Turning can create complex parts for the medical, military, electronics, automotive and aerospace industries. Read on to learn ten machining operations performed on a lathe.
Lathes are capable of performing numerous machining operations to create parts with the desired properties. Turning is a common name for lathe processing. However, turning is only one type of lathe operation.
Changes in tool cutting edge and kinematic relationship between tool and workpiece result in different operations on the lathe. The most common lathe operations include turning, facing, grooving, parting off, threading, drilling, reaming, knurling and tapping.
1
Turning point
Turning is the most common lathe machining operation. During the turning process, turning tools remove material from the outer diameter of the rotating part. The main objective of turning is to reduce the diameter of the workpiece to the desired size. There are two types of turning operations: rough turning and finish turning.
The goal of a rough turning operation is to machine the part to a predetermined thickness by removing as much material as possible in the shortest possible time, regardless of the precision and surface finish. Finish turning produces a smooth surface finish and brings the part to its correct final dimensions.
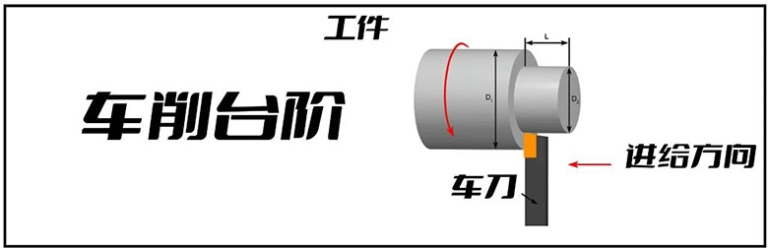
Different parts of a turned part can have different outside diameters. The transition between two surfaces of different diameters can have several machining styles, namely steps, cones, chamfers and contours. To produce these features, multiple radial depths of cut may be required.
1.1 Filming in stages
Step turning creates two surfaces of different diameters by abruptly changing the diameter between the two surfaces. The final feature looks like a milestone.
1.2 conical turning
Taper turning uses a tilting motion between the workpiece and the turning tool to produce an inclined transition between two surfaces of different diameters.

1.3 Turning and chamfering
Similar to step turning, chamfer turning creates an angular transition from an otherwise square edge between two surfaces with different turning diameters.

1.4 Copy filming
During contour cutting operations, the turning tool moves axially along a path of predefined geometry. Multiple passes of the contour turning tool are required to create the desired contour on the part.

However, forming tools (here called non-standard tools, custom tools, as shown in the picture) can obtain the contour shape immediately due to the special structure of the tool.

Photos of Special Shaped Car Blades
2
Rotating end face
During machining, the length of the part is slightly longer than the final part should be. Dressing is a machining operation allowing the end of a part to be machined perpendicular to the axis of rotation. During turning, the turning tool moves along the radius of the part, producing the desired part length and a smooth surface by removing thin layers of material.

3
Grooving
Slotting is a turning operation used to create narrow cuts, or “notches,” in a part. The size of the cut depends on the width of the knife. Larger grooves require several turns to complete. There are two types of grooving operations, namely radial grooving and face grooving. In radial grooving, the tool enters the side of the workpiece radially and removes material in the direction of the cut. In face grooving, the tool cuts a face groove on the surface of the part.

4
Cutting processing
Cutting off is a machining operation which results in the section of the part at the end of the machining cycle. This process uses a tool with a specific shape to penetrate the workpiece vertically and make a step-by-step cut as the workpiece rotates. When the tip of the turning tool reaches the center of the workpiece, the workpiece slides down.

5
Turn the wires
Threading is a turning operation in which a tool moves along the side of a part, cutting threads on the exterior surface. A thread is a uniform spiral groove with a specified length and pitch. Deeper threads require multiple passes of the tool.

6
Knurling
Knurling is a machining operation that creates a textured pattern on the surface of a part. Knurling can increase the gripping friction and visual effect of a workpiece. This machining process uses a unique knurling tool that contains one or more engraved cylindrical wheels (cam wheels) that rotate in a knurled tool holder. The engraved wheel has teeth that roll across the surface of the part to create a tooth-like pattern. The most common knurling pattern is the diamond pattern.
PS: Regarding the knurling process, we will also consider a technical sharing article in the future (introduction to foreign knurling tools, selection of knurling tools, etc., so stay tuned)

7
Turning and drilling
Drilling operations remove material from inside the part. The result of drilling is a hole with a diameter determined by the drill bit. The drill bit is usually placed on the tailstock or tool holder of the lathe.

8
Turning and boring
Reaming is a dimensional finishing operation used for finishing holes. In a boring operation, the hole is reamed lengthwise to the end in the part and the existing hole is machined to the diameter of the drawing. Reaming removes a small amount of material and is usually done after drilling to achieve a more precise diameter and smoother interior surface.

9
Twisting and boring
In a boring operation, the boring tool enters the part lengthwise and removes material along the interior surface to create different shapes or enlarge existing holes.

10
Spin and tap
Tapping is a process in which a tap penetrates a part lengthwise and creates threads in an existing hole. Before tapping, the bottom hole size of the hole to be processed should have the corresponding size (tapping if the bottom hole size is incorrect will easily cause the risk of tool breakage). Tapping is a finishing process of machining holes. Compared with CNC tapping, turning and tapping have average stability, but are more economical than CNC tapping.

Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.