Unleashing the Power of Water-Conductive Laser Technology: Revolutionizing Industrial Manufacturing
Introduction
The pursuit of precision and efficiency has always been at the forefront of industrial manufacturing. With the advent of water-conductive laser technology, a new era of innovation has emerged. This cutting-edge technology has been gaining traction across various industries, including aerospace, semi-conductors, and new energy. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the technical principles, characteristics, and applications of water-conductive laser technology, as well as the current state of its development in China and abroad.
Technical Principles and Characteristics
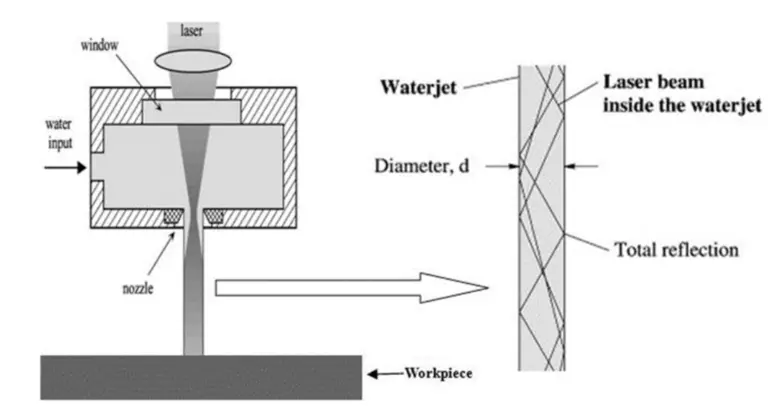
Water-conductive laser technology is based on the principle of associating a laser beam with a high-pressure micro-unulator jet and guiding it onto the surface of the material through a water jet. This system consists of a series of optical elements, such as lenses and mirrors, which collimate and concentrate the laser beam. The water jet then forms a tiny channel through which the laser beam is directed towards the surface of the material.
The water-refractive index is different from that of air, requiring a precise optical design to ensure the stability and concentration of the laser beam. This technology can achieve a precision level of microns or even nanometers, making it ideal for applications that demand high precision and quality.
High Precision, High Efficiency, and Reduced Thermal Damage
Water-conductive laser technology boasts several advantages, including:
- High precision: With a precision level of microns or even nanometers, water-conductive laser technology can achieve the desired level of precision for various applications.
- High efficiency: By directly transmitting the laser beam through the water jet, energy loss and diffusion in the air are significantly reduced, resulting in improved efficiency and quality of treatment.
- Reduced thermal damage: The rapid cooling effect of the water jet minimizes the thermal affected area (HAZ), reducing the likelihood of thermal deformation and damage to the material.
Applications
Water-conductive laser technology has far-reaching applications across various industries, including:
- Aerospace: This technology is widely used in the aerospace industry, where high-performance materials and components are required. It can be applied to engine blades, turbine discs, and aerospace vehicle combustion chambers.
- Semi-conductors: Water-conductive laser technology is used in the semi-conductor manufacturing process, where precision and quality are of utmost importance. It can be used to cut and engrave silicon wafers, pack and test chips, and even manufacture microelectronic components.
- New Energy: This technology is being explored in the new energy sector, particularly in the production of solar panels and fuel cells. It can be used to cut and engrave silicon slices, improve electrode patterns, and increase the efficiency of fuel cells.
Challenges and Problems
Despite its many advantages, water-conductive laser technology is not without its challenges and problems, including:
- Stability of water beam flow: The unstable flow of water through the nozzle can cause fluctuations in cutting speed, surface roughness, and even damage to the material.
- Laser and water beam coupling efficiency: The efficiency of coupling the laser beam and water beam is critical, as low coupling efficiency can lead to energy loss and reduced treatment effectiveness.
- Technical requirements for nozzle holes: The precision and quality of nozzle holes are crucial, as even minor defects can compromise the stability and consistency of the water beam.
- Environmental adaptability problems: Water-conductive laser equipment is sensitive to environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and vibrations, which can impact performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Water-conductive laser technology is a game-changer in the world of industrial manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision, efficiency, and reduced thermal damage. As this technology continues to evolve, it is likely to play a significant role in various industries, including aerospace, semi-conductors, and new energy. With its current applications and developments in China and abroad, we can expect to see increased adoption and innovation in the years to come.
About the Author
[Name], [Title], is a leading expert in the field of water-conductive laser technology. With years of experience in research and development, [Name] has been instrumental in driving innovation and growth in the industry. His extensive knowledge and insight into the latest technologies make him an authority in his field.