The Fundamentals of 3D Printing Screws and Threads: A Guide to Understanding the Basics
As the use of 3D printing continues to grow, so does the need for accurate and reliable fastening systems. Screws and threads are a crucial component of many 3D printed parts, and understanding their fundamentals is essential for successful design and fabrication. In this article, we will delve into the world of screws and threads, exploring the differences between the two, the various types of threads, and the considerations for 3D printing these components.
What is the Difference between Screws and Threads?
A screw is a fastening element used to form a removable connection, whereas a thread is the primary characteristic of a screw. In other words, threads are not exclusive to screws, and can be found on pipes, linear discs, worms, and many other devices. [H2] Basic Terms
Before designing threads, it is essential to understand certain key terms and concepts. The following terms are crucial for a comprehensive understanding of threads:
- External or Internal Thread: The external thread, or male thread, protrudes from the cylindrical surface, while the internal thread, or female thread, is found on the back of the external thread, immediately on a negative cylindrical surface. For example, bolts use external threads, while nuts use internal threads.
- Thread Direction: The thread direction refers to the rotation direction of the screw. Right-hand threads turn in the direction of a watch’s hands, while left-hand threads turn in the opposite direction. If a right-hand thread is turned in the opposite direction, it will unscrew.
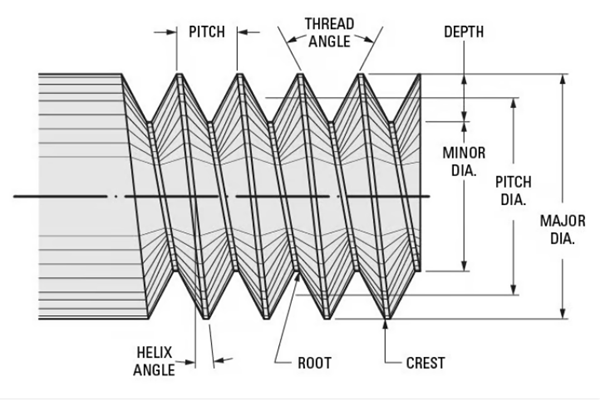
- Thread Profile: The thread profile is the two-dimensional shape of the thread, characterized by a specific transverse section. The common thread profile is triangular or trapezoidal.
- Root: The root is the bottom of the groove surrounding the threaded body.
- Summit: The summit is the highest point of the thread profile.
Types of Threads
There are various types of threads, including:
- Metric Threads: Mainly used in Europe and Asia
- Imperial Threads: Used in the United States and the United Kingdom
- Left-Hand Threads: Found in hot water handles, such as in showers or sinks
Designing Threads for 3D Printing
When designing threads for 3D printing, it is crucial to consider the following factors:
- Thread Diameter: The cylindrical diameter surrounding the top of the external thread or the root of the internal thread.
- Thread Pitch: The distance between the peak of one thread to the peak of the next.
- Thread Length: The length of the thread.
- Thread Profile: The two-dimensional shape of the thread, characterized by a specific transverse section.
- Nozzle Size: The size of the nozzle, which affects the minimum step size that can be printed.
- Layer Height: The height of each layer, which affects the precision of the thread.
Best Practices for 3D Printing Threads
When designing and printing threads, it is essential to follow these best practices:
- Test Print: Test print a small sample to ensure the accuracy of the thread design and the printer’s capabilities.
- Use a Small Nozzle: Use a small nozzle to achieve high precision and accuracy in printing threads.
- Optimize Layer Height: Optimize the layer height to achieve the desired level of precision.
- Use a Slow Print Speed: Use a slow print speed to ensure accurate and precise printing.
- Post-Processing: Perform post-processing techniques, such as sanding or polishing, to refine the thread surface.
Common Challenges and Solutions
When 3D printing threads, some common challenges arise, including:
- Large Diameter: When printing large diameter threads, it is essential to use a large nozzle and optimize the layer height to achieve the desired level of precision.
- Small Diameter: When printing small diameter threads, it is crucial to use a small nozzle and optimize the layer height to achieve the desired level of precision.
- Thread Tolerance: To achieve the desired level of thread tolerance, it is essential to use a small nozzle and optimize the layer height.
By following these guidelines and best practices, you can successfully design and print high-quality threads for your 3D printed parts. Remember to test print and refine your designs to ensure the highest level of precision and accuracy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, designing and printing threads for 3D printing requires a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles, terms, and considerations. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, you can overcome common challenges and achieve high-quality, reliable, and functional threads for your 3D printed parts.