It’s no secret that additive manufacturing affects many sectors and industries. In particular, it offers significant advantages in terms of productivity, cost, customization and manufacturing time.One of the most important applications of 3D printing is dentistry. In this branch of medicine, technology makes it possible to provide personalized dental solutions to each patient. According to a study by Markets and Markets, global dental 3D printing market revenue is expected to reach $8.1 billion by 2029, with a compound annual growth rate of 19%. This growth can be explained in particular by the continued development of 3D technologies and different materials.
Dentistry3D printing encompasses a variety of processes, from stereolithography to metal fusion to fused deposition. Various technologies allow parts to be created from resin, filament, metal, etc. Dental additive manufacturing, for its part, facilitates the manufacture of surgical guides, crowns, splints or dental prostheses, making it possible to adapt each solution very precisely to the patient. But what are the most widespread 3D technologies and what are their applications? What are their strengths in this area and what is their future? We tell you everything!
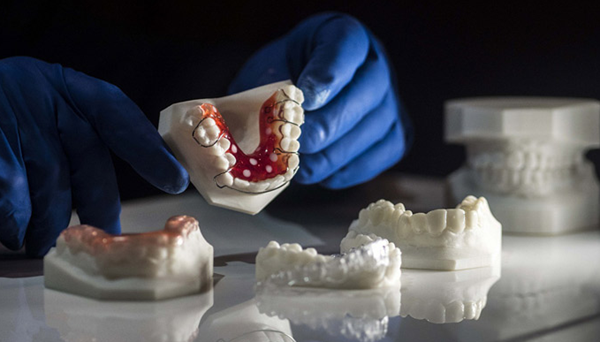
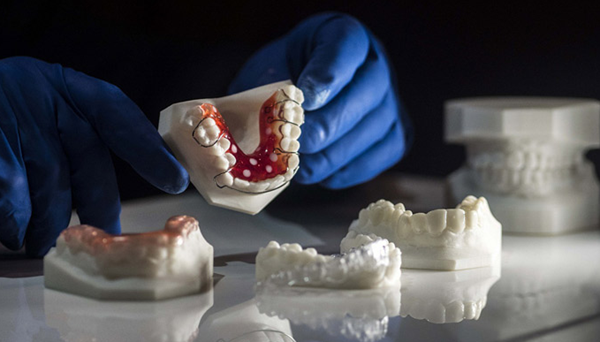
The dental industry can be divided into two broad categories: dental clinics and denture laboratories. Traditionally, they work together to create tailor-made medical devices (gutters, crowns, bridges, etc.). In effect, the dentist takes an impression of the patient’s tooth and sends it to a laboratory which then creates the appliance, usually made of plaster. The process takes several days, not including the return trip between the dentist and the laboratory. For the patient, they have to make another appointment and there is no guarantee that their device will fit the first time. As a result, traditional processes are time-consuming, expensive and can lack accuracy. However,The arrival of 3D technology is shaking up organizations and completely dematerializing workflows.
Dentistry3D printing technology and materials
When talking about additive manufacturing in dentistry, it is important to understand that there are many different types of technologies. The choice depends mainly on the application to be carried out and the compatible materials.Olivier Bellaton, director and founder of BIOSUMMER Dental, emphasizes that each process obviously has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, FDM will make it possible to “produce parts at a cost of several tens of cents and without post-processing after printing”. On the other hand, speed, precision and biocompatibility are not available. » Generally speaking, this technology will allow orthodontics to create dental models that will be used in thermoformed orthodontic appliances, whether for correction, whitening or retention. However, we are starting to see biocompatible dental solutions using PEEK 3D printing emerge. The 3D printer manufacturer IEMAI3D specifies: “The advantages of PEEK partial dentures are numerous. It is a strong and lightweight material that improves patient comfort. The prosthetic framework does not contain metal and is completely odorless. »

PEEK 3D printing equipment (Photo credit: Juvora)
Another process used in dentistry, and probably one of the main ones, is resin.3D printing. Whether stereolithography (SLA) or DLP, the technology offers higher resolution and significant levels of detail. The ETEC team explains: “Combined with CE/FDA approved materials, photopolymerization allows for more precise printing, resulting in a more flexible device. The complexity of finishing is much less, thus reducing manufacturing time. Additionally, materials and print designs can be easily modified to suit different applications, benefiting the dental industry as practitioners can treat patients more quickly.”
Finally, metal additive manufacturing is also a process widely used in dentistry to produce implants, prostheses or crowns in nickel-chromium or titanium. Within the family of metal technologies, the most common in this field are powder bed-based technologies. These include laser powder bed fusion and electron beam fusion.BIOSUMMER Dental notes: “The technology requires continuous production to amortize the investment, which can amount to hundreds of thousands of euros, with more skills in industry than in dentistry. » Metal machines cost much more than other technologies, sometimes more post-processing. work is required, which reduces the productivity of some people. When talking with the dental technician, he explained to us that machining the crown requires 15 minutes of working time, while metal 3D printing requires 5 hours of printing time. However, in terms of unit cost, additive manufacturing is much more interesting (75 cents compared to more than 7 euros).
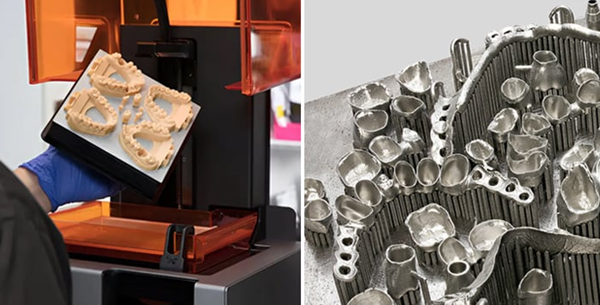
On the left, thanks to stereolithography technology3D printed model; on the right, a metal part for a dental application.
3D scanning and printing: a win-win combination in dentistry
We can see that the dental3D printing is more precise and reduces manufacturing time. In fact, it can be reduced from working days to just a few hours, allowing in certain cases to provide a solution to the patient in a single consultation. But what are the steps to create a 3D printed dental appliance? The first examination is carried out at the dental clinic, where after an initial diagnosis by a specialist, an intra-oral scan of the patient’s entire mouth is carried out. We thus obtain digital images which allow us to create 3D models of the complete shape. It should be noted that in addition to intraoral 3D scanners, there are also laboratory solutions designed to scan parts and impressions obtained in the patient’s mouth.
Once the scanning phase is completed, the generated fileThe 3D files will be sent to the dental laboratory via a secure web platform. The laboratory will then reread the digital impression and model the shape of the crown or implant in its design software (CAD). The modeling process will take into account gingival constraints, interference with other scanned teeth and even the shape of the patient’s smile using a facial scanner. Finally, the manufacturing of the parts is carried out by 3D printers, preferably designed for this purpose. Unlike many standard additive manufacturing solutions, dental 3D printers deliver the superior surface quality, precision and speed required in the field. In addition to being able to manufacture parts from biocompatible materials, they enable large workflows and the ability to produce work immediately.
As we have seen, dentists and dental technicians must have the appropriate equipment. Either3D scanners, 3D printers or mastery of CAD software can present obstacles for many professionals today. The Formlabs dental product development team clarified: “The fundamental pillars of these new ways of working are 3D scanners, CAD software and 3D printing. Generally speaking, we observe a point of resistance at the software level, at this stage of training and it is not easy. “

New manufacturing processes include software,3D scanners and printers (Photo credit: Shining 3D)
What is the future of dental additive manufacturing?
As we can see,3D technology brings enormous benefits to the dental industry, so the future of the industry is encouraging. However, many practitioners still face barriers to adopting these technologies. This is usually because they require new organization and work logic, software training, and upfront costs for 3D scanners and printers. Today, many laboratories are equipped with 3D scanners and processing machines, including 3D printers. ETEC concluded: “The majority of practitioners are very receptive and open to new digital technologies. It simply requires clinicians and dental industry professionals to fully understand and trust new digital technologies and their impact on them, their business and their patients in terms of benefits. Of course, education and training play an important role, which is why many manufacturing companies are investing in this area to better understand the technology and its clinical applications.
In summary, dentists who adopt digital technology will save time and money, increase productivity and improve user experience with minimally invasive procedures. In return, they will be able to offer competitive services and attract or retain more patients, especially against competitors who do not understand the latest technological advances.
If we focus on dentistryIn the 3D printing market, we will see that competition is becoming increasingly fierce. This is further reinforced by the arrival of new players and the battle for market share between established players. This competition gradually drives prices down as companies try to differentiate themselves. Additionally, the cost of materials, equipment and labor is expected to increase across the board in the coming years, requiring dental companies to maintain profitability and competitive pricing.

Most dental professionals are willing to try new techniques (Photo credit:RADIUS SHAPE)
source:3dnatives
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.