1
Milling processing method
1) Basic milling processing
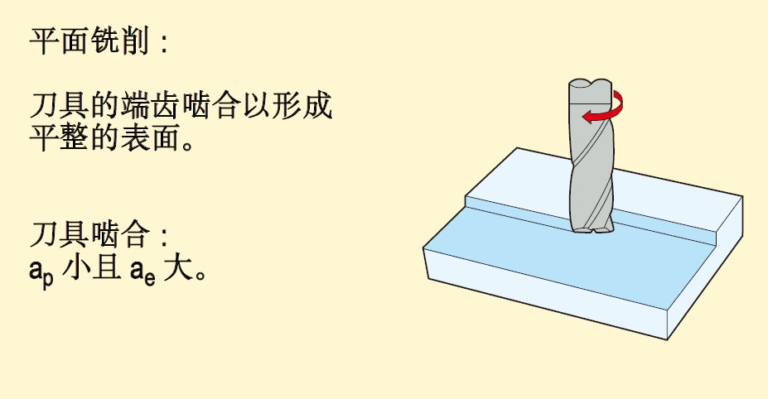
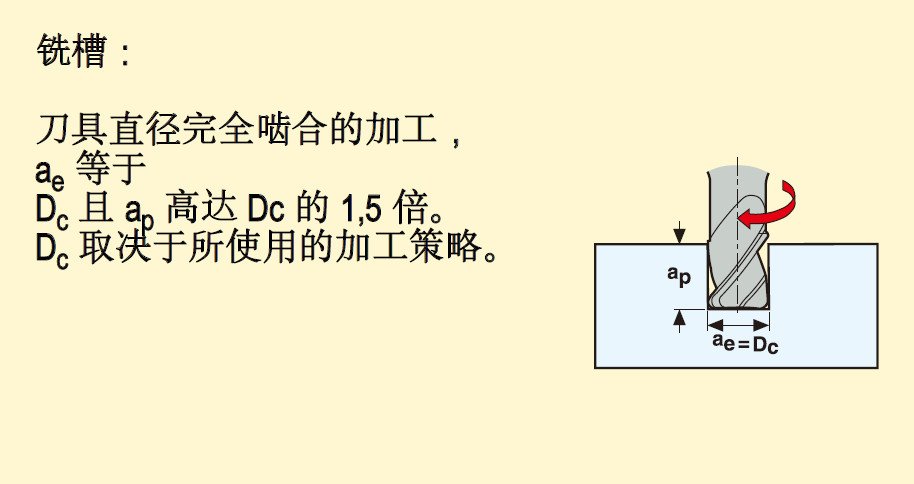
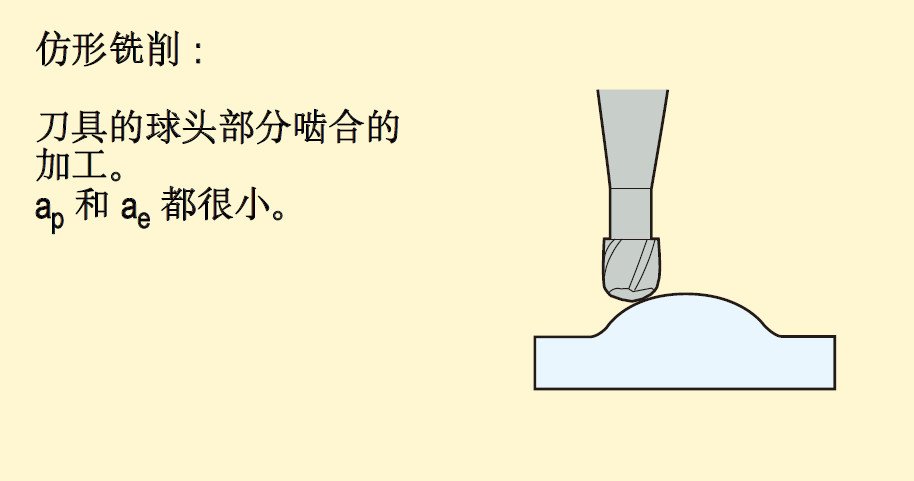
Including: surface milling, groove milling, side milling, copy milling.

2) Advanced milling processing
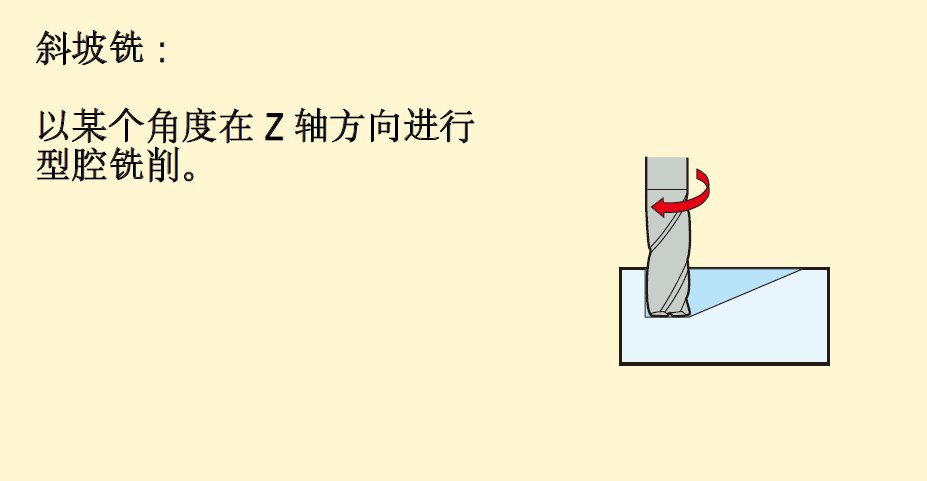
Including: ramp milling, thread interpolation, trochoidal milling, push-pull copy milling, plunge milling, contour milling and drilling.
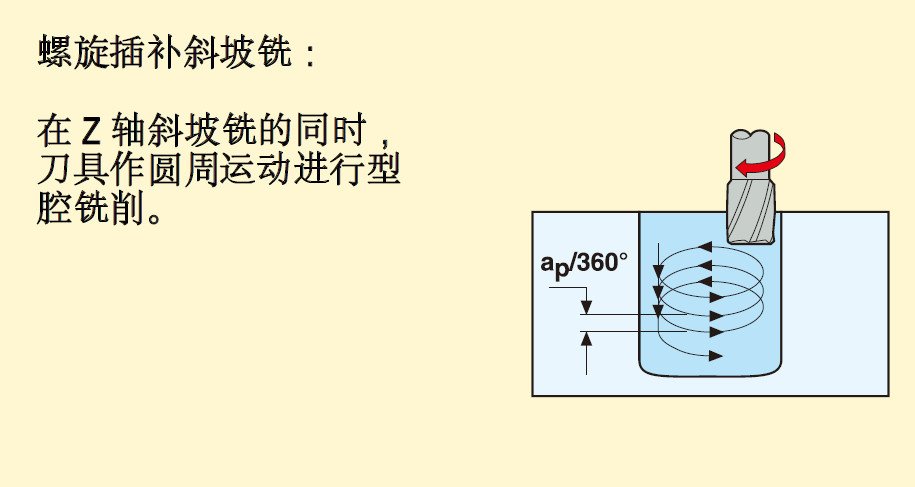
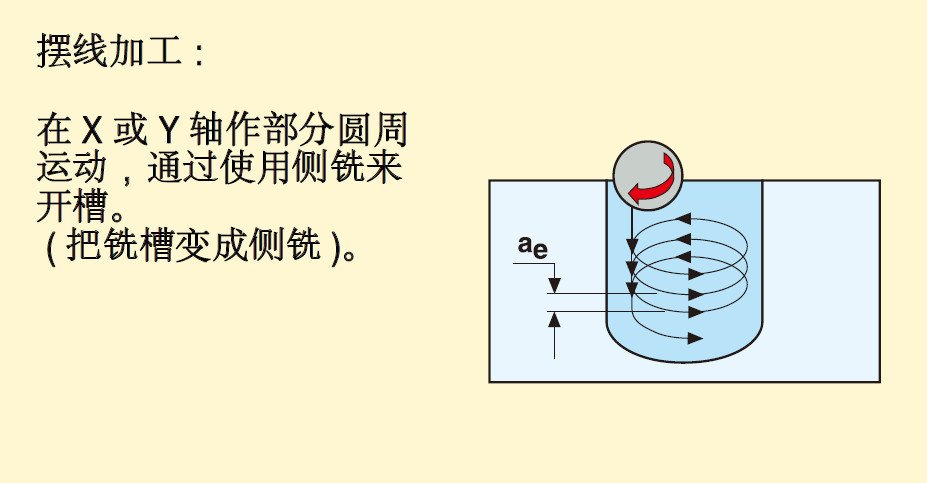
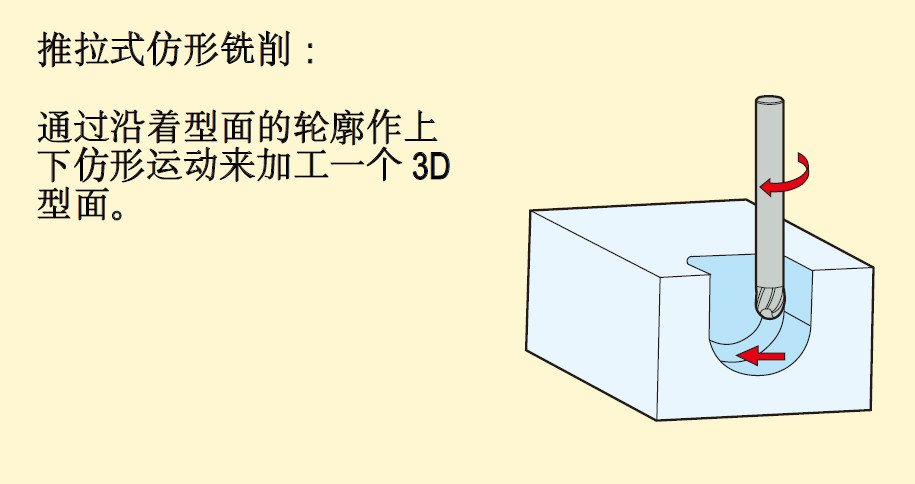
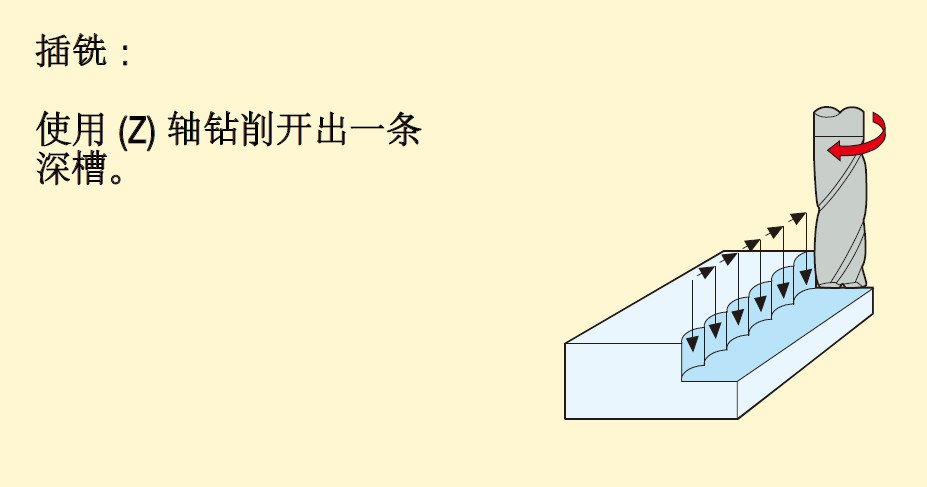
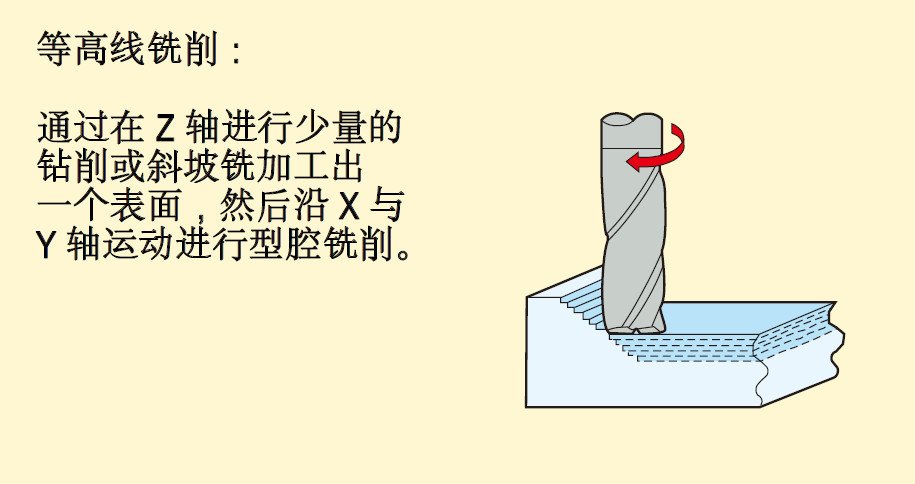
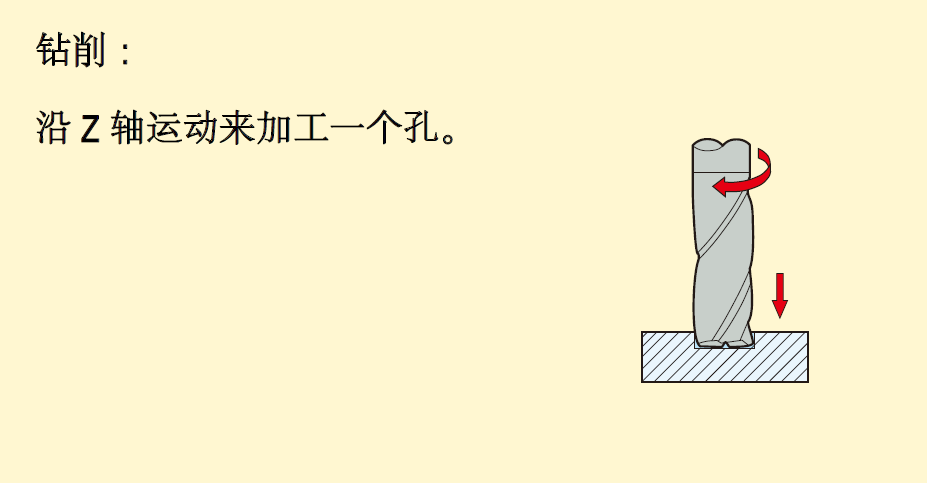
2
Definition of the milling strategy
(1) Ordinary treatment
This is a general-purpose processing strategy. The ratio of cutting width to cutting depth may vary depending on the type of operation.
1) Tool characteristics: The tool has a relatively long cutting edge and a small core diameter, and does not have high requirements for precision.
2) Machine tool requirements: no special requirements.
3) Application areas: With basic CNC technology, difficult advanced processing methods are not feasible; the metal removal rate can only reach an average level; Application areas typically include small batch sizes and a wide range of materials.
(2) High-speed processing
It is a machining strategy that combines low radial cutting depth, high cutting speed and high feed rate, depending on the method used, to achieve a high material removal rate high and low Ra value; Typical characteristics of this strategy are low cutting forces, less heat transferred to the tool and workpiece, reduced burr formation and high dimensional accuracy of the workpiece; Under high-speed machining, using faster cutting speeds than ordinary machining, high metallurgy can be achieved. rate and good surface roughness.
1) Tool characteristics: stable (larger core diameter and shorter cutting length), clear and well-formed chip space, which promotes good chip removal and coating.
2) Machine tool requirements: high-speed CNC control, high rotation speed and fast worktable feeding speed.
3) Application areas: Semi-finishing and finishing of hardened steel (48-62 HRC) in mold industry, with short delivery time. This technology can also be applied to many other materials using the right tools and advanced machining methods.
(3) High performance processing
This is a machining strategy that achieves very high material removal rates. The typical characteristics of this strategy are that the cutting width is 1 times Dc and the cutting depth is 1 to 1.5 times Dc, depending on the workpiece material, a machining method with a load much higher than usual chippings; machining is used. Capable of achieving extremely high metal removal rates.
1) Tool features: Specially developed chip-containing structure on the tool flute, tool tip is protected by 45°, tip facet or arc, particularly smooth chip-containing space, coating, with or without side fixing rod.
2) Machine tool requirements: high stability, high power requirements and high rigidity clamping system.
3) Application areas: In mass production and processing, production efficiency is a key indicator, or the processing of one-piece product requires a high metal removal rate.
(4) High power processing
This is a high-feed machining strategy that combines complete cutting across the entire tool diameter with a shallow depth of cut. When machining at high feed rates, it is possible to achieve high metal removal rates and good surface roughness by using faster feed rates than normal machining.
1) Tool features: specially developed tip, extremely short cutting length, coating.
2) Machine tool requirements: high stability and the possibility of high feed rate.
3) Application areas: From mild steel to hardened steel, titanium alloy and stainless steel, it is very effective as a pretreatment before high-speed machining. It can also be used for the treatment of deep cavities. One of the advantages of this technology is that it is very user-friendly for simple, safe and fast programming in CAM. Thanks to the so-called contour milling strategy, complex shapes can be programmed more easily without extensive programming experience.
(5) Micro-processing
This is a machining strategy that uses extremely small tool diameters.
1) Tool features: diameter range Ø0.1-2.0mm, short cutting length, wide outer diameter reduction range, high precision and coating.
2) Machine tool requirements: high spindle precision, high speed, CNC and thermal stability to prevent spindle elongation.
3) Areas of application: Various cavity treatments on many types of materials.
3
Milling parameters and calculation formulas
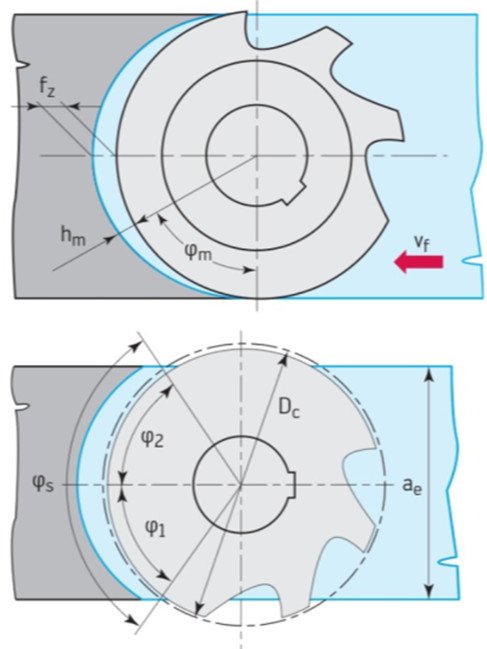
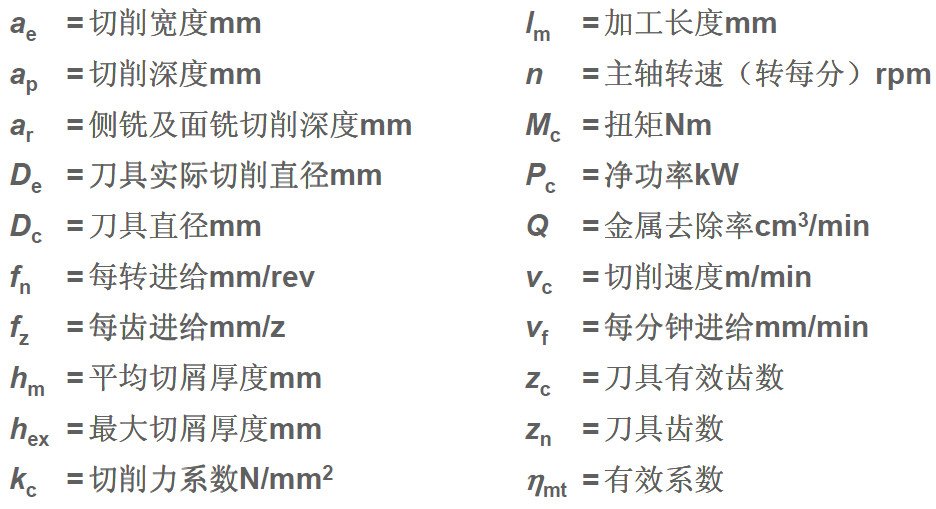
Formula for calculating cutting parameters:


4
Milling Summary
1) Check the power and rigidity of the machine tool to ensure that the diameter of the cutter used can keep the tool overhang on the machine tool as short as possible;
2) The number of teeth of the cutter is moderate to ensure that there are not too many blades engaging the workpiece at the same time to cause vibration during processing. When milling narrow parts or cavities, there must be sufficient engagement between the blade and the workpiece;
3) Proper feed per tooth to achieve good cutting results when the chips are thick enough to reduce tool wear. Use inserts with positive cutting angle geometry to achieve smooth cutting results and minimal power;
4) Diameter of the cutter adapted to the width of the workpiece;
5) Correct lead angle (45 degrees is suitable for general milling);
6) Proper position of the cutter;
7) Use cutting fluid only when necessary, dry milling generally has better tool life.

Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.