Introduction to Food Freshness Monitoring
Ensuring the freshness and quality of fruits and vegetables during transportation and storage is a significant challenge in the food industry. Traditionally, our reliance on the five senses—sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing—to assess the freshness of food has been sufficient for personal consumption. However, with the strict quality requirements in the food industry, a more rigorous and reliable method is necessary. Recent advancements in technology have led to the development of innovative solutions, combining 3D printing and deep neural networks (DNNs) to monitor the freshness of fruits and vegetables in real-time.
The Role of 3D Printing in Food Freshness Monitoring
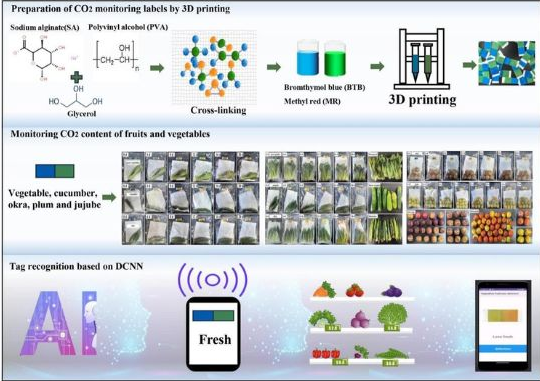
3D printing technology has emerged as a critical component in developing solutions for monitoring food freshness. By creating labels with color indicators that can detect changes in carbon dioxide levels associated with the decomposition of fruits and vegetables, 3D printing offers a non-invasive and accurate method for assessing food quality. These labels are made from biocompatible materials such as sodium alginate, starch, and polysaccharides, ensuring the safety of food packaging.
How 3D Printing Enables Real-time Monitoring
The process begins with the design and printing of labels that contain color indicators sensitive to carbon dioxide levels. As fruits and vegetables decompose, they release carbon dioxide, which reacts with the indicators to change the color of the label. This color change can be correlated with the freshness of the food. By analyzing the color change, it is possible to determine the degree of freshness, ranging from fresh to slightly fresh to spoiled.
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) in Image Analysis
Deep Neural Networks, particularly Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs), play a pivotal role in interpreting the data collected from the 3D printed labels. DCNNs are a type of artificial neural network designed to process data with grid-like topology, such as images. In the context of food freshness monitoring, DCNNs are used to analyze images of the labels, interpreting the color changes to categorize the food into different freshness levels.
Integration of DCNNs for Enhanced Precision
The integration of DCNNs with 3D printing technology significantly enhances the precision of food freshness evaluation. By training the neural network on a dataset of images of labels at various stages of freshness, the system can learn to recognize patterns and make predictions based on new, unseen data. This capability allows for the development of mobile applications where users can scan the labels and receive an instant diagnosis of the food’s freshness.
Applications and Future Directions
The combination of 3D printing and DCNNs opens new avenues for monitoring the food supply chain. This technology can be extended beyond fruits and vegetables to include other perishable products like meat and dairy by integrating additional sensors to measure temperature and humidity. Furthermore, the incorporation of antibacterial agents into the printed labels could potentially extend the storage time of food, further reducing waste and improving food safety.
Extending the Technology
Future developments may include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create a real-time monitoring system that can alert suppliers, retailers, and consumers about the freshness of the products. This could significantly reduce food waste, improve food safety, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
The fusion of 3D printing and deep neural networks presents a groundbreaking approach to monitoring the freshness of fruits and vegetables. By leveraging the strengths of both technologies, it is possible to create a reliable, non-invasive, and real-time method for assessing food quality. As this technology continues to evolve, its potential applications in the food industry are vast, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges in food safety and waste reduction.
References
- Jiangnan University Study on 3D Printing and DCNNs for Food Freshness Monitoring
- Applications of 3D Printing in Food Packaging
- Deep Learning Techniques for Image Analysis in Food Quality Assessment
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: How does the 3D printing and DCNN system work?
A: The system uses 3D printed labels with color indicators that change in response to carbon dioxide levels. DCNNs analyze images of these labels to determine the freshness of the food. - Q: Can this technology be used for other types of food?
A: Yes, the technology has the potential to be extended to other perishab