The TC4 titanium alloy has excellent properties such as high resistance, high temperature thermal resistance, high heat resistance and good corrosion resistance, it has therefore become a material with prospects for extremely wide application in the aerospace industry. At the same time, due to its strong chemical activity, its small deformation coefficient and its low thermal conductivity, it becomes a typical material difficult to treat. Currently, cemented carbide is the main material of the tool to cut TC4 titanium alloys, and indexable cemented carbide inserts are becoming more and more used. During the processing process, the type of indexable insert groove has a great influence on the cutting process. Steel cut by cutting tools of three -dimensional groove tools The rupture mechanism was studied and it was found that control of the contact surface was an important factor affecting the breaking of the fleas. Kazuo Nakayama believes that the chips are pressed and completed due to the moment of flexion applied by the circuit breaker of the chip, and believes that different types of circuit breaker will lead to various performance of breaking of fleas. Worthington et al. Fang Ning studied the influence of the type of blade groove on flea break performance and applied the method of multiple linear disintegration to establish two mathematical models to predict the breaking performance of new blades.
To summarize, current research on the impact of the type of groove on the cut in the cut are mainly focused on the direction of the breaking of the fleas. In fact, the shape of the groove of the blade also has a great impact on the wear of the blade itself, especially when cutting the TC4 titanium alloy at high speed, the tool is very quickly. The wear of the blade becomes more important. This article uses the types of SM and QM grooves of Sandvik Coromant CNMG120408 blades for research.
1 equipment and test conditions
1.1 Test equipment
The test was selected as CNC Lathe Cak6150 produced by Shenyang First Machine Tool Factory (as shown in Figure 1), with the maximum speed of the 1800r / min.
Observation of the wear of the blades is carried out using the three-dimensional microscopy system with ultra-production field Keenx VHX-1000c (as shown in Figure 2).
1.2 Geometric parameters and characteristics of the blade grooves
The blade note used in the test is H13A. treatment.
The blade model is CNMG120408 and the geometry parameters of the tool after installation are presented in Table 1.
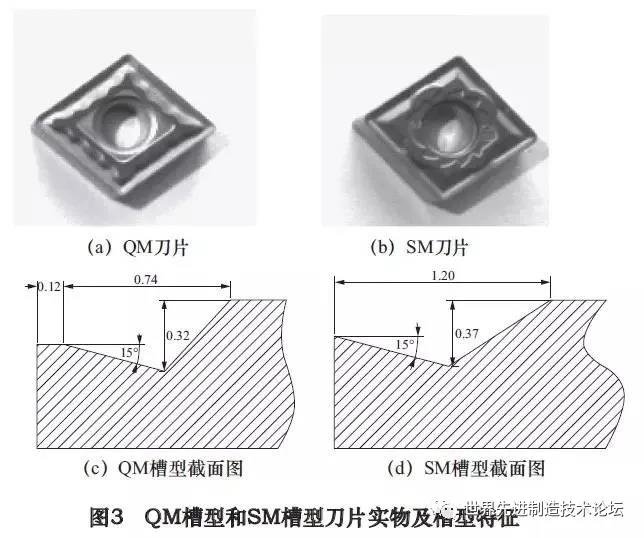
The experience used two types of grooves of CNMG120408, namely the type of QM groove and the SM Groove type blade for comparison and study. The structural characteristics of the two types of blade grooves are illustrated in Figure 3. Their front angles are both 15 °. and depth. The width of the edge strip of the type of SM groove is small and can be essentially ignored, so the blade is sharp, the type of groove is soft and the width and the depth are relatively large.

1.3 Test plan
The commonly used cutting speed of the TC4 titanium alloy is 40 ~ 50 m / min. The cutting speeds were: 95 m / min respectively. The specific cutting conditions are presented in Table 2.
2 results and test analyzes
2.1 The shape of the wear of the tool when the cutting speed is 95 m / min
Figure 4 shows the wear of the two groove inserts at the cutting speed of 95 m / min. On the surface of the front knife, the morphology of the wear of the two groove blades is mainly a crescent wear, and the wear of the QM groove blades is even more serious. . On the back plane, due to the large rebound in the titanium alloy, the contact constraint between the basket bottom and the part increases, and the temperature in the cutting zone increases, the wear of the basket of tool is relatively serious only when cutting other materials. In Figure 4, the wear of the rear blade of the QM groove blade in the two groove blades is much more serious than that of the SM groove blades. Once the tool material is softened to high temperature. The rear blade of the SM Groove blade has light wear, resulting in minor mechanical wear, and no obvious groove is seen.
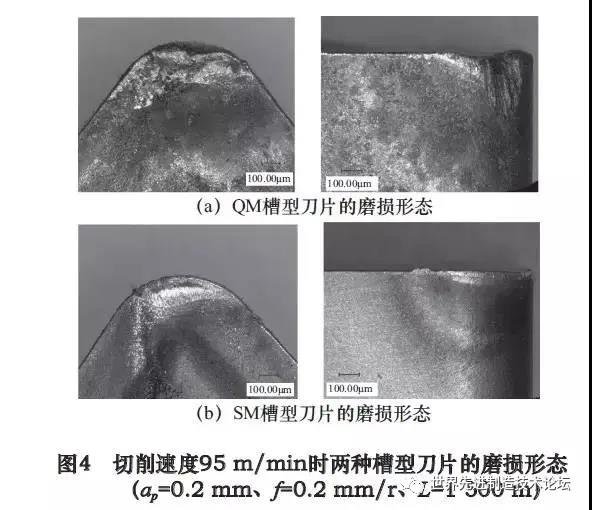
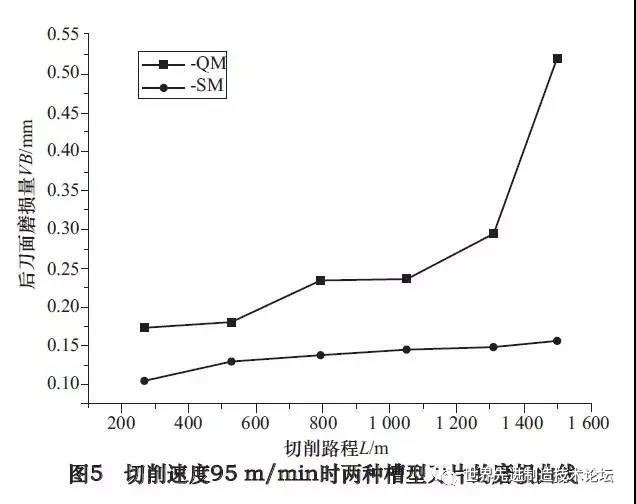
Figure 5 shows the wear curves of the two groove inserts at a cutting speed of 95 m / min. The groove type insert has a long section. The normal groove QM -rain insert stadium is much shorter, and the wear of the surface of the rear plane reaches 0.25 mm when the cutting distance is 1300 m. , the wear of the basket bottom exceeded 0.5 mm. When the cutting speed is 95 m / min, the wear of the SM groove blade is much smaller than that of the QM groove blade, and the SM Groove blade has better cutting performance.
2.2 The shape of the tool wear when the cutting speed is 139 m / min
Figure 6 shows the wear of the two groove blades when the cutting speed is 139 m / min. The sagging of the croissant on the surface of the front blade of the two groove blades is seriously worn, and a plastic deformation caused by a high temperature can be observed. On the rear blade, the two groove blades can clearly observe the bond wear caused by high temperature and the wear of the furrow caused by high temperature softening of the tool material, and the surface of the blade surface rear of the SM groove type blade is more worn.

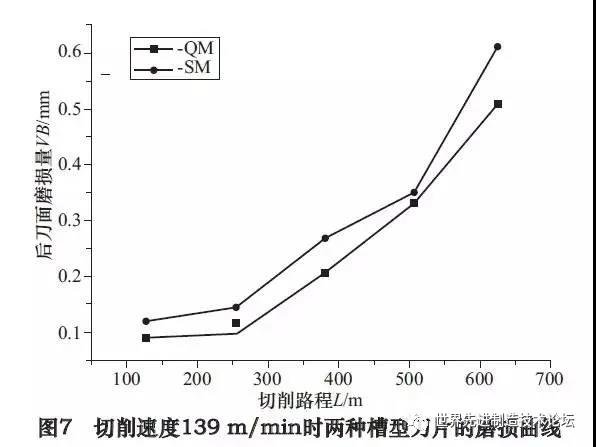
Figure 7 shows the wear curve of the two groove inserts when the cutting speed is 139 m / min. Continue, the two groove type inserts are wear is fast, the main reason is that the contact frequency between the tool and the part increases during the high speed cut, the heat dissipation time ‘Tool is shortened, causing an acute slice Increase in the cutting zone and the wear speed of the tool is accelerated. Unlike the cutting speed is 95 m / min, the wear of the QM groove blade is relatively small at that time. 250 m, the SM Groove blade is that it has entered a net wear stage and the normal wear phase is shorter. Compared to the cutting speed of 95 m / min, the two groove blades wear much faster. When the wear of the rear plane of the SMP groove type insert reaches 0.3 mm, the cutting distance is less than 450 m and the lifespan of the tool is considerably reduced compared to when the cutting speed is 95 m / min. When the wear of the basket of the insert of the type Rainure QM reaches 0.3 mm, the cutting distance is around 500 m and the lifespan of the tool is less than half the speed of Cut when it is 95 m / min. Throughout the wear process, the wear of the QM groove blade is lower than that of the SM groove blade, and the QM groove blade has better cutting performance.
2.3 Analysis of performance differences between two two -speed grooves inserts
By comparing Figures 5 and 7, it is not difficult to see that the cutting performance of the two two -speed grooves are exactly the opposite. In relatively low cutting conditions, the type of SM groove has better cutting performance than the QM groove type insert, while in relatively high cutting conditions of 139 m / min, wear of the QM groove type insert has always been lower than that of the QM groove type of insertion.
As shown in Figure 3, analyzing the difference between the type of SM groove and the type of QM groove, we can see that the SM groove blade has a pointed edge, a small blade with a thick and blunt blade with a large blade . During the cutting process, the temperature of the cutting zone is a decisive factor affecting the mechanism and the wear rate of the tools, and the temperature of the cutting zone is determined by the rate of generation and dispersion of heat heat cut during the cut. In other words, after the heat generated per unit of time is dissipated by the shavings, the tool, the room and the surrounding environment, the heat remaining in the cutting zone determines its cutting temperature, which in turn determines the wear mechanism and the speed of the tool.
When you use a cutting speed of 95 m / min, due to the pointed edge of the SM groove blade, the shavings flow from the surface before the more fluid surface, less friction heat is generated and the temperature to The tip of the cutting area is relatively low, so the SM groove blade in a door less.
When a cutting speed of 139 m / min is used, the cutting heat rate of the two groove inserts in high speed cutting conditions is much higher than that of the 95 m / min lower speed. The cutting area is used in the cutting area. The outing of the cutting heat during the dry cut, with the exception of chips and the dissipation of the heat from the room, the dissipation of the heat of the tool is an important way to cut the heat to to transmit. The heat dissipation of the tool seems more important. At that time, although the SM groove blade produces less heat, its conditions of heat dissipation are relatively mediocre. In this way, in the contradiction between the generation and the dispersion of the cutting heat, the Rainure QM type blade wins and the temperature at the forefront of the Groove QM type blade in the cutting zone is lower than that of the type type of groove sm. At the same time, the cutting temperature of the two groove type inserts is much higher than the cutting temperature at 95 m / min, and the wear of the link becomes the main form of wear of the tool to this moment. The edge of the QM groove blade is thick and dull, which is more conducive to resistance to the binding of the materials of the part, thus reducing the wear of the tools. Therefore, the QM groove insert has better cutting performance when the cutting speed is 139 m / min.
3 Conclusion
This article studies the impact of the type of blade groove on its wear when transforming the TC4 titanium alloy at high speed and draws the following conclusions:
(1) The main forms of wear during the transmission of TC4 titanium alloys in H13 -quality cemented carbide tools are mechanical wear and wear of the link.
(2) When you use a cutting speed of 95 m / min, the main wear shape of the two groove blades is mechanical wear. The tip of the blade.
(3) When you use a cutting speed of 139 m / min, mechanical wear and wear of the links are both called important forms of wear of the two groove inserts.
(4) For indexable carbide reversal inserts, if the edge is clear is not necessarily linked to the wear rate of the blade. The cutting temperature can therefore be relatively high. Consequently, when cutting titanium alloys at high speed, the selection of the type of on -board groove must be combined with the cutting speed and in depth considering the conditions of heat production and thermal dissipation in the area cutting.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















