finish
Mainly divided into two categories: adding corresponding processes and improving the original processes
Add corresponding processes: adding polishing, grinding, scraping, rolling and other processes can not only improve smoothness but also improve precision. In addition, ultrasonic rolling technology at home and abroad combines the plastic fluidity of metal, which is different from it; traditional lamination. Cold work hardening can increase the roughness by 2-3 levels and improve the overall performance characteristics of the material.
Improvements over the original process:
6.1 Choose the cutting speed reasonably. Cutting speed V is an important factor affecting surface roughness. When processing plastic materials, such as medium and low carbon steel, lower cutting speeds are prone to chipping, and medium speeds are prone to built-up edges, which will increase the roughness. Avoiding this speed range will reduce the surface roughness value. Therefore, constantly creating conditions to increase the cutting speed has always been an important direction for improving the level of the process.
6.2 Choose the quantity of food reasonably. The amount of feed directly affects the surface roughness of the workpiece. Generally, the smaller the feed, the smaller the surface roughness and the smoother the workpiece surface.
6.3 Reasonably select the geometric parameters of the tool. Front and back corners. Increasing the cutting angle can reduce the deformation and friction during extrusion when the material is cut, as well as the overall cutting resistance, which is beneficial for chip removal. When the cutting angle is constant, the larger the clearance angle, the smaller the obtuse radius of the cutting edge and the sharper the blade. In addition, it can also reduce the friction and extrusion between the flank surface and the machined surface and the transition; Surface, which is beneficial to reduce the value of surface roughness degree. Increasing the arc radius of the tool tip r can reduce its surface roughness value; Reducing the secondary deflection angle Kr of the tool can also reduce its surface roughness value.
6.4 Select appropriate tool materials. Tools with good thermal conductivity should be selected to transfer cutting heat timely and reduce plastic deformation in the cutting zone. In addition, the tool must have good chemical properties to prevent it from having an affinity with the material to be treated. When the affinity is too high, it is easy to produce accumulated edges and flaky thorns, resulting in excessive surface roughness. If the surface is coated with carbide or ceramic materials, an oxidation protective film will be formed on the blade surface during cutting, which can reduce the friction coefficient with the machined surface, so it is beneficial to improve surface finish.
6.5 Improve the performance of part materials. The toughness of the material determines its plasticity. The higher the toughness, the greater the possibility of plastic deformation. When machining, the surface roughness of the workpiece will be greater.
6.6 Select the appropriate cutting fluid. Correct selection of cutting fluid can significantly reduce surface roughness. The cutting fluid has the functions of cooling, lubrication, chip removal and cleaning. It can reduce the friction between workpiece, tool and chips, eliminate a lot of cutting heat, lower the cutting zone temperature and discharge small chips timely.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.