Wire typeIncluding American standard thread, unified standard thread, wheat thread, round thread, pipe thread, square thread, trapezoidal thread, zigzag thread and ball thread, etc.
The top and root of the American standard threads are both flat, with better strength. The thread angle is also 60 degrees. Specifications are expressed in terms of number of threads per inch. This type of thread can be divided into coarse thread (NC). ), fine thread (NF), extra fine teeth (NEF) level three. Including UNC, UNF, UNEF, UN, UNS and other types, each type has coarse teeth and fine teeth.
Specifications, dimensions, tolerance codes, etc. of these threads have corresponding regulations to ensure interchangeability and consistency of threads. American standard wires are widely used in various fields such as machinery, electronics and construction, especially in aerospace and automobile manufacturing.
It should be noted that there are large differences between American standard threads and Chinese standard threads. Therefore, when importing or exporting American standard thread products, you should pay special attention to matching thread specifications and standards.
The Unified Standard Thread was jointly formulated by the United States, the United Kingdom and Canada. This is the commonly used British thread. Its specifications are expressed in number of threads per inch. This thread can be divided into coarse thread (UNC). , fine thread (UNF) and special fine tooth thread (UNEF). Level three.
Unified standard threads are widely used in various fields such as machinery, electronics and construction, especially in aerospace and automobile manufacturing. The advantages of this wire are high strength and good wear resistance, and it also promotes product interchangeability and consistency.
It should be noted that there is a big difference between unified standard threads and Chinese standard threads. Therefore, when importing or exporting products with unified standard threads, special attention should be paid to matching thread specifications and standards.
Whitworth thread is a thread adopted by the British National Standard, also known as British thread. Its thread angle is 55° and is suitable for manufacturing by rolling. Specifications for Hui type threads are usually expressed in terms of nominal diameter (in inches) and number of teeth per inch. For example: 1/4″-20 represents a coarse thread with a nominal diameter of 1/4″, and 20 represents 20 threads per inch.
The round thread is the standard thread defined by the German DIN standard. Suitable for connecting bulbs and rubber tubes. The symbol is “Rd”.
Trapezoidal thread is a commonly used transmission thread with high precision requirements. Its tooth shape is isosceles trapezoidal, and it is generally used for the transmission of some mechanisms, such as the lead screw of lathes and the lead screw of medium and small skateboards. Trapezoidal thread marking includes thread code, tolerance zone code and screw length code. The common trapezoidal thread in China is metric, while in the UK it is imperial.
Zigzag wire is a transmission wire with a zigzag tooth shape, which has good transmission performance and high wear resistance. Mainly used to transmit motion and power, suitable for high precision transmission. The markings of zigzag wires are similar to those of regular wires, but the shape of the teeth is different.
Pipe threads are threads located on the pipe wall for connection. These are threads used to prevent leaks and are often used to connect gas or liquid pipe fittings. Square thread has high transmission efficiency, second only to ball thread, but its disadvantage is that it cannot be adjusted with a nut after wear.
Common pipe threads mainly include the following types:
NPT: This is the standard American 60 degree spinal wire, used in North America.
PT (BSPT): It is a 55 degree sealed tapered pipe thread, which belongs to the Whitworth thread family and is mainly used in Europe and Commonwealth countries.
G: This is a 55 degree unthreaded sealing pipe thread, which belongs to the Whitworth thread family. Marked G means cylindrical thread. Water pipe joints are generally British threads, that is, the thread code is G thread.
The above contains relevant information about pipe threads. I hope this will be helpful in resolving your issue.
Trapezoidal thread is also called Acme thread. Zigzag threads, also called diamond threads, are only suitable for one-way transmissions, such as screw jacks, presses, etc. The ball thread is the thread offering the best transmission efficiency. It is difficult to manufacture and extremely expensive. It is used in precision machines.
Ordinary thread is a kind of standard thread, including coarse thread and fine thread. They have differences in marking, size, tolerance code, screw length, etc.
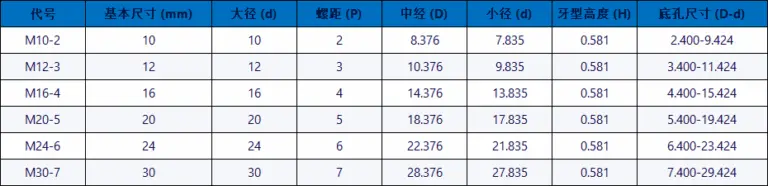
The characteristic code of ordinary thread is M, and the size code includes nominal diameter and pitch. For example, “M10” refers to an ordinary single-threaded thread with a nominal diameter of 10 mm and a pitch of 1.5 mm. “M10 × 1” refers to an ordinary single-line fine thread with a nominal diameter of 10mm and a pitch of 1mm.
The tolerance area code of ordinary threads includes tolerance level and basic deviation, such as 5g6g, 6g, 6H, 7H, etc.
The screwing lengths of ordinary threads are divided into three types: long, medium and short, which are represented by the codes L, N and S respectively. For example, “M10-5g6g-S” indicates an engagement length thread short and “M10-7H-L” indicates a long engagement length thread. When the thread is of medium screw length, the N code is not marked. When special needs are required, the screw length value can be indicated.
In addition, ordinary yarns are divided into coarse yarns and fine yarns. Ordinary fine thread threads are mainly used on precision parts and thin-walled parts. The pitch must be indicated in the mark, while the pitch of ordinary coarse threads is generally not marked.
Thread turning methods include:
Ordinary turning tool cutting method: use a single-edged turning tool or thread insert, select the correct turning tool model according to the diameter and pitch of the workpiece, and perform cutting with a lathe or threading machine.
Double-edged boring tool cutting method: Use a double-edged boring tool to cut a long threaded groove on the workpiece, and then insert the tap into the threaded groove before processing.
Rolling cutting method: use a baking sheet or roller to roll on the workpiece, which effectively reduces the difficulty and cost of processing, and can process multiple wires at the same time.
Cold Extrusion Forming Method: In early processes, pressure and heat treatment are used to harden the center of the workpiece. The finished part is placed on a special lathe and cold extrusion is used to form threads.
Grinding method: Use a grinding head to facilitate thread processing. Inner round grinding wheels, outer round grinding wheels, pointed grinding wheels, etc.
Thread milling:
It is a method of machining threads, usually using a CNC machine tool, that uses the rotating and feeding motion of a spindle to cut the workpiece.
During the milling process, the tool advances along the workpiece axis, cutting threads through rotation and feed motion. Compared with traditional thread turning, thread milling can process more complex thread shapes and sizes with higher machining accuracy and surface quality.
Additionally, thread milling can be used to process multiple threads of the same or different sizes, as well as threads with different thread sizes in the axial direction.
It should be noted that thread milling requires the use of specialized thread milling cutters and CNC machine tools, so the cost is higher. Additionally, for some small batch production or single part production needs, since milling requires the use of CNC machine tools, this may not be applicable.
In short, thread milling is an efficient and high-precision processing method suitable for mass production or complex thread processing.
Here is the calculation formula for commonly used threads:
Thread with 60° profile angle:
Medium diameter = Large diameter – 0.25 spiral distance
Small diameter = large diameter – 1.0 spiral distance
Thread height = 0.5*thread pitch
Thread with a profile angle of 55° (i.e. inch thread):
Medium diameter = Large diameter – 0.25 spiral distance
Small diameter = large diameter – 1.05 spiral distance
Thread height = 0.5 pitch + (groove width – 0.366 pitch)/2
Calculation formulas for certain types of wires:
Trapezoidal thread: crest width = 0.366P-0.536ac; alveolar base = 0.366P-0.536ac-0.46P; ridge width = 0.366P-0.536ac-2F’.
Zigzag wire: peak width = 0.4P; peak width = 0.2P-0.268P; alveolar base = 0.366P-0.536ac.
Triangular spiral: average diameter = large diameter – 0.6495P; small diameter = large diameter – 1.0825P;
leaf:
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.