Electroplating is a finishing process that involves applying a thin layer of metal to an object.EveryoneYou may have heard of gold plated jewelry, which is much cheaper than solid gold jewelry but looks almost the same.
EveryoneMetal can be coated with another metal, or a metal can be coated with a polymer; in fact, anything that conducts electricity can be galvanized. This includes plastic 3D Print,ThisNot only improves the appearance of the part, but also its strength and durability without having to resort to much more expensive metal. 3D The path to printing.
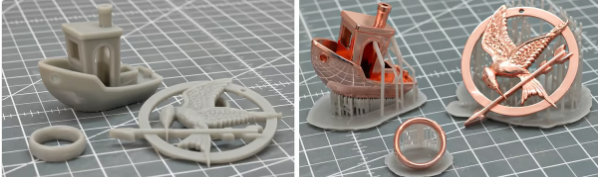
These 3D The printed parts were sanded, graphite sprayed, polished, electroplated with copper, then polished again to a mirror finish (via YouTube)
For many applications, electroplating provides an economical alternative to filling plastics and metals. 3D Print the mechanical gaps between parts, or evenNASAFuture space applications are also being explored. Plating is completely different from painting or dipping parts in metal slurry. It is a chemical process that uses electricity and can be done at home or in a laboratory, but is most commonly done in manufacturing plants.
In this article,Mohou.com will work with you allLearn all about the process, its pros and cons, how it works, and who uses it. 3D Print parts.
Learn more about electroplating

3D Printing and plating YouTuber Hen3drik and his homemade plating device for plating large objects, like this sword
(source:Hen3drik aka Hendrik VogelpohlSince YouTube)
Electroplating uses controlled electrolysis to achieve the electrodeposition of metal cations from a positively charged raw material (anode) onto a negatively charged substrate (cathode). In other words: when you will 3D When a printed object is placed in an electrolyte solution with the metal to be used as a coating and electricity is applied, metal fragments pass through the solution and adhere to the printed object. 3D on the printed part.
When an electronic charge is introduced, the positively charged ions (cations) dissolve through oxidation and follow the electric current to deposit a metallic layer on the part. The most common metals used for electroplating are copper, nickel, gold, silver, palladium, tin, zinc and chromium.
If applied to more fragile plastic materials, these metals can improve the mechanical properties of the final part, such as tensile modulus and ultimate tensile strength, but not as much as full metals. 3D Print parts. Therefore, plated objects can be considered both plastic and metal. 3D The midpoint between printing where plating can make resin 3D The ultimate strength of printed parts is doubled.

Basic setup explaining the principles of electroplating (source:Fast Direct)
The three main methods of tank plating are barrel plating, rack plating, and coil plating. Barrel plating tumbles the substrate into a barrel to promote an even coating. It is useful for high volume production since many parts can be placed in the bucket. Rack plating secures the part to the rack. This method is used for complex or precision parts that are not suitable for roll rolling. The rack plating method is also the closest to DIY Plating as the required parts are held in place with wires. The final process, roll-to-roll plating, is ideal for plating specific areas of the substrate. Due to its high plating rate, it is very economical and efficient when carrying out high volume plating operations.
Each process takes place under immersion in a conductive electrolyte solution, which usually contains the metal salt to be plated, sulfuric acid and solvents as well as other additives such as acids, bases or brighteners. Use caution when handling this solution as it is very corrosive. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves and goggles and never pour used electrolyte down the drain, but dispose of it in a suitable collection location!
Remember that electroplating is a balancing act of depositing metal onto a part, and the current and electrolyte will corrode the coating you just applied. The success of electroplating depends on a variety of factors, the most important of which are exposure time, part geometry, and amperage. Electroforming also allows selective multi-material coating of parts, which can improve functionality and reduce material costs if only certain areas need to be conductive.

SAT Electroplating These ear probe tips are selectively plated with three different metals (Source:SAT plating)
3D Printed parts must be electrically conductive to ensure that metal cations flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode. Therefore, non-conductive plastic prints must be properly set up to ensure successful plating. How to do this is explained in detail below.
Preparedness and Safety Measures

A clean and safe facility is essential to ensure the protection of people and the environment (Source:SRA)
In addition to electrolyte solutions which should be handled and disposed of with care, prepare 3D Proper protective equipment should always be used when printing parts and plating them.Appropriate clothing, gloves, goggles and a respirator are required. Spraying and electroplating should also be carried out in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhalation of harmful substances. Also follow the instructions for handling and storing the materials used. Now let’s see the necessary steps before electroplating.
3D Print parts
when plastic 3D When printing for electroplating, the most common technique is YEARS And FDM。YEARS Printing has a competitive advantage due to the detailed resolution that can be achieved. In both cases, the higher the printer resolution and the lower the layer thickness, the less post-processing the part will require. In terms of materials, anything that can adhere to a conductive paint will do.3DPrint. Some professional service providers can even print and plate nylon and AT A GLANCE and other industrial materials.
grinding parts
One of the most fundamental requirements of electroplating is a smooth surface in order to produce good results on fragile films only a few hundred microns thick. The smoother the surface, the shinier the final metallic coating will be. especially for FDM Printing the part involved several rounds of vigorous sanding and spraying with putty. The polyurethane varnish also makes it possible to fill in any gaps in the print.
Clean parts
Equally important for a smooth surface is to clean it, not only before the plating process begins, but also between each stage. Dust and grease are the enemies of electroplating because they prevent fillers, conductive paint, and subsequent metal coatings from adhering evenly to the part. Clean and degrease the parts thoroughly before placing them in the plating tank, and clean them with distilled water between plating steps.
Make parts conductive
To make the room electrically conductive, apply a coat of conductive paint. Copper or nickel paints are most commonly used, but cheaper graphite paints will also work if sanded again before dipping in the electrolyte. However, not all fillers are compatible with graphite coatings.There have also been attempts to print with conductive filament to avoid applying layers of conductive paint, but with mixed results, so spraying is recommended, especially for beginners.
Soak the parts
Set up the circuit by connecting the electrodes to a power source. The anode must be connected to the metal forming the plating. The cathode will be connected to your part. Cut the wire to length and shape it so that 3D Printed, primed and cleaned parts can be placed inside. a few 3D If you want the print to float, hold it with thread. Remember to reposition the part periodically during plating, otherwise it will be soldered to the wires. Fill a glass or plastic container with the appropriate electrolyte and make sure the part to be plated is completely submerged.
Electrolytic parts
Everything is set up and ready to power on. The required current depends on the thickness, surface area and volume of the model tank. There are online calculators that can help you determine the voltage you need. For best results, it is a good idea to increase the power as the deposited layer becomes progressively thicker. Too much current can result in uneven coatings, rough, gritty deposits, and faster electrolyte degradation. Low current will cause insufficient metal deposition, resulting in a thin or uneven coating.

Brush plating uses the same principles as tank plating, but uses a brush as an anode to apply the coating (Source: Gold Solution Plating)
Further processing of parts
The plated parts can then be plated with other metals such as nickel, gold or palladium. This can be accomplished by additional electrolysis or other methods such as brush plating. The part can also be chemically cleaned to further increase the reflectivity of the film.
Veneer Troubleshooting

The rough surface of the ring may be caused by the degradation of the leveling agent present in the aged electrolyte (source:Garage science)
Electroplating is a complex process that requires a high level of diligence and experience to achieve satisfactory results. This section summarizes some of the most common pitfalls, how they occur, and what can be done to avoid them.
Part geometry defects and problems
Part geometry plays a vital role in ensuring successful plating. Traditional manufacturing substrates made by plastic injection molding or metal casting often have surface irregularities that make even metal deposition difficult. For example, cold stopping occurs when material hardens at various stages of the injection process, leaving visible marks or flow lines. Another common problem is pitting, which refers to small holes in the surface of the substrate.
3D Similar issues in the printing world are layer lines and under- or over-extrusion of material. These process-specific phenomena can cause deviations in final part dimensions. They must be treated by sanding and priming before electroplating because once the metal film has been deposited, such apparent irregularities cannot be repaired.
Even intentional part geometries (such as sharp edges) or complex designs (such as lattices) can cause problems during the plating process due to today’s distribution issues. The higher current density at sharp edges means that excess coating occurs in these areas, resulting in a weak and brittle layer. The opposite is shadow, which can be understood as the sun casting a shadow. The part of the substrate covered by the anode will be subject to fewer deposits. This problem can be solved by rearranging the anodes or continually rotating the substrate in the electrolyte for distributed partial exposure.
Poor adhesion
Poor adhesion between the substrate and the metal finish can have several causes. First, if the plastic part and the conductive coating don’t fit together well, they will separate, and with it the metal plating, even if it was deposited as it should. Finding the right combination of plastic coatings and paint is crucial. In addition to good bond quality, the work surface must be free of grease, dust or oxidation, all of which can affect adhesion. Since plastics and metals expand differently when heated, if the part is exposed toEven a perfect coating can crack and peel over time. In this case, a different combination of materials is used for plating or metal.3DPrinting is probably the best solution.
Uneven plating
Suppose the finished veneer is not only dull but also rough. In this case, the electrolyte can degrade and become contaminated by particles deposited on the substrate, leaving an irregular coating. Filtering or replacing electrolytes can help.
Excessive current can also cause uneven plating; therefore, reducing the current can often alleviate the problem. Bubbles formed on the substrate are usually a telltale sign. However, if the current is too low, the coating may be too thin, or even irregular and incomplete. Finding the right balance is one of the most critical aspects of successful plating.
The plating is dull and fuzzy
It can be frustrating when the plating is successful but does not have the desired shine and reflectivity. This happens for many reasons. A chemical imbalance (such as too much sulfate, chromic acid, or dissolved contaminants in the electrolyte) may be the cause, so replacing the electrolyte may improve results. Incorrect temperature could be another cause.130 has 140°F The intermediate temperature is ideal for both the plating solution and the substrate.
Incorrect current density or a damaged power supply causing interruption in current flow can also be the cause. The parts themselves may also be placed too high in the container. Make sure it is at least four inches from the surface. Finally, insufficient rinsing between plating steps can lead to the formation of chemical residue or dirt and a resulting dull appearance. If none of these repair methods bring the desired effect, using a brightener can also help improve the final result, as it will prevent large crystals from forming on the part and make it shine even more.
Advantages and disadvantages of electroplating

Electroplating can achieve a stunning finish, but not all that glitters is gold (Source:Gold Plating Solutions)
Like any technology, electroplating has advantages and disadvantages, some of which were mentioned in the article and will be summarized here. In addition to plating-specific considerations, combine them with 3D There are a few other factors that need to be considered when combining prints. The following list summarizes these advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of electroplating
Improve surface appearance
Protects substrates from mechanical wear, corrosion or tarnishing
Improve part properties such as tensile strength, stiffness and weight
Create new properties such as magnetism or conductivity
Can be plated with different metals including copper, tin, nickel, gold, palladium, chrome, etc.
Metal 3D An inexpensive alternative to printing to improve the metallic properties of plastic parts
Disadvantages of electroplating
Although better than metal 3D Cheap to print, but the materials required are expensive and increase the cost of the final part
A tedious manual process with process-specific defects such as cold sealing, pinholes, sharp edges, split stitches and loss of adhesion, making the process difficult to master, especially in amateur environments.
Over time, the different thermal expansion characteristics of plastics and metals can cause the coating to crack and separate from the substrate.
The mechanical properties are not close to those of metal parts
The lengthy process can take anywhere from a few hours to a few days, depending on the work required.
Toxic substances create hazardous waste that can harm the environment if not properly handled and disposed of.
Electroplating Applications
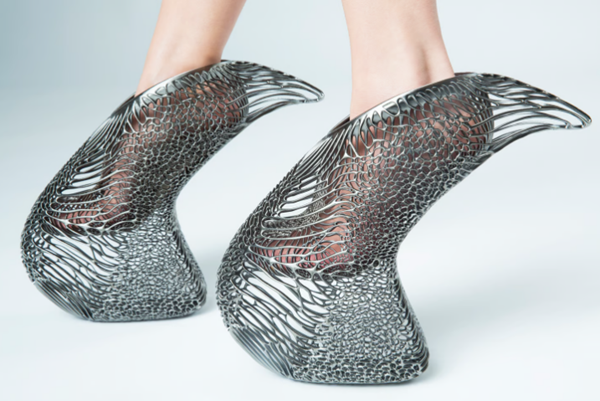

Shoe brand Ica & Kostika SLS Use copper, nickel and chrome 3D Print it and post it Mycelium shoe(source:By & Kostika)
As electroplating is a well-established finishing technology, most manufacturing industries, including additive manufacturing, use it in selected applications to improve part properties such as conductivity, durability, visual enhancement or strength . These industries include the automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical, and fashion industries. Among these, shoe designers and jewelry manufacturers use it to give their products a more luxurious look and feel. Electroplating a microscopic layer of gold onto a plastic or metal ring would be cheaper but give the same elegant look. It also allows makers who do not have access to goldsmithing equipment to upgrade their equipment at a relatively low cost. 3D Print plastic parts.

Cardacino of 6 feet art sculpture named“shark vacuum»showing that electroplating works well on large objects (source:Michael Cardacino)
This also applies to hobbyists such as modelers and modelers who want to 3D SLA Printed designs transform into shiny, heavier statues or realistic accessories that look like polished metal. Many artists also 3D Combine the versatility of printing with a stunning electroplated look to create Michael Cardacino of“The Shark’s Void”and other works of art, this is one 6 foot-high hollow shark sculpture, made of EOS P730 transmitted SLS printed, divided into parts, assembled and transmitted Repliform Galvanized copper and nickel.

3D SLA Before and after printing to increase antenna complexity and reduce weight (Source:Elliptical)
Turn to industry 3D Experts in printing and plating, RF and microwave products and solutions Elliptical Use additive manufacturing to design complex RF antennas that weigh less than all-metal antennas 80%but the performance is the same as an all-metal antenna. The company has also managed to reduce costs compared to traditional methods. 90% cost 3D Print high-performance antenna parts, making low-volume part production faster and more cost-effective. In the automotive industry, electroplating is also often used to improve the visual appeal of concept cars or to create aftermarket replicas of classic models.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















