A good horse needs a good saddle and uses advanced CNC machining equipment if the wrong tools are used it won’t do any good! Selecting the appropriate tool material has a great impact on tool life, processing efficiency, processing quality and processing cost. This article provides useful information about knife knowledge, collect it and pass it on, let’s learn together.
1
Tool materials must have basic properties
The selection of tool materials has a significant impact on tool life, processing efficiency, processing quality and processing cost. Tools must withstand high pressures, high temperatures, friction, impact and vibration when cutting. Therefore, tool materials must have the following basic properties:
(1) Hardness and wear resistance. The hardness of the tool material should be greater than the hardness of the workpiece material, which generally should be greater than 60HRC. The higher the hardness of the tool material, the better the wear resistance.
(2) Strength and toughness. Tool materials must have high strength and toughness to withstand cutting forces, shock and vibration, and prevent brittle fracture and chipping of the tool.
(3) Heat resistance. The tool material has good heat resistance, can withstand high cutting temperatures, and has good oxidation resistance.
(4) Process performance and economics. Tool materials should have good performance in forging, heat treatment, welding, grinding, etc., and should pursue a high performance-price ratio.
2
Types, properties, characteristics and applications of tool materials
1. Diamond tool materials
Diamond is an allotrope of carbon and is the hardest material found in nature. Diamond cutting tools have high hardness, high wear resistance and high thermal conductivity, and are widely used in the processing of non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials. Especially in high-speed cutting of aluminum and silicon-aluminum alloys, diamond tools are the main type of cutting tools that are difficult to replace. Diamond tools capable of achieving high efficiency, high stability and long service life are indispensable and important tools in modern CNC machining.
⑴ Types of diamond tools
① Natural diamond tools: Natural diamonds have been used as cutting tools for hundreds of years. Natural single crystal diamond tools have been finely ground to make the cutting edge extremely sharp. The cutting radius can reach 0.002 μm, achieving an ultra-fine cutting edge. It can process extremely high workpiece precision and extremely low surface roughness. It is a recognized, ideal and irreplaceable ultra-precision machining tool.
② PCD diamond cutting tools: Natural diamond is expensive, and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) is widely used in cutting. Since the early 1970s, polycrystalline diamond (Polycrystaine) prepared using high temperature and high pressure synthesis technology. After the successful development of diamond, or PCD blades for short, natural diamond cutting tools were replaced by artificial polycrystalline diamond in many cases. The source of PCD raw materials is only a few tenths to one tenth of that of natural diamond cutting tools. It is impossible to grind an extremely sharp edge, and the surface quality of the processed workpiece is not as good as that of natural diamond. It is not yet practical to manufacture PCD blades with chip breakers in the industry. Used for precision cutting of non-ferrous metals and non-metals, it is difficult to achieve ultra-precise mirror cutting.
③ CVD diamond cutting tools: From the late 1970s to the early 1980s, CVD diamond technology appeared in Japan. Diamond CVD refers to the use of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to synthesize a diamond film on a heterogeneous matrix (such as cemented carbide, ceramic, etc.). CVD diamond has exactly the same structure and characteristics as natural diamond. The performance of CVD diamond is very close to that of natural diamond. It has the advantages of natural single crystal diamond and polycrystalline diamond (PCD) and overcomes their shortcomings to a certain extent.
⑵ Performance characteristics of diamond tools
① Extremely high hardness and wear resistance: Natural diamond is the hardest substance found in nature. Diamond has extremely high wear resistance. When processing high hardness materials, the life of diamond tools is 10 to 100 times that of carbide tools, or even hundreds of times.
② Has a very low coefficient of friction: the coefficient of friction between diamond and some non-ferrous metals is lower than that of other cutting tools, the coefficient of friction is low, the deformation during processing is small, and the cutting force can be reduced.
③ The cutting edge is very sharp: The cutting edge of the diamond tool can be sharpened very sharply. The natural single crystal diamond tool can reach 0.002 ~ 0.008 μm, which can achieve ultra-fine cutting and ultra-precision processing. .
④ High thermal conductivity: Diamond has high thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity, so the cutting heat is easily dissipated and the temperature of the cutting part of the tool is low.
⑤ Has a lower thermal expansion coefficient: the thermal expansion coefficient of diamond is several times lower than that of cemented carbide, and the change in tool size caused by cutting heat is very small, which is particularly important for precision and ultra-precision machining which requires high dimensional precision.
⑶ Application of diamond tools
Diamond tools are mainly used for fine cutting and reaming of non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials at high speeds. Suitable for processing various wear-resistant non-ferrous metals, such as fiberglass powder metallurgy blanks, ceramic materials, etc. ; various wear-resistant non-ferrous metals, such as various silicon-aluminum alloys and finishing processing of various non-ferrous metals; .
The disadvantage of diamond tools is that they have poor thermal stability. When the cutting temperature exceeds 700℃~800℃, they completely lose their hardness. Additionally, they are not suitable for cutting ferrous metals because diamond (carbon) reacts easily with them. iron at high temperature. The atomic action converts carbon atoms into graphite structure and the tool is easily damaged.
2. Tool material cubic boron nitride
Cubic boron nitride (CBN), the second ultra-hard material synthesized using a diamond-like method, is second only to diamond in hardness and thermal conductivity. It has excellent thermal stability and can be heated up to 10,000°C in the atmosphere. oxidation occurs. CBN has extremely stable chemical properties for ferrous metals and can be widely used in the processing of steel products.
⑴ Types of cubic boron nitride cutting tools
Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is a substance that does not exist in nature. It is divided into monocrystalline and polycrystalline, namely CBN monocrystalline and polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (polycrystalline cubic boron nitride, PCBN for short). CBN is one of the allotropes of boron nitride (BN) and has a structure similar to diamond.
PCBN (polycrystalline cubic boron nitride) is a polycrystalline material in which fine CBN materials are sintered together through bonding phases (TiC, TiN, Al, Ti, etc.) under high temperature and pressure. It is currently the second hardest artificially synthesized material. Diamond tool material, along with diamond, is collectively called super hard tool material. PCBN is mainly used to make knives or other tools.
PCBN cutting tools can be divided into solid PCBN blades and carbide sintered PCBN composite blades.
PCBN composite blades are manufactured by sintering a layer of PCBN with a thickness of 0.5-1.0mm onto cemented carbide with good strength and toughness. Its performance combines good toughness with high hardness and wear resistance. and difficult welding of CBN blades.
⑵ Main properties and characteristics of cubic boron nitride
Although the hardness of cubic boron nitride is slightly lower than that of diamond, it is much higher than that of other high hardness materials. The exceptional advantage of CBN is that its thermal stability is much greater than that of diamond, reaching temperatures above 1200°C (diamond is between 700 and 800°C). Another notable advantage is that it is chemically inert and does not react with iron. Reaction at 1200-1300°C. The main performance characteristics of cubic boron nitride are as follows.
① High hardness and wear resistance: CBN crystal structure is similar to diamond and has hardness and strength similar to diamond. PCBN is especially suitable for processing high hardness materials that could only be ground beforehand and can obtain better surface quality of the workpiece.
② High thermal stability: The thermal resistance of CBN can reach 1400 ~ 1500 ℃, which is almost 1 times that of the thermal resistance of diamond (700 ~ 800 ℃). PCBN tools can cut high temperature alloys and hardened steel at high speeds 3 to 5 times higher than carbide tools.
③ Excellent chemical stability: It has no chemical interaction with iron-based materials up to 1200-1300°C and will not wear as abruptly as diamond. At this stage, it can still maintain the hardness of cemented carbide tools; for cutting hardened steel parts and chilled cast iron, can be widely used in high-speed cutting of cast iron.
④ Good thermal conductivity: Although the thermal conductivity of CBN cannot keep up with that of diamond, among various tool materials, the thermal conductivity of PCBN is second only to diamond and much higher than that of high speed steel and carbon. cemented carbide.
⑤ Has a lower coefficient of friction: A low coefficient of friction can lead to a reduction in cutting force when cutting, a reduction in cutting temperature, and an improvement in the quality of the machined surface.
⑶Application of cubic boron nitride cutting tools
Cubic boron nitride is suitable for finishing various difficult-to-cut materials such as hardened steel, hard cast iron, high temperature alloys, cemented carbide and surface spray materials. The processing precision can reach IT5 (the hole is IT6), and the surface roughness value can be as small as Ra1.25~0.20μm.
Cubic boron nitride tool material has poor toughness and bending resistance. Therefore, cubic boron nitride turning tools are not suitable for rough machining at low speeds and high impact loads. At the same time, they are not suitable for cutting materials with high plasticity (such as aluminum alloys, copper alloys, nickel-based alloys). high plasticity steels, etc.), because cutting of these important built-up edges will occur during metalworking, damaging the machined surface.
3. ceramic tool materials
Ceramic cutting tools have the characteristics of high hardness, good wear resistance, excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, and are not easy to bond with metal. Ceramic tools play a very important role in CNC machining. Ceramic tools have become one of the leading tools for high-speed cutting and processing of difficult-to-machine materials. Ceramic cutting tools are widely used in high-speed cutting, dry cutting, hard cutting and cutting of difficult-to-machine materials. Ceramic tools can effectively process very hard materials that traditional tools cannot process at all, realizing “turning instead of grinding”; the optimal cutting speed of ceramic tools can be 2-10 times that of carbide tools, thereby significantly improving cutting production; efficiency. The main raw materials used in ceramic tool materials are the most abundant elements in the earth’s crust. Therefore, the promotion and application of ceramic tools is of great significance to improve productivity, reduce processing costs and save strategic precious metals. will also greatly promote the development of cutting technology progress.
⑴ Types of ceramic tool materials
The types of ceramic tool materials can generally be divided into three categories: alumina-based ceramics, silicon nitride-based ceramics, and silicon nitride-alumina composite ceramics. Among them, ceramic tool materials based on alumina and silicon nitride are the most widely used. The performance of silicon nitride ceramics is superior to that of alumina ceramics.
⑵ Performance and characteristics of ceramic cutting tools
① High hardness and good wear resistance: Although the hardness of ceramic cutting tools is not as high as that of PCD and PCBN, it is much higher than that of carbide and steel cutting tools fast, reaching 93-95HRA. Ceramic cutting tools can process very hard materials that are difficult to process with traditional cutting tools and are suitable for high-speed cutting and hard cutting.
② High temperature resistance and good heat resistance: ceramic cutting tools can still cut at high temperatures above 1200°C. Ceramic cutting tools have good mechanical properties at high temperatures. A12O3 ceramic cutting tools have particularly good oxidation resistance, even if the cutting edge is red hot, it can be used continuously. Therefore, ceramic tools can achieve dry cutting, eliminating the need for cutting fluid.
③ Good chemical stability: Ceramic cutting tools are not easy to bond with metals, and are corrosion resistant and chemically stable, which can reduce the bonding wear of cutting tools.
④ Low coefficient of friction: The affinity between ceramic tools and metal is low, and the coefficient of friction is low, which can reduce the cutting force and cutting temperature.
⑶ Ceramic knives have applications
Ceramic is one of the tool materials mainly used for high-speed finishing and semi-finishing. Ceramic cutting tools are suitable for cutting various cast irons (gray cast iron, ductile iron, malleable cast iron, chilled cast iron, high alloy wear-resistant cast iron) and steel materials (carbon structural steel, structural steel alloy, high strength steel, high manganese steel, hardened steel, etc.), can also be used to cut copper alloys, graphite, engineering plastics and composite materials.
The material properties of ceramic cutting tools have problems of low bending strength and poor impact resistance, making them unsuitable for cutting at low speeds and under impact loads.
4. Coated tool materials
Coating cutting tools is one of the important ways to improve tool performance. The emergence of coated tools has led to a major advancement in the cutting performance of cutting tools. Coated tools are coated with one or more layers of refractory compounds with good wear resistance on the tool body and good toughness. They combine the tool die with the hard coating, thereby significantly improving tool performance. Coated tools can improve processing efficiency, improve processing precision, extend tool life and reduce processing costs.
About 80% of cutting tools used in new CNC machine tools use coated tools. Coated tools will be the most important tool variety in CNC machining in the future.
⑴ Types of coated tools
According to different coating methods, coated tools can be divided into chemical vapor deposition (CVD) coated tools and physical vapor deposition (PVD) coated tools. Coated carbide cutting tools generally use the chemical vapor deposition method, and the deposition temperature is around 1000°C. Coated high-speed steel cutting tools generally use the physical vapor deposition method, and the deposition temperature is about 500°C;
According to the different substrate materials of coated tools, coated tools can be divided into carbide coated tools, high speed steel coated tools, and ceramic and superhard material (diamond and cubic boron nitride) coated tools.
According to the properties of the coating material, “hard” coated tools can be divided into two categories, namely “hard” coated tools and “soft” coated tools. The main goals pursued by tools with “hard” coating are high hardness and wear resistance properties. the main advantages are high hardness and good wear resistance. This is a TiC and TiN coating. The goal of “soft” coating tools is a low coefficient of friction, also called a self-lubricating tool. Its coefficient of friction with the workpiece material is very low, only about 0.1, which can reduce adhesion and friction. , reduce the cutting force and cutting temperature.
Nanocoating cutting tools have recently been developed. Such coated tools can use different combinations of coating materials (such as metal/metal, metal/ceramic, ceramic/ceramic, etc.) to meet different functional and performance requirements. Properly designed nano-coatings can give tool materials excellent friction-reducing and anti-wear functions as well as self-lubricating properties, making them suitable for high-speed dry cutting.
⑵ Characteristics of coated cutting tools
① Good mechanical and cutting performance: Coated tools combine the excellent properties of the base material and the coating material. They not only maintain the good toughness and high strength of the base material, but also have high hardness, high wear resistance and low friction. coefficient. Therefore, the cutting speed of coated tools can be increased by more than 2 times compared with that of uncoated tools, and higher feed rates are allowed. The lifespan of coated tools is also improved.
② Strong versatility: Coated tools have high versatility and greatly expand the processing range. A coated tool can replace several uncoated tools.
③ Coating thickness: As the coating thickness increases, the tool life will also increase, but when the coating thickness reaches saturation, the tool life will no longer increase by significantly. When the coating is too thick, it will easily cause peeling; when the coating is too thin, the wear resistance will be poor.
④ Re-sharpenability: Coated blades have low re-sharpenability, complex coating equipment, high process requirements and long coating time.
⑤ Coating material: Tools with different coating materials have different cutting performance. For example: when cutting at low speed, TiC coating has advantages; When cutting at high speed, TiN coating is more suitable.
⑶Application of coated cutting tools
Coated tools have great potential in the field of CNC machining and will be the most important tool variety in the field of CNC machining in the future. The coating technology has been applied to end mills, reamers, drills, composite hole processing tools, gear hobs, gear shaping cutters, gear shaving cutters, gear broaches. forming and various machine-clamped indexable inserts to meet the various requirements of high-speed cutting processing. Material requirements such as steel and cast iron, heat-resistant alloys and non-ferrous metals.
5. Carbide tool materials
Carbide cutting tools, especially indexable carbide cutting tools, are the main products of CNC machining tools. Since the 1980s, the varieties of various integral and indexable carbide cutting tools or inserts have been expanded to various types of cutting tools. which indexable carbide tools have evolved from simple turning tools and face mills to various fields of precision, complex and forming tools.
⑴ Types of carbide cutting tools
According to the main chemical composition, cemented carbide can be divided into tungsten carbide-based cemented carbide and titanium carbon (nitride)-based cemented carbide (TiC(N)).
Cemented carbide based on tungsten carbide includes three types: tungsten-cobalt (YG), tungsten-cobalt-titanium (YT) and rare added carbide (YW). Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The main components are tungsten carbide (WC) and titanium. tungsten carbide (TiC), tantalum carbide (TaC), niobium carbide (NbC), etc. The commonly used metal bonding phase is Co.
Titanium Carbon (Nitride) Cemented Carbide is a cemented carbide whose main component is TiC (some add other carbides or nitrides). Commonly used metal bonding phases are Mo and Ni.
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) divides cutting carbide into three categories:
K class, including Kl0~K40, is equivalent to my country’s YG class (the main component is WC.Co).
P category, including P01~P50, is equivalent to my country’s YT category (the main component is WC.TiC.Co).
M class, including M10~M40, is equivalent to my country’s YW class (the main component is WC-TiC-TaC(NbC)-Co).
Each grade represents a series of alloys ranging from high hardness to maximum toughness with a number between 01 and 50.
⑵ Performance characteristics of carbide cutting tools
① High hardness: Carbide cutting tools are made from carbides of high hardness and melting point (called hard phase) and metal binders (called bond phase) through powder metallurgy, with a hardness of 89 to 93HRA, much higher than that of high speed steel. At 5400°C, the hardness can still reach 82~87 HRA, which is the same as the hardness of high speed steel at room temperature (83~86 HRA). The hardness value of cemented carbide changes with the nature, quantity, particle size of carbides and the content of metal bonding phase, and generally decreases with the increase of the content of metal bonding phase. When the binder phase content is the same, the hardness of YT alloy is higher than that of YG alloy, and alloys added with TaC (NbC) have higher high temperature hardness.
② Bending strength and toughness: The bending strength of commonly used cemented carbide is 900-1500 MPa. The higher the metal binder phase content, the higher the flexural strength. When the binder content is the same, the strength of the YG type alloy (WC-Co) is higher than that of the YT type alloy (WC-TiC-Co), and as the TiC content increases, resistance decreases. Cemented carbide is a brittle material, and its impact resistance at room temperature is only 1/30 to 1/8 that of high-speed steel.
⑶ Application of commonly used carbide cutting tools
YG alloys are mainly used for processing cast iron, non-ferrous metals and non-metallic materials. Fine grain cemented carbide (such as YG3X, YG6X) has higher hardness and wear resistance than medium grain carbide with the same cobalt content. It is suitable for processing some special hard cast irons, austenitic stainless steel, heat-resistant alloys and titanium. alloy, hard bronze and wear-resistant insulation materials, etc.
The outstanding advantages of YT type cemented carbide are high hardness, good heat resistance, higher hardness and high temperature compressive strength than YG type, and good oxidation resistance. Therefore, when the knife needs to have higher heat and wear resistance, a grade with higher TiC content should be selected. YT alloys are suitable for processing plastic materials such as steel, but are not suitable for processing titanium alloys and silicon-aluminum alloys.
YW alloy has the properties of YG and YT alloys and has good comprehensive properties. It can be used to process steel, cast iron and non-ferrous metals. If the cobalt content of this type of alloy is increased appropriately, the strength can be very high and can be used for rough machining and interrupted cutting of various difficult-to-machine materials.
6. High speed steel cutting tools
High speed steel (HSS) is a high alloy tool steel that adds more alloying elements such as W, Mo, Cr and V. High speed steel cutting tools have excellent overall strength performance , toughness and ease of processing. In complex cutting tools, especially those with complex blade shapes such as hole processing tools, milling cutters, threading tools, broaching tools, gear cutting tools, etc. ., high speed steel still occupies a dominant position. High speed steel knives are easy to sharpen to produce sharp edges.
According to different uses, high-speed steel can be divided into general-purpose high-speed steel and high-performance high-speed steel.
⑴ General purpose high speed steel cutting tools
General purpose high speed steel. Generally, it can be divided into two categories: tungsten steel and tungsten-molybdenum steel. This type of high speed steel contains 0.7% to 0.9% (C). According to the different tungsten contents of the steel, it can be divided into tungsten steel with a W content of 12% or 18%, tungsten-molybdenum steel with a W content of 6% or 8% and molybdenum steel with a W. content of 2% or no W. . General-purpose high-speed steel has a certain hardness (63-66HRC) and wear resistance, high strength and toughness, good plasticity and good processing technology, so it is widely used in the manufacturing of various complex tools.
① Tungsten steel: The typical grade of general-purpose tungsten steel is W18Cr4V (referred to as W18). The high temperature hardness at 6000C is 48.5HRC and can be used for manufacturing. various complex tools. It has the advantages of good grindability and low decarburization sensitivity, but because of its high carbide content, uneven distribution, large particles and low strength and toughness.
② Tungsten-molybdenum steel: refers to a high-speed steel obtained by replacing part of the tungsten in tungsten steel with molybdenum. The typical grade of tungsten-molybdenum steel is W6Mo5Cr4V2 (referred to as M2). The carbide particles of M2 are fine and uniform, and its strength, toughness and high temperature plasticity are better than those of W18Cr4V. Another type of tungsten-molybdenum steel is W9Mo3Cr4V (W9 for short). Its thermal stability is slightly higher than that of M2 steel, its bending strength and toughness are better than those of W6M05Cr4V2, and it has good processability.
⑵ High performance high speed steel cutting tools
High-performance high-speed steel refers to a new type of steel that adds a certain content of carbon, vanadium and alloying elements such as Co and Al to the composition of general-purpose high-speed steel, thereby improving its resistance to heat and wear. . There are mainly the following categories:
① High carbon high speed steel. High carbon high speed steel (such as 95W18Cr4V) has high hardness at room temperature and high temperature. It is suitable for the manufacturing and processing of ordinary steel and cast iron, drills, reamers, taps and milling cutters with high wear resistance requirements. or tools for processing harder materials. It is not suitable to withstand significant impacts.
② High speed steel with high vanadium content. Typical grades, such as W12Cr4V4Mo (called EV4), have an increased V content of 3% to 5%, have good wear resistance and are suitable for cutting materials that cause high tool wear, such as fibers, hard rubber, plastics. , etc., and can also be used to process materials such as stainless steel, high-strength steel and high-temperature alloys.
③ Cobalt high speed steel. It is an ultra-hard high speed steel containing cobalt. Typical grades, such as W2Mo9Cr4VCo8 (called M42), have a very high hardness that can reach 69-70HRC. use high-strength heat-resistant steels, high temperature alloys, titanium alloys, etc. Processing materials: M42 has good grindability and is suitable for manufacturing precision and complex tools, but it is not suitable for working under impact cutting conditions.
④ Aluminum high speed steel. It is an ultra-hard high-speed steel containing aluminum. Typical grades are, for example, W6Mo5Cr4V2Al (called 501). The high temperature hardness at 6000C also reaches 54HRC. suitable for manufacturing milling cutters, drill bits, reamers, gear cutters and broaches, etc., used for processing materials such as alloy steel, stainless steel, high strength steel and high temperature alloys.
⑤ Ultra-hard nitrogen high-speed steel. Typical grades, such as W12M03Cr4V3N, called (V3N), are ultra-hard high-speed steels containing nitrogen. The hardness, strength and toughness are equivalent to M42. They can be used as a substitute for high speed steels containing cobalt. -high-speed steels and are used for low-speed cutting of difficult-to-machine materials and processing of low-speed, high-precision steels.
⑶ Smelting of high speed steel and powder metallurgy high speed steel
According to different manufacturing processes, high speed steel can be divided into smelting high speed steel and powder metallurgy high speed steel.
① Smelting of high-speed steel: Ordinary high-speed steel and high-performance high-speed steel are manufactured by smelting methods. They are made into knives through processes such as smelting, ingot casting, plating and rolling. A serious problem that easily occurs when melting high speed steel is carbide segregation. Hard and brittle carbides are unevenly distributed in high-speed steel, and the grains are coarse (up to tens of microns), which affects the wear resistance and toughness of high-speed steel. high speed steel tools and negatively affect cutting performance.
② Powder metallurgy high speed steel (PM HSS): Powder metallurgy high speed steel (PM HSS) is a liquid steel melted in a high frequency induction furnace, atomized with high pressure argon or l pure nitrogen, then quenched to obtain fine and uniform crystals (high speed steel powder), then press the resulting powder into a knife blank at high temperature and high pressure, or make a billet first of steel, then forge it and roll it into the shape of a knife. Compared with high speed steel made by smelting method, PM HSS has the following advantages: the carbide grains are fine and uniform, and the strength, toughness and wear resistance are much improved compared with molten high-speed steel. In the field of complex CNC tools, PM HSS tools will continue to develop and occupy an important place. Typical grades, such as F15, FR71, GFl, GF2, GF3, PT1, PVN, etc., can be used to make large, heavily loaded and high impact cutting tools, as well as cutting tools of precision.
3
Principles of CNC tool material selection
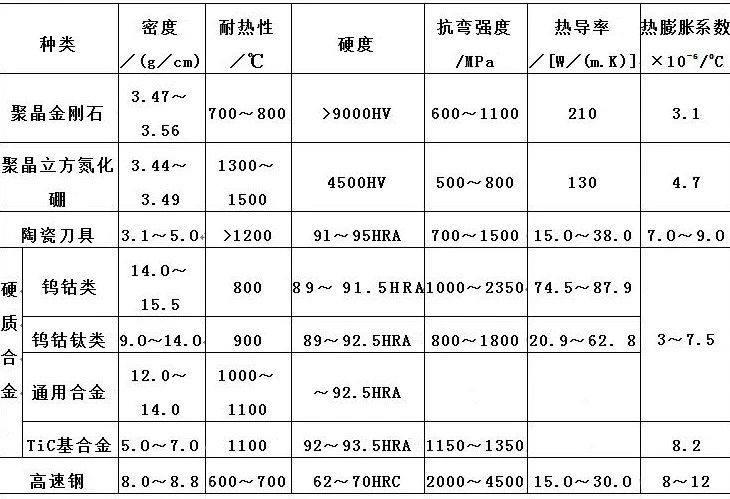
Currently, the widely used CNC tool materials mainly include diamond tools, cubic boron nitride tools, ceramic tools, coated tools, carbide tools, high speed steel tools, etc. There are many grades of tool materials and their properties vary greatly. The following table shows the main performance indicators of various tool materials.
Main performance indicators of various tool materials
Tool materials for CNC machining should be selected based on the workpiece and the nature of processing. The selection of tool materials should be reasonably matched to the processing object. The matching of cutting tool materials and processing objects mainly refers to the matching of the mechanical, physical and chemical properties of the two to achieve the longest tool life and maximum cutting productivity.
1. Match the mechanical properties of materials of cutting tools and processing objects
The problem of matching the mechanical properties of cutting tools and workpieces mainly refers to the matching of mechanical property parameters such as strength, toughness and hardness of the cutting tool and the processing material. the room. Tool materials with different mechanical properties are suitable for processing different workpiece materials.
① The order of tool material hardness is: diamond tool > cubic boron nitride tool > ceramic tool > tungsten carbide > high speed steel.
② The order of bending strength of tool materials is: high speed steel > cemented carbide > ceramic tools > diamond and cubic boron nitride tools.
③ The order of toughness of tool materials is: high speed steel > tungsten carbide > cubic boron nitride, diamond tools and ceramics.
Workpiece materials with high hardness should be processed with higher hardness tools. The hardness of the tool material should be greater than the hardness of the workpiece material, which generally should be greater than 60HRC. The higher the hardness of the tool material, the better its wear resistance. For example, when the cobalt content of cemented carbide increases, its strength and toughness increase and its hardness decreases, making it suitable for rough machining; as the cobalt content decreases, its hardness and wear resistance increase, making it suitable for finishing.
Tools with excellent mechanical properties at high temperatures are particularly suitable for high-speed cutting. The excellent high temperature performance of ceramic cutting tools allows them to cut at high speeds, and the allowable cutting speed can be 2-10 times that of cemented carbide.
2. Match the physical properties of the cutting tool material to the machined object
Tools with different physical properties, such as high-speed steel tools with high thermal conductivity and low melting point, ceramic tools with high melting point and low thermal expansion, diamond tools with high thermal conductivity and low melting point thermal expansion, etc., are suitable for processing different workpiece materials. When processing workpieces with low thermal conductivity, tool materials with better thermal conductivity should be used so that the cutting heat can be quickly transferred and the cutting temperature can be reduced. Due to its high thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity, diamond can easily dissipate cutting heat without causing significant thermal deformation, which is especially important for precision machining tools that require high dimensional accuracy.
① The heat resistance temperature of various tool materials: diamond tools are 700 ~ 8000 C, PCBN tools are 13000 ~ 15000 C, ceramic tools are 1100 ~ 12000 C, cemented carbide based on TiC (N) is 900 ~ 11,000 C, ultra-thin based on WC. Grain carbide is 800~9000C, HSS is 600~7000C.
② The order of thermal conductivity of different tool materials: PCD>PCBN>WC-based cemented carbide>TiC(N)-based cemented carbide>HSS>Si3N4-based ceramic>A1203-based ceramic.
③ The order of thermal expansion coefficients of different tool materials is as follows: HSS>WC-based cemented carbide>TiC(N)>A1203-based ceramic>PCBN>Si3N4-based ceramic>PCD.
④ The order of thermal shock resistance of different tool materials is as follows: HSS>WC-based cemented carbide>Si3N4-based ceramic>PCBN>PCD>TiC(N)-based cemented carbide>Si3N4-based ceramic base of A1203.
3. Match the chemical properties of the cutting tool material to the machined object
The problem of matching chemical properties of cutting tool materials and processing objects mainly refers to the matching of chemical performance parameters such as chemical affinity, chemical reaction, diffusion and dissolution of tool materials and room materials. Tools with different materials are suitable for processing different workpiece materials.
① The bonding temperature resistance of various tool materials (with steel) is: PCBN>ceramic>tungsten carbide>HSS.
② The oxidation resistance temperature of various tool materials is: ceramic> PCBN> tungsten carbide> diamond> HSS.
③ The diffusion force of tool materials (for steel) is: diamond > Si3N4 ceramics > PCBN > A1203 ceramics. The diffusion intensity (for titanium) is: Ceramic based on A1203>PCBN>SiC>Si3N4>diamond.
4. Reasonable selection of CNC tool materials
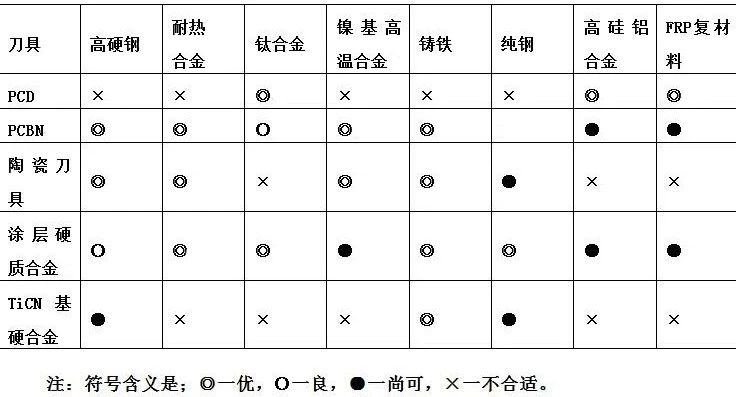
Generally speaking, PCBN, ceramic, coated carbide and TiCN-based carbide tools are suitable for CNC processing of ferrous metals such as steel, while PCD tools are suitable for non-ferrous metal materials such as Al, Mg, Cu and their alloys. Processing of non-metallic materials. The table below lists some of the workpiece materials for which the above tool materials are suitable for processing.
Some workpiece materials suitable for processing by tool materials
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.