Unleashing Industrial Potential: EtherCAT – The Backbone of Modern Automation
Introduction
In the landscape of Industry 4.0, where precision, speed, and seamless communication define success, EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) has emerged as a revolutionary industrial Ethernet protocol. Designed for real-time control, EtherCAT transcends traditional limitations, delivering unprecedented performance in motion control, robotics, and high-precision automation. This protocol redefines efficiency by processing data on the fly, eliminating bottlenecks and enabling complex applications from semiconductor fabrication to automated logistics. Its adaptability across diverse industrial ecosystems makes it a cornerstone of next-generation manufacturing.
Six Real-World EtherCAT Integration Scenarios
EtherCAT’s versatility shines in hybrid industrial environments. Here are six practical implementations:
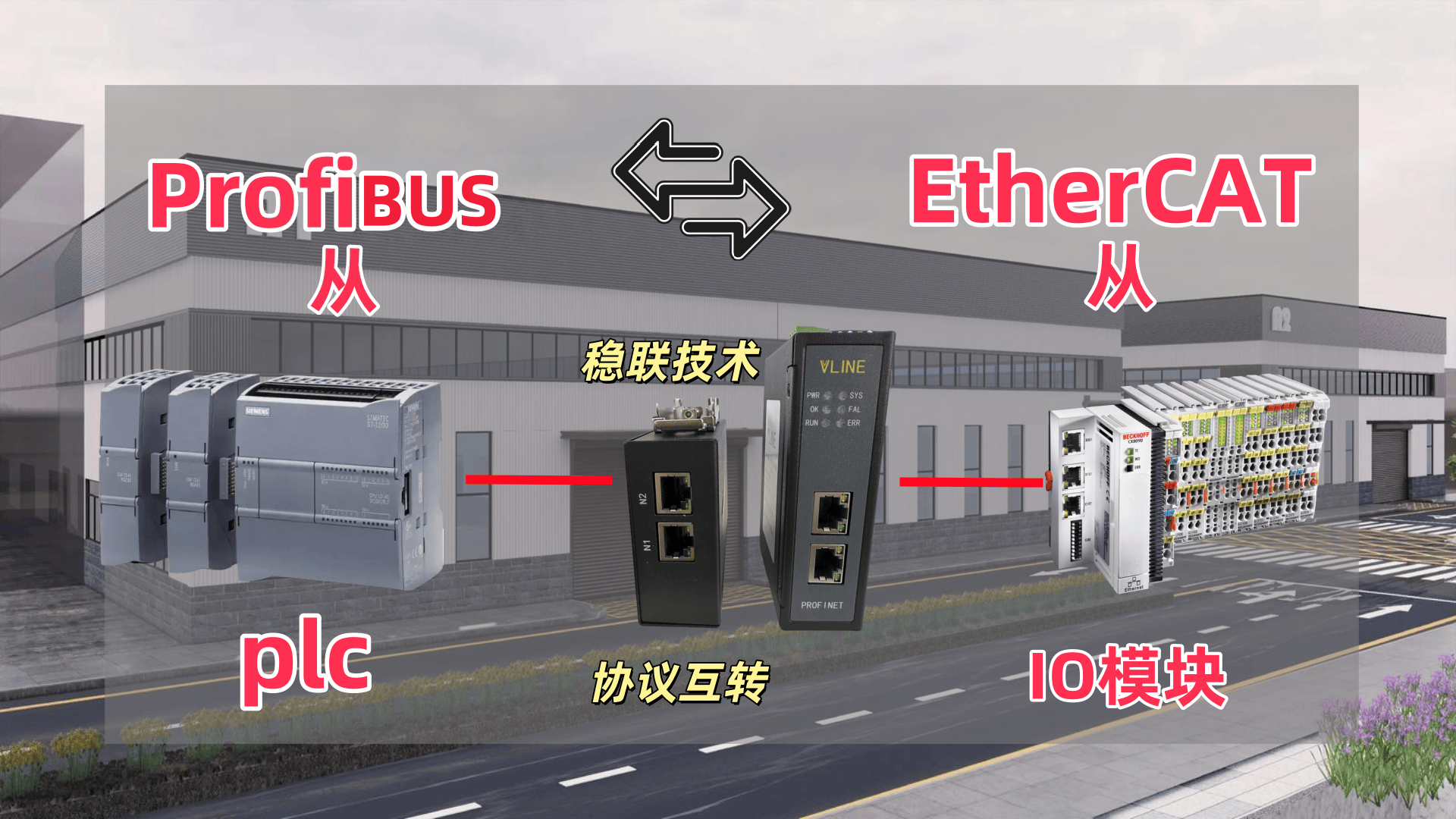
Profinet Integration: Automotive Production Lines
Siemens PLCs communicate with EtherCAT servo drives (e.g., Beckhoff AM8000) via a Profinet master station. This setup synchronizes robotic arms and conveyor systems in automotive assembly, leveraging EtherCAT’s precision for seamless motion control across the production floor.Profibus DP Modernization: Legacy System Upgrade
Aging factories retrofit Siemens Profibus DP networks (connecting devices like inverters) by integrating EtherCAT I/O modules (e.g., Beckhoff EK1100). Despite a minor latency increase (0.5–2 ms), this hybrid approach bridges old and new technologies using protocol gateways.

Modbus TCP Interfacing: Textile Machinery HMI
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) like Weintek touchscreens visualize EtherCAT motion controller data via Modbus TCP, enabling operators to monitor loom speeds and thread tension in real time.

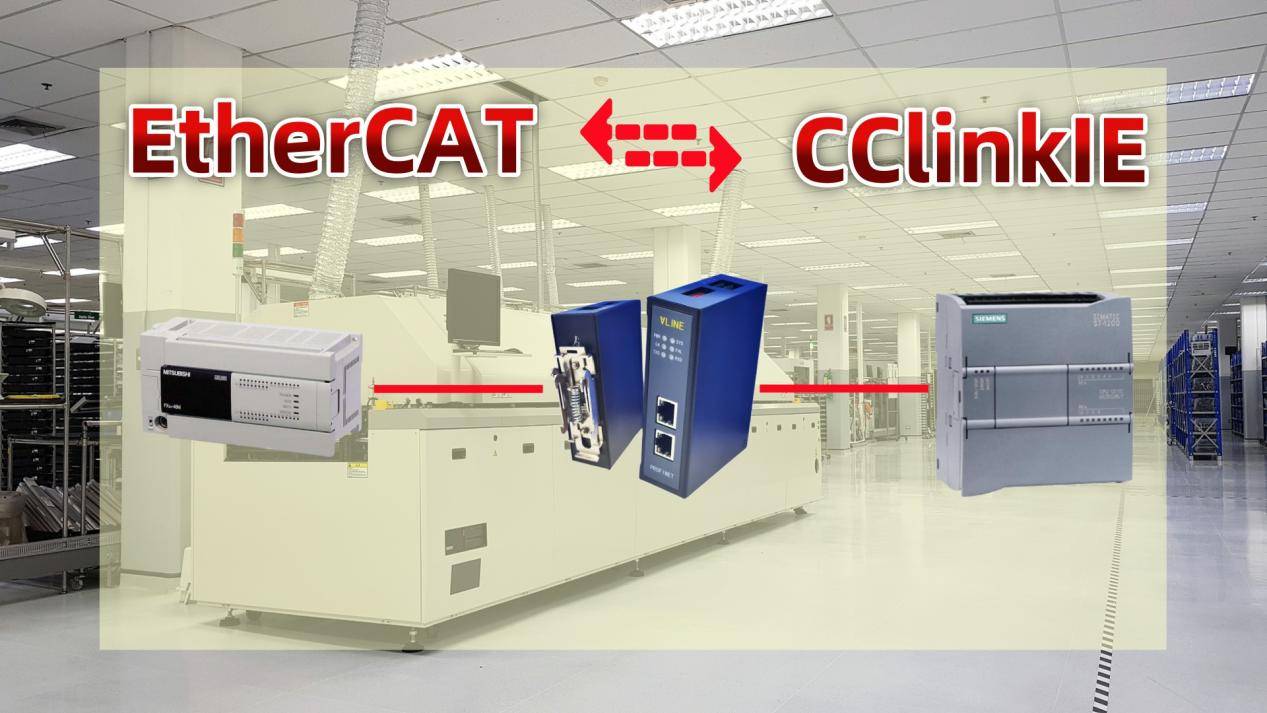
CC-Link IE Fusion: Cross-Platform Semiconductor Tools
Japanese Mitsubishi robotics (using CC-Link IE) interoperate with European EtherCAT systems in cleanroom environments. Real-time communication ensures synchronized wafer handling and inspection modules.

Ethernet/IP Coexistence: Packaging Lines
Rockwell Automation ecosystems ingest data from EtherCAT sensors via Ethernet/IP, optimizing filling and labeling processes. This hybrid model supports high-speed OEE tracking without protocol conflicts.

- Modbus RTU Bridge: Food Processing Sensors
Temperature controllers (e.g., Omron E5CC) using RS485 communicate with EtherCAT masters via Modbus RTU. In bakery ovens, this ensures ±0.1°C accuracy with minimal wiring.

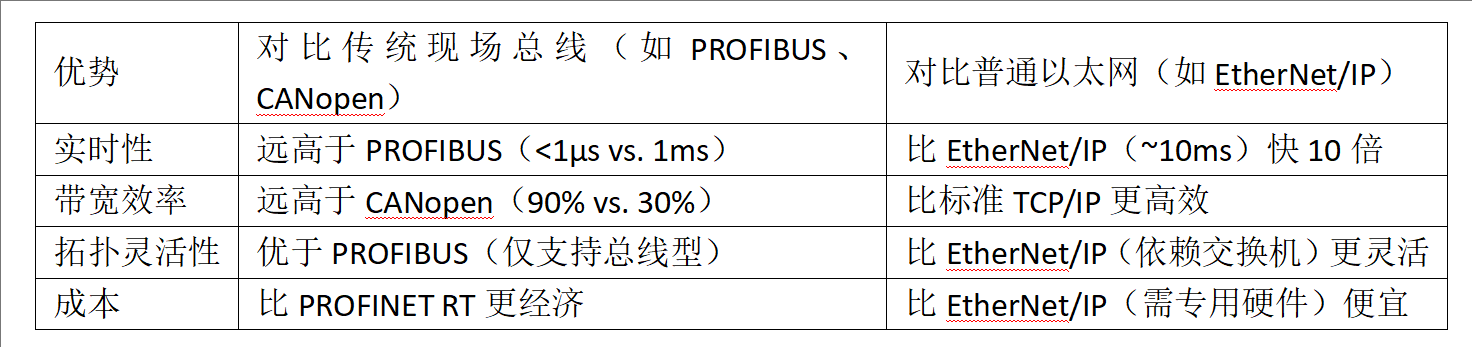
Why Industry Chooses EtherCAT: Six Strategic Advantages
EtherCAT’s dominance stems from these core strengths:
Real-Time Precision
- Ultra-Low Latency: Sub-microsecond delays (<1 µs).
- Processing On-the-Fly: Data is read/written during frame transmission—no buffering or repackaging.
- Nano-Sync: Distributed Clocks (DC) synchronize devices within 100 nanoseconds, enabling 100+ axis motion coordination.
Bandwidth Efficiency
- Single Ethernet frame supports multi-device communication.
- Achieves >90% usable data throughput (vs. 30–40% for standard Ethernet).
Flexible Topology
Supports linchpin-free networks:- Daisy-chained lines (reduced cabling).
- Stars (via unmanaged switches).
- Trees (for scalable architectures).
Cost-Effective Deployment
- Uses standard RJ45 or fiber optics.
- No proprietary ASICs—runs on off-the-shelf hardware.
- Shrinks CAPEX by minimizing switches and cables.
Robust Diagnostics
- Real-time CRC error detection.
- Hot-swap capability for zero-downtime maintenance.
- Protocol Agnosticism
Coexists with TCP/IP, Profinet, and CANopen while supporting FL-net devices, sensors, actuators, and HMIs.
Conclusion: EtherCAT as the Nervous System of Smart Factories
From robotic cells to photovoltaic plants, EtherCAT redefines industrial networking. Its fusion of sub-microsecond latency, topology flexibility, and multi-protocol resilience addresses the trifecta of Industry 4.0: speed, scalability, and synergy. As manufacturers globally embrace digital transformation, EtherCAT’s open architecture ensures it remains the bedrock of next-generation automation—turning complex challenges into seamless operations.
Industries Transformed: Robotics, CNC Machinery, Semiconductor Fabs, Logistics Automation, and New Energy.