 ▲ 3D printing is used to optimize key elements of the IGNITER hydrogen energy equipment project
▲ 3D printing is used to optimize key elements of the IGNITER hydrogen energy equipment project
© RWTH DAP Institute for Digital Additive Manufacturing Production at RWTH Aachen University
“Additive manufacturing technology offers multiple solutions to the challenges of the hydrogen economy, including:
Resource-saving components:Produce lightweight, optimally designed components to reduce material usage and increase energy efficiency.
Materials adapted to the request:Material properties are tailored to the needs of specific applications to improve performance and durability.
Environmentally friendly component surface:Improve the environmental performance of components through coatings and other surface treatment technologies, such as reducing hydrogen penetration and improving corrosion resistance. “
Decarbonization and sustainable energy are topics at the heart of social and political discussions. We need clean alternatives to the fossil fuels that drive climate change and pollute the environment. Hydrogen is a possible alternative.
However, hydrogen poses a challenge to businesses and the energy sector: existing infrastructure must be converted from fossil feedstocks and energy sources, requiring significant investments. Furthermore, the efficiency and profitability of hydrogen production, especially green hydrogen, is currently limited. Hydrogen also has different combustion and corrosion properties. This changes requirements for materials used in combustion and transportation components, requiring new materials and improved designs.
Additive manufacturing for the hydrogen economy is one of the key technologies to achieve a sustainable energy transition and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Several projects of RWTH Aachen University, IGNITER, H2MAT3D, HyInnoBurn, promote the development of hydrogen-based combustion systems through additive manufacturing technology to achieve energy utilization more efficient and more environmentally friendly.
![]() IGNITER Project
IGNITER Project
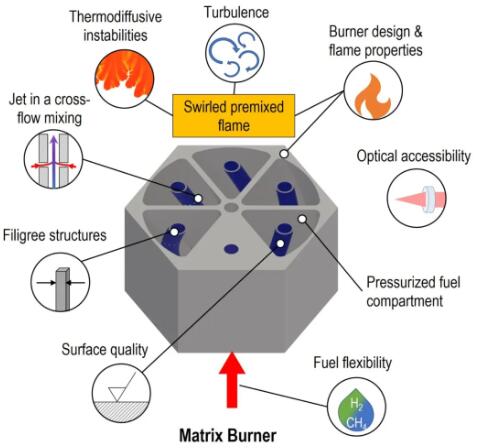
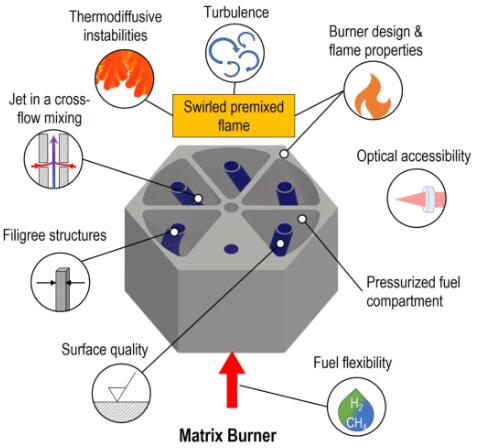
The objective of this project is to develop and apply a simulation-based design process for flexible fuel burners for use with hydrogen-based fuels. Additive manufacturing technology plays an important role in this process, as it enables the design and manufacturing of complex geometries that can be difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Through a combination of simulation and additive manufacturing, researchers can optimize combustion chamber designs to meet strict emissions and performance standards. This includes:
Fuel flexibility: Burners designed to accommodate different fuel types, including natural gas and hydrogen.
Emissions control:Optimize the combustion process to reduce harmful emissions such as nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Performance optimization:Ensure the burner remains efficient and stable under various operating conditions.
![]() H2MAT3D project
H2MAT3D project
H2MAT3D – (Analysis of the interaction between hydrogen-based combustion systems, high temperature materials and laser additive manufacturing)
RWTH Aachen University collaborates with the Institute of Technical Thermodynamics at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and TU Berlin MfAM to study the complex interaction between hydrogen combustion systems and materials produced by additive manufacturing. The research focuses on identifying high-temperature materials that can improve the efficiency and stability of hydrogen combustion while pushing the boundaries of 3D printing technology.
These projects are key to advancing the understanding of hydrogen-based combustion systems and additive manufacturing, paving the way for the development of future carbon-free energy technologies.
The H2MAT3D project focuses on analyzing the interaction between hydrogen-based combustion systems, high-temperature materials and laser additive manufacturing. The research focuses on identifying and developing high-temperature materials that can improve the efficiency and stability of hydrogen combustion. This implies:
Material selection:Develop high-performance, durable and efficient materials adapted to hydrogen environments.
Multi-material additive manufacturing:By optimizing the combination of materials layer by layer, customized material properties are achieved, combining wear resistance, corrosion resistance and functionality.
Surface functionalization:Using ultra-fast coating technology, pipes and others are provided with environmentally friendly internal and external surfaces for optimal corrosion protection and reduced hydrogen penetration.
 ▲ Understand the relevance of additive manufacturing process materials
▲ Understand the relevance of additive manufacturing process materials
© RWTH DAP Institute for Digital Additive Manufacturing Production at RWTH Aachen University
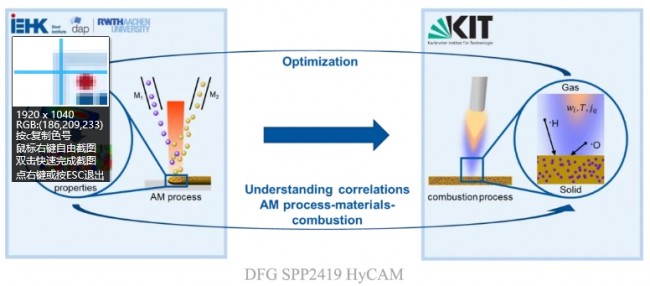
As part of H2MAT3D, the RWTH DAP Institute for Digital Additive Manufacturing at RWTH Aachen University and its research partners experimentally and numerically investigated the interaction between fuel-based combustion systems. hydrogen and additive manufacturing materials. This will bridge the gap between AM burner design and process-material interactions during combustion.
To achieve this, high temperature resistant materials separated from nickel-based superalloys by thermodynamically alloy selection can also be processed by additive manufacturing AM, in particular by laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) and by ultra-high laser applications. -high speed (EHLA). ) to produce materials processed by additive manufacturing processes, enabling the development of high-throughput alloys. This work relies on microstructural simulations that will provide insights into the factors influencing high temperature strength, degradation behavior and crack formation during additive manufacturing. The researchers studied samples produced during hydrogen combustion experiments and characterized them before and after operation to reveal degradation mechanisms. Experimental combustion work is complemented by combustion simulations aimed at understanding the influence of materials on flames due to thermal conductivity and surface reactions. The fundamental understanding gained in H2MAT3D will be used to coordinate additive manufacturing process conditions and high-temperature materials to achieve a more efficient combustion process. The results of this study could be used in additively manufactured combustion systems, where custom alloys and complex geometries help increase efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of the combustion process.
![]() HyInnoBurn Project
HyInnoBurn Project
Developed with partners from the RWTH DAP of the Additive Manufacturing Center ACAM Aachen, the HyInnoBurn project focuses on the development of industrial gas burners optimized for safe and flexible operation with natural gas and hydrogen. Since hydrogen flames behave differently from natural gas flames, the project will develop burner geometries optimized to meet specific burner requirements, such as low emissions or safe operation in harsh environments such as steelworks. The burner must also be scalable to meet the specific requirements of different end users. Additive manufacturing is becoming the key production technology to give the burner design the greatest possible freedom as well as easy scalability.
 ▲HylnnoBurn Project
▲HylnnoBurn Project
© ACAM Additive Manufacturing Center Aachen
Members of the HyInnoBurn project combined process analysis from the Institute of Power Plant, Steam and Gas Turbine Technology and focused on the development of a universal industrial burner for flexible operation with a mixture of fuel composed of natural gas (EG) and hydrogen.
 © Kueppers Solutions (left) and SMS-group (right)
© Kueppers Solutions (left) and SMS-group (right)
A preliminary study of currently used burner configurations forms the basis for the development of suitable numerical and geometric models for H2 burner systems that represent the phenomenology of combustion and emission formation of different gas compositions. Through simulation and experimental analysis of the burner, flexible optimization of the hydrogen content of the fuel gas is achieved. Among them, it is crucial to realize a large number of optimization options by producing the engraver via a 3D printing additive manufacturing process.
Through these projects, RWTH Aachen University demonstrates the potential of additive manufacturing technologies to boost the hydrogen economy and enable a sustainable energy transition. These studies not only help develop more efficient hydrogen-based combustion systems, but also pave the way for the development of future carbon-free energy technologies. As technology develops and costs fall, hydrogen is expected to become a significant part of future energy supplies.

Knowing is deep, practicing goes a long way. Drawing on a global network of superb manufacturing expert think tanks, 3D Science Valley provides industry with in-depth insight into additive and intelligent manufacturing from a global perspective. For more analysis on the field of additive manufacturing, please pay attention to the white paper series published by 3D Science Valley.
Download the white paper l Join the 3D Science Valley QQ group: 106477771
Website Submission l Send to [email protected]
Welcome to the reprint l Please indicate the source of the reprint l 3D Science Valley l Link to the original text from the 3D Science Valley website
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.