These veterans have been counting with their fingers for many years and can be considered experienced machining experts. But do you know why a trick is called a trick? Why is the processing of parts with a lathe called “lathe”?
Before tackling old photo series today, we might as well first do a little popular science.
Open the dictionary and the word “car” is explained like this:
“Car” means to turn. Rotating machines in ancient China are generally called “XX carts”, which are machines that use the rotation of axles to work, such as “spinning wheels” for spinning yarn, “water wheels” for lifting water, the “cylindrical wheels”, the “turning wheels”. “, etc. .
Do you feel like you have a sudden enlightenment? Turns out the “car” in “tour” means this. It is a machine that uses the rotation of a wheel axle to perform work. This feature is summarized very well.
Looking back, aren’t ox carts, horse-drawn carriages, handcarts, bicycles and automobiles all machines that use wheels and axles to work? Then using a lathe to process parts is undoubtedly called lathe parts.

①Furniture on which people can lie and sleep. ②Bed type devices: ice beds, machine tools. ③Certain soils like beds: seed beds, river beds.
In ancient times, a bed was a device on which people could sit and lie, unlike today, it is only used for sleeping. “Shuowen”: “The bed, a place to sit and settle down. » An Shen means to stabilize the body.
It is inferred that what plays a supporting and stabilizing role is in fact the base, so there are piano beds, machine tools, lathes and enclosure beds. The central meaning of the compound word “bed” is: a stable base.
Based on the meaning, it is quite appropriate that the trick is called tower!

What is a ride?
A lathe is a machine tool that primarily uses turning tools to turn rotating parts. Drills, reamers, reamers, taps, dies and knurling tools can also be used on lathes for corresponding processing. Lathes are mainly used for processing shafts, discs, sleeves and other parts with rotating surfaces. They are the most widely used type of machine tools in machine manufacturing and repair plants.

Well, let’s get down to business after popularizing science. Today we are going to talk about the past and present life of the lathe, known as the “Mother of Machines”.
The prototype of a tower
To facilitate the use of work tools by human ancestors, the shaft lathe, the first prototype machine tool, was born probably more than 2,000 years ago.
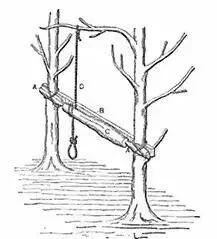
In the 13th century, prototypes of machine tools were also developed, and it was not always possible to hang them on trees. At that time, there was a “pedal lathe” that used a pedal to turn the crankshaft and drive the flywheel, then transmitted it to the main shaft to turn. It was also called an elastic shank lathe. the tools were made of metal, the principle of operation was still the same as before.

In China, during the same period, the Ming Dynasty published a strange book called “Tiangong Kaiwu”, which recorded various technologies of the Ming Dynasty and previous dynasties. After reading it, you will know what “wisdom of the ancients” is.
This book also records the structure of the grinder, which uses a principle similar to that of a treadle machine in the European Middle Ages. It uses a pedal to spin a metal disk and uses sand and water to process jade.
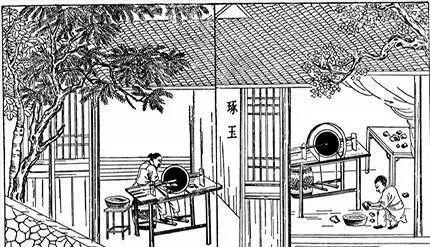
The structure of the crusher in “Tiangong Kaiwu”

“Start of work” “Photo by Tie Ming”
This is similar to boring in modern machining. A special weight is used to grind the jade inside little by little. Think of the ancient craftsmen, they are truly skilled craftsmen.

“Start of work” “Photo of the room”
The birth of machine tools
In 1774, the Englishman Wilkinson invented the barrel drill, which was the first real drill in the world.
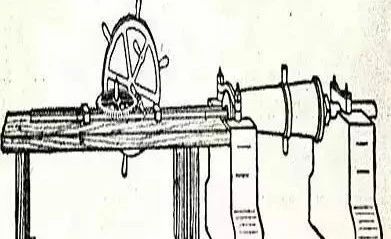
The barrel drilling machine invented by Wilkinson was originally used to cast munitions.
In 1775, Wilkinson used the cylinder bored by this barrel boring machine to remanufacture Watt’s loophole-filled cylinder to meet the requirements of Watt’s steam engine.
In order to bore larger cylinders, in the same year he built a cylinder boring machine driven by a water wheel, which promoted the development of steam engines.
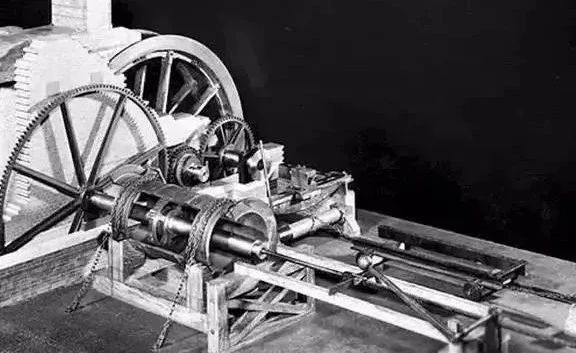
Wilkinson cylinder boring machine for forging larger cylinders
From then on, machine tools began to be driven by steam engines via crankshafts. For machine tools and steam engines, they helped each other promote common development, and a vigorous era of industrial revolution reached its peak.
The birth and popularization of the prototype of the modern lathe
While writing this, I must mention the “father of the lathe” – Henry Maudsley, a British inventor. He was to the wheel what Watt was to the steam engine.
In 1797, Maudsley made the first threaded lathe. This was a modern lathe with a threaded shank and a polished shank. It used a sliding tool holder and could turn threads at different pitches.
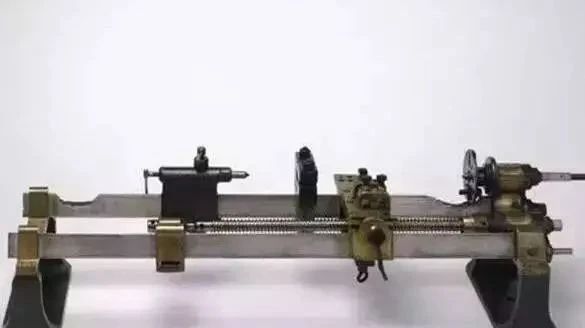
Maudsley Tower 1797
Since then, Maudsley has continued to improve the trick. In 1800 he replaced the triangular iron rod frame with a solid cast iron lathe bed, used an idler gear to exchange gear pairs, and replaced screws with different pitches to turn threads with not different.
It is the prototype of the modern lathe, a historic tool-carrying lathe that played a major role in the British industrial revolution.
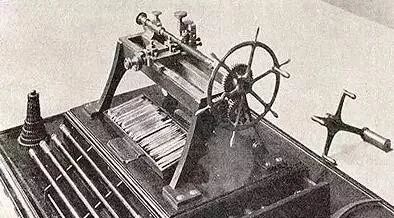
Maudsley Tower 1800
Strictly speaking, Maudsley did not invent the lathe, he simply reinnovated the lathe taking inspiration from its predecessors and gave it the automatic cutting function. But it was precisely thanks to Maudsley’s reinvention that the application of tricks was greatly popularized and the trick was truly born.
Chinese lathes: from belt lathe to five-axis hitch
For historical reasons, it can be said that China almost completely missed the first three industrial revolutions. The real development of Chinese towers began after the founding of the People’s Republic of China.
At the beginning of the founding of New China, the equipment manufacturing industry, including machine tools, was almost completely empty. China’s first batch of machine tools was successfully rolled off the production line thanks to the hard work of workers in “poor and wasteful” conditions.
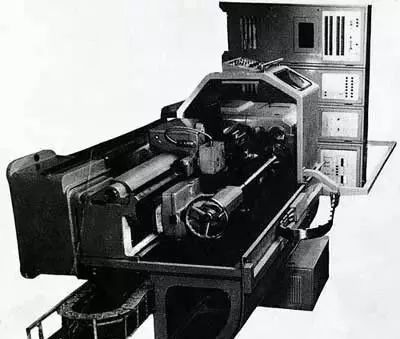
In 1949, New China’s first lathe, the six-foot belt lathe, was finally born in Shenyang No. 1 Machine Tool Factory.
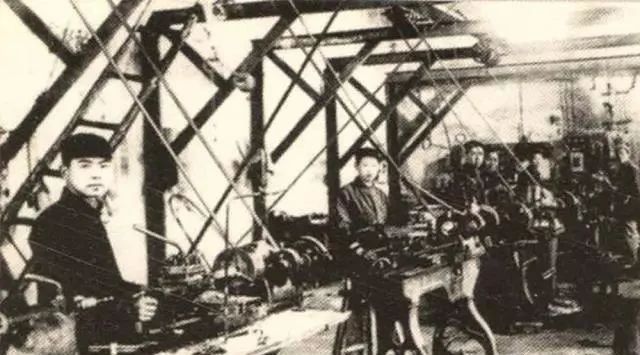
The photo shows workers operating a belt lathe.
The advent of these machine tools and their subsequent mass production strongly supported the construction of the country’s industrialization and created many production miracles in the future.
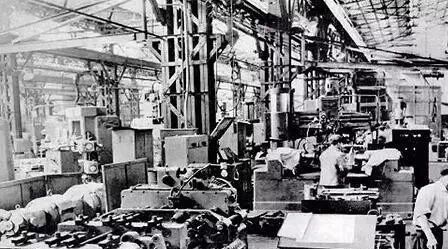
First machine processing workshop of a machine tool factory in Shenyang
During the “First Five-Year Plan” period, the state renovated some machinery repair factories and established new enterprises, and identified 18 key production enterprises. These 18 companies are the famous “eighteen Arhats” of the machine tool industry.
The “Eighteen Arhat Factory” continued to develop new machine tool products with technical assistance from the Soviet Union.
For example, after Shenyang First Machine Tool Factory produced the first lathe in New China in 1949, it developed China’s first C620-1 horizontal lathe in 1955 and started mass production;
In the same year, the Dalian Machine Tool Factory began to produce a new machine tool – a universal shovel machine, and the Shanghai Machine Tool Factory successfully tested a new cylindrical grinder;
In 1956, Jier Machine Tool mass-produced gantry planers and spiral friction presses (the factory successfully developed China’s first large-scale gantry planer and the first large-scale mechanical press in 1953 and 1955 respectively);
The lathes produced by Shenyang First Machine Tool Factory began to be exported, and Shanghai Machine Tool Factory developed the 3153M grinder.

But right now it looks like regular towers will continue to exist for a while. After all, for small batch orders, ordinary lathes are time-saving and more cost-effective, and the intelligent transformation of machine replacement wants to “unify the world”. It will take a relatively long time to complete the evolutionary transition.
However, regular towers will eventually exit the market.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















