Nowadays, forMore types of plastics than ever before can be 3D printed. As the variety of plastics increases each year, it becomes increasingly difficult to differentiate between different types of wire and their best uses.
PLA may be suitable for most consumer applications, but what if you need a stronger or more flexible material? Carbon fiber nylon, on the other hand, can cover most industrial applications, but what if you need greater resistance to impact or extreme temperatures?
To find the answer, there is only one place to start: the material data sheet orTDS. These documents, typically available from resellers or 3D printing services, correspond to a specific filament and list the performance of sample parts made from that filament in several standardized laboratory tests, including strength, flexibility and other important mechanical properties for the final part.
EveryoneAll you have to do is compareTDS, you will then have a clear idea of which material is the best choice.

ThreadTensile strength test of the sample (Source:Ultimaker)
Unfortunately, material manufacturers use different methods to measure properties. There are different terms for the same thing, different international testing methods (ISO, ASTM, etc.), different units of measurement, different quoted results (maximum, average, etc.) and a host of other variations make direct comparison of data sheets almost impossible.
In this article, Mohou.com will learn and understand with everyoneSome tips to help you understandTDS and mechanical properties of specific polymers.
First of alllearnThe following material strength and flexibility concepts detailed in the datasheet, and how they relate to the properties required for the final print, will help you make more accurate material choices.
A,ThreadStrength and how to measure it
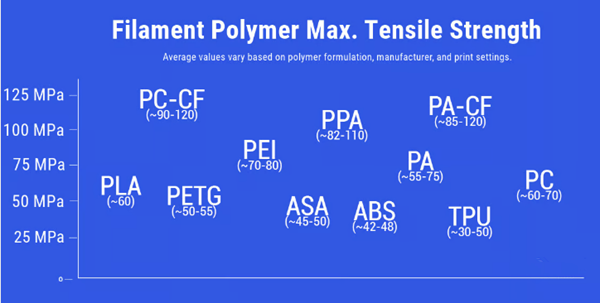
Get a comprehensive understanding of the most commonly used toolsComparison of tensile strength of 3D printed polymer filaments (Source: All3DP)
There are many scientific ways to measure force. You will generally find at least three on the wire data sheets:
tensile strength
Bending resistance
Shock resistance
What is tensile strength?
Tensile strength (also called ultimate tensile strength, breaking strength, ultimate strength,Ftu) refers to the tension or stress a material can withstand when taken apart before breaking. Testing for tensile strength actually involves placing the material in a vise-like machine and pulling in the opposite direction.
From a more practical point of view, this measurement concerns how fast or fragile the part is. Higher tensile strength means the material can withstand more force before breaking. For reference,PLA wireThe tensile strength is approximately30 MPa, the tensile strength of carbon fiber nylon is about 100 MPa, and the tensile strength of stainless steel is 860 MPa.
The tensile strength and many other properties of a 3D printed part depend on whether the part stretches along or across the fold lines (more on this below), so you may see two or three tensile strengths in a TDS measurement.
Reported tensile strength values may be average values, typical values, or extreme values (i.e. maximum values). This can be the elasticity value or the breaking value. The problem with many datasheets is that they don’t state what value is listed.
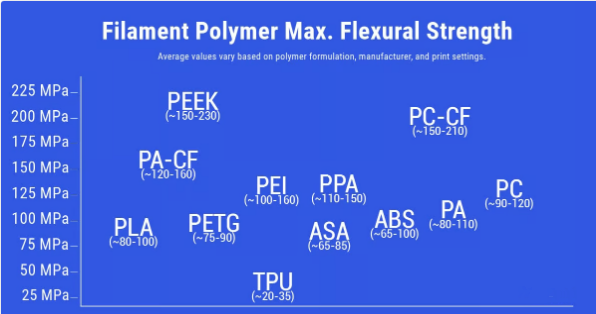
Get a broad understanding of the most commonly used toolsBending resistance of 3D printed polymer filaments (Source: All3DP)
What is bending strength?
This property (also called yield strength, modulus of rupture, or flexural strength) refers to the extent to which a material can bend or bend without breaking. (Do not confuse it with flexural modulus, which is the degree to which a material resists bending.) Flexural strength is an important property of a material in applications where it is subjected to a load that causes it to bend. causes it to bend rather than compress or stretch. This is an essential property for materials used in applications where they must support loads without buckling, such as brackets, hooks and other structural components.
In a typical bend test, a sample (usually in the form of a rectangular beam) is placed on two supports and a force is applied to the center of the beam until it bends or breaks. in commonly usedAmong polymer filaments for 3D printing, PEEK, PEI, and their carbon fiber-reinforced nylon generally have the highest flexural strength.
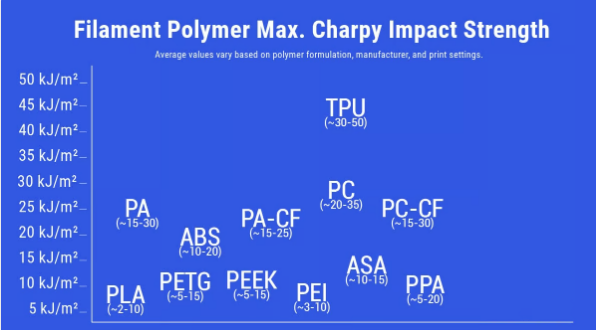
Get a comprehensive understanding of the most commonly used toolsComparison of the impact resistance of 3D printed polymer filaments (Source: All3DP)
What is impact resistance?
Impact resistance (also called Izod impact resistance or Charpy impact resistance, often called toughness) refers to the degree to which a component breaks when dropped, or the ability of a component to resist cracking when dropped. a sudden force is applied. These forces can be measured in joules/ square meter (J/m2) or foot-pound/square inch (ft·lb/in2).
Impact resistance indicates the amount of energy a polymer can absorb before breaking when subjected to high-velocity or high-intensity impact. This property is important in determining the durability and toughness of a polymer, especially in applications where the material may be exposed to impacts, drops, or dynamic forces, such as sports equipment or automotive parts.
Polycarbonate (PC) and ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) are two common wires with high impact resistance.
lay flat, upright or on edge
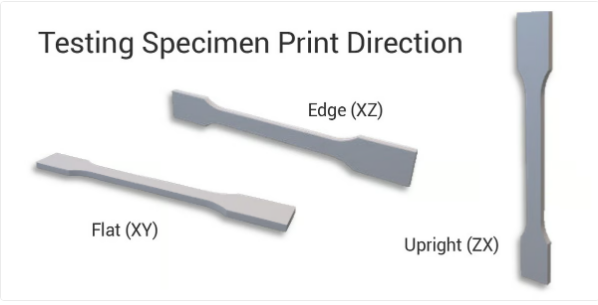
existIn 3D printing, due to the layer-by-layer nature of the process, the orientation of the printed part affects its mechanical properties, including its tensile strength. This is why there are generally three different methods for measuring tensile strength depending on which direction the sample is printed:
flatXY (or X) direction: This is the tensile strength measured along the length of the part, parallel to the build plate. In this orientation, the layers are stacked horizontally, so the material strength is primarily affected by how well the material is deposited and bonded along the length of the part.
edgeXZ direction (or transverse direction): Measures the tensile strength across the width of the part, also parallel to the build plate but perpendicular toX axis. Similar to the X direction, the resistance in this direction is determined by the connection between adjacent extrusions in each layer.
rightZX (or vertical) direction: Measures the tensile strength over the height of the part (perpendicular to the build plate). In this direction, the strength of the material is mainly affected by the interlayer bond, which is generally stronger than the flat bond (direction X or Y) weak. Therefore, the tensile strength in the Z direction tends to be lower than that in the X and Y directions.
Three intensity measurements reflect3D printed parts are anisotropic, meaning the mechanical properties are not the same in all directions. Understanding direction-dependent resistance can help design components strong enough for their intended use, especially when dealing with load-bearing or highly stressed components. Unfortunately, some datasheets only provide a number and often do not reveal which direction the value represents.
2. ThreadFlexibility and how to measure it

ColorFabb brand Varioshore TPU yarnParts can be produced with varying flexibility depending on your printing setup (Source:ColorFabb)
If you need a certain level of flexibility in your final part, you should pay attention to a few key flexibility metrics:
Flexural modulus
Young’s modulus
hardness
Elongation at break
What is flexural modulus?
Flexural modulus (also called flexural modulus) is the tendency of a material to resist bending, aka its stiffness. A high flexural modulus means the material is less flexible. For example, most carbon fiber reinforcedPA12 is both rigid, with a maximum flexural modulus of approximately 14 Gpa. The flexible PA 11 has a bending modulus of 0.65. Note that you will see the flexural modulus expressed in megapascals (MPa) or gigapascals (GPa, which is MPa times 1000).

Get a broad understanding of the most commonly used toolsComparison of the elasticity of 3D printed polymer filaments (Source: All3DP)
What is Young’s modulus?
Young’s modulus (also called modulus of elasticity, tensile modulus, compressive modulus or modulus of elasticity) is used to evaluate the elasticity of a material, which is the ratio of the strain of the material to the power necessary to deform it. For example, a typicalTPU wireThe Young’s modulus of is approximately50 MPa (very elastic), while most PEEK filamentsYoung’s modulus of4,000 MPa (inelastic).
What is Shore hardness?
Hardness seems to be a vague term when it comes to polymer filaments. It can refer to resistance to scratches, abrasion and abrasion, or a component’s resistance to dents. The hardness of plastics is usually expressed in terms of Rockwell or Shore hardness, which has little to do with the strength or flexibility of the material.
Shore hardness is a term you often hear when talking about polymers, but it is more general than the measurements discussed so far. For example, all elastomers and flexible wires(asTPU) all have Shore A hardness, and within Class A they have distinct values, such as Shore 95A. In comparison, ABS has a Shore D hardness, and many polymer manufacturers don’t bother to list a Shore value for a material that is not at all flexible.
What is elongation at break?
While it’s not the most useful measure of flexibility, it’s the easiest to imagine. When the elongation at break of a material isAt 4%, you can imagine that your media would bend 4% (typical ABS value) from horizontal under load before breaking, whereas nylon has an elongation at break of 120%, which means that it will bend more before breaking.
This metric is usually expressed as a percentage of the original length of the material. A high percentage means the part can withstand greater stretching or deformation before breaking, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility, toughness, or impact resistance.
three,No metric tells the whole story
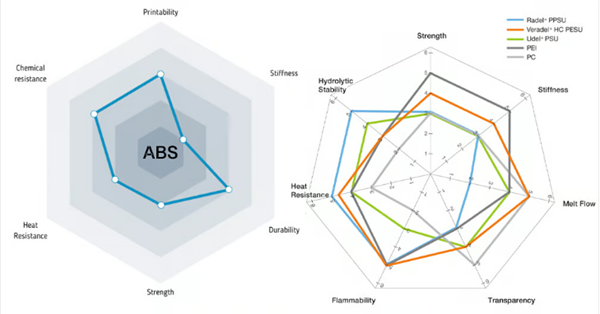
ABS performance presentation table (source: fiberlogy.com) and Solvay wirePerformance comparison table (source:Solvay)
Tensile strength is an important metric for evaluating the performance of polymers in bicycle frame mounts, but it may not be the best metric on its own, you need to consider a set of material properties based on the forces to which the support is subjected.
In addition to tensile strength, the best bike rack materials should also have high flexural strength, with impact resistance being less important.
To illustrate some of the above properties and their interrelationships, some material manufacturers have begun using spider diagrams of key properties to provide you with an at-a-glance summary. These diagrams are useful snapshots of the interrelationships between the main characteristics of the yarn.
Unfortunately, no manufacturer selects the same properties of six or seven threads or displays them in the same order, so they are not very useful for comparing different threads from different brands.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















