With the continuous improvement of quality requirements for mechanically processed products, people have invested a lot of time and energy in the exploration of methods and measures to improve the quality of the products, but they have ignored the impact of The machining supplier on product quality during the machining process. As long as there is a margin during the transformation, this will not have much impact on the quality of the product. In the actual treatment of mechanical products, it turns out that the size of the parts of the parts directly affects the quality of the product.
If the machining supplier is too small, it will be difficult to eliminate residual form errors and surface defects in the previous process; If the supplier is too large, this will not only increase the machining workload, but will also increase the consumption of materials; , tools and energy. What is more serious is that the heat generated by the abolition of a large amount of machining elevator during treatment will deform parts, will increase the difficulty of processing parts and will affect the quality of the product. strictly control the machining elevator of the parts.
1
The concept of machining supplier
The machining supplier refers to the thickness of the metal layer which is removed from the machined surface during the machining process. The machining supplier can be divided into processing of process machining and total machining. The processing supplier of the process refers to the thickness of the metal layer removed from a certain surface during a process. It depends on the difference between the dimensions of the process before and after the adjacent processes. The total machining supplier refers to the total thickness of the metal layer removed from a certain surface during the entire treatment of the part, from the flan to the finished product, that is to say the difference between the size of the FLAN and the size of the room on the same surface on the part. The total machining supplier is equal to the sum of the machining quarrels of each process.
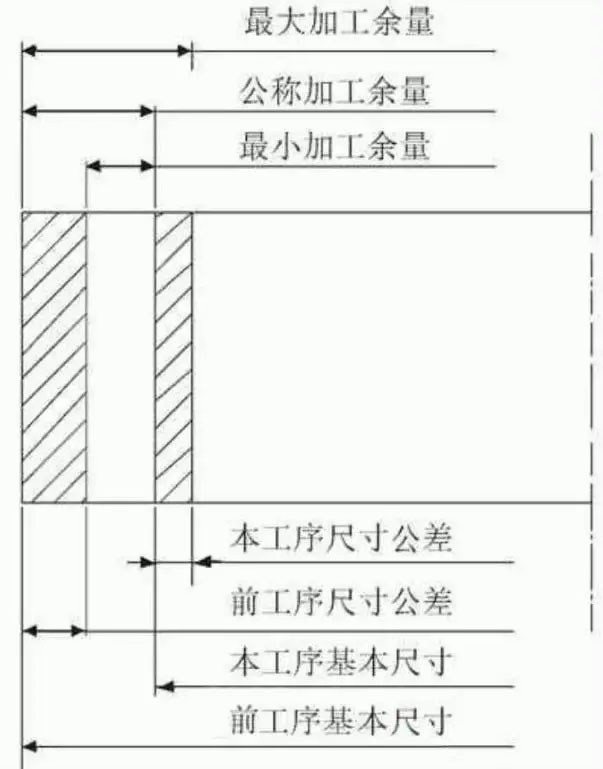
Since there are inevitable errors in the manufacture of the drain and in the dimensions of each process, the total machining supplier and the processing of the process are variable values, and there are minimum machining amounts and maximum machining suppliers. The machining supplier and tolerance are indicated in Figure 1. In the figure, the minimum machining supplier is the difference between the minimum size of the previous process and the maximum size of the process of this process. The maximum machining supplier refers to the difference between the maximum size of the previous process and the minimum size of the process; size of this process. The range of variation in the processing supplier of the process (the difference between the maximum machining volume and the minimum machining election) is equal to the sum of the dimensional tolerances of the previous process and this process. The process tolerance zone of the process is generally specified in the entry direction of the room. For tree parts, the basic size is the maximum size of the process, while for holes, it is the minimum size of the process.
2
Analysis of the influence of the machining supplier on the machining precision
2.1 The impact of an excessive machining supplier on the precision of the machining
Parts should generate cutting heat during machining. Part of this cutting heat is evacuated by the iron shavings and the cutting fluid, a part is transferred to the tool and a part is transferred to the room, causing an increase in the temperature of the room. The temperature has a large relationship with the machining supplier. If the machining supplier is important, the draft time will inevitably become longer and the quantity of cut will also increase appropriately, which will increase the cutting heat and an increase in the temperature of the room. The greatest damage caused by the increase in the temperature of the parts is the deformation of the parts, in particular of the materials sensitive to the temperature changes (such as stainless steel), and this thermal deformation spreads throughout the process of treatment process , making the treatment more difficult and the quality of the product affected. . Influence.
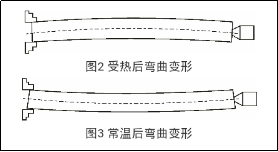
For example, when processing thin shaft parts such as screw rods, due to the method of treatment with a pliers, a top, the degree of freedom lengthwise is limited at this time , if the room temperature is too high. , thermal dilation will occur. When the extension in the direction of the length is blocked, the part will bend and inevitably deform under the influence of the stress, which will pose major problems during subsequent treatment. The flexion deformation diagram of the part after heating is illustrated in Figure 2. If the treatment continues at that time, the protruding part will be treated until the finished product. After cooling at normal temperature, the parts will undergo a opposite deformation under the action of the stress, causing errors of shape and position and affecting quality. The partition deformation diagram of the part after normal temperature is presented in Figure 3. After expansion in the direction of the diameter, the extended part will be deleted and cylindrical and dimensional errors will occur after the room cooling. When grinding precision screws, the thermal deformation of the part will also lead to step errors.
2.2 The impact of a too small machining supplier on the precision of the machining
The wallpaper of the parts must not be too large or too small. If the machining supplier is too small, residual geometric tolerances and surface defects in the previous process cannot be eliminated, thus affecting the quality of the product. In order to guarantee the quality of processing of parts, the minimum machining supplier left in each process must be able to meet the basic requirements of the minimum machining of the previous process. The schematic diagram of the components of the minimum machining supplier for the inner hole in a certain part is presented in Figure 4. Figure 4A) shows the part to be machined with an inner hole. If the O1-O1 axis deviates from the OO reference axis when the hole is treated in the previous process, there will be a position N and the inner hole will have a cylindrical error P (such as Conicité, Ellipse , etc.) and an error of surface roughness H (as shown in Figure 4b)), then in order to eliminate geometric tolerance before bore, the minimum machining elevator on one side of the bore process must include the values of the above errors and faults. Considering that there is inevitably an installation error in the room during the bore in this process, that is to say the Error E between the axis of the OO origin hole and the axis of Rotation O’-O ‘after the installation of the part (as shown in Figure 4C). , and the bore in this process the dimensional tolerance t of the hole, therefore the minimum supplier of machining Z for this process can be expressed by the following formula:
Z≥T/2+H+P+N+E (Marge on one side)
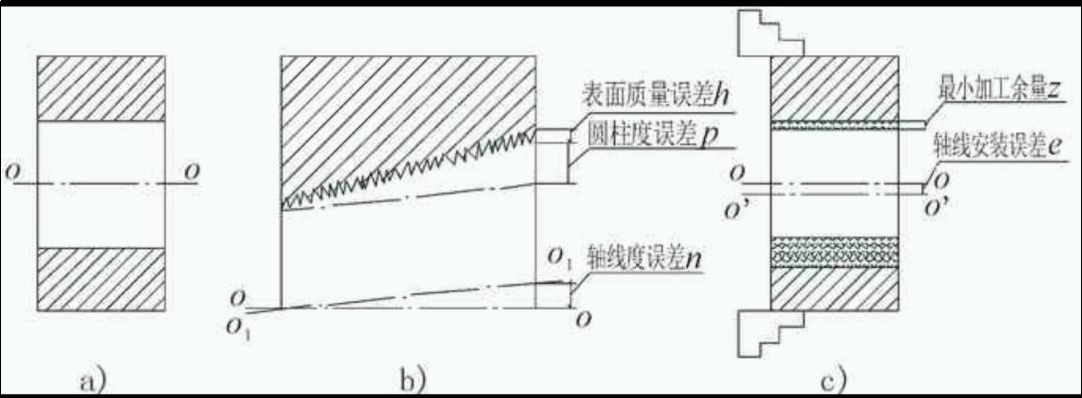
Figure 4 Illustration of the components of the minimum machining supplier
For different parts and different processes, the values and manifestations of the above errors are also different. They must be treated differently when determining the machining quarrels. For example, the thin tree is subject to bending and deformation, and the linear error of the omnibus bar exceeds the diameter tolerance range. The processing supplier of the process must be enlarged appropriately for the process of using tools such as floating bores for positioning. The treatment surface itself, the installation error does not need to be taken into account. E, the processing supplier of the process can be reduced accordingly for certain finishing processes which are mainly used to reduce the roughness of the surface, the size of the processing of the process is only linked to; The roughness of the surface h.
3
Reasonable choice of machining supplies
3.1 Principles of parts for machining parts
The choice of part processing allocation is closely linked to the materials used, the size, the precision level and the part processing method, and depends on the specific situation. The following principles must be respected when determining the factors in the machining of the parts:
(1) The minimum machining supplier should be used to shorten the processing time and reduce the cost of treatment of parts.
(2) Sufficient treatment margin should be left, especially in the final process. The machining supplier must be able to guarantee the accuracy and roughness of the surface specified on the drawing.
(3) When determining the machining supplier, the deformation caused by the heat treatment of the parts must be taken into account, if not waste could be produced.
(4) When determining the machining supplier, the treatment method and equipment should be taken into account, as well as possible deformations during treatment.
(5) It is necessary to take into account the size of the parts to be treated when determining the machining supplier. The larger the part, the greater the machining the machining. Because as the size of the part increases, the possibility of deformation caused by cutting forces, internal constraints, etc. will also increase.
3.2 Method of determination of machining suppliers
3.2.1 Empirical estimate method
The empirical estimate method is commonly used in production practice. This is a method to determine the machining supplier based on the design experience of the craftsman or by comparison with parts of the same type. For example, the machining quarrels for the rudder wick, the rudder axis, the intermediate tree and the rear tree of the ship under construction are determined on the basis of the many years of experience in the design of craftsmen. Given the importance of the room, coupled with the influence of factors such as its large size and high constraints on the draft forge, a 6 mm semi-finishing elevator is left after the coarse filming of the circle Exterior, an extra 3mm thin shooter is left after the semi-finition, and a 3 mm fine filming extra thickness is left after a fine filming of 1 mm. In order to avoid an insufficient machining supplier and to produce falls, the machining supplier estimated by the empirical estimation method is generally too large. This method is often used for the production of unique parts and small lots.
3.2.2 Research correction method in tables
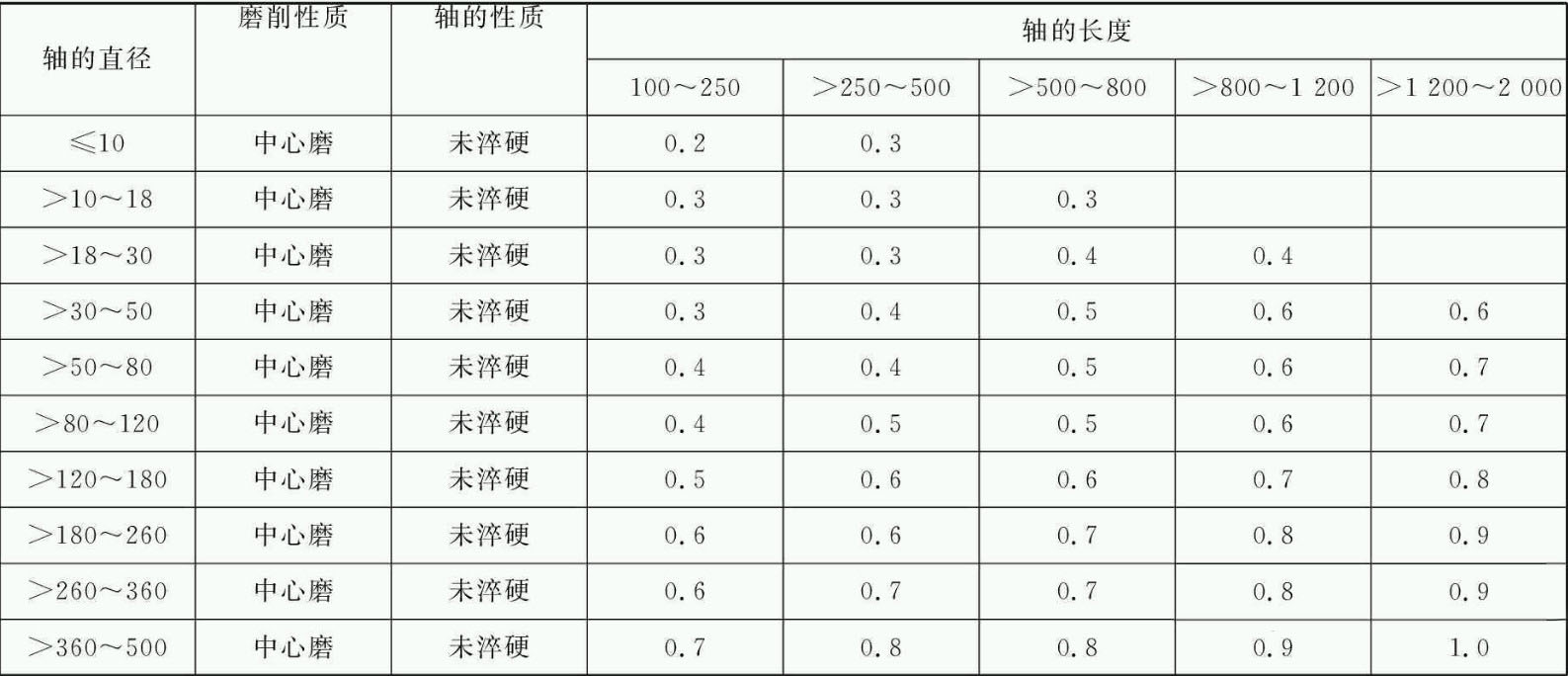
The consultation table correction method is a method that is compiled in a table based on data on the machining supplier accumulated in production practice and experimental research, and revised according to the real processing conditions to determine the machining supplies. This method is widely used. . The machining quarrels for the finely turned exterior circle and the rectified external circle of the ride parts after coarse filming are indicated respectively in Table 1 and Table 2.
3.2.3 Analysis and calculation method
The analytical calculation method is a complete analysis and calculation method of various factors that affect the machining supplier on the test of test data and calculation formulas to determine the machining supplier. The machining supplier determined by this method is precise, economical and reasonable, but it requires the accumulation of relatively complete data. It is not as simple and intuitive as the two methods above, this method is therefore currently rarely used.
4
Conclusion
In real production, the production methods of many draft parts are temporarily determined. For example, the stainless steel sleeve flowed by centrifugation consists of laminated and welded steel plates; The cooler end cover, the engine base and the sand -molded parts of the gearbox are replaced by sanded sand parts. Welded parts, wait. There are many uncertain factors in the production process of these parts and their form errors are difficult to predict. Consequently, the three methods of determining the machining supplier of the parts presented in this article are not suitable to determine the exhaustion of these parts. They can only be used in practice. Be flexible during the production process.
Table 1 Ouration of machining in mm of the exterior circle of the tree parts after filming outline after drainage of drafts
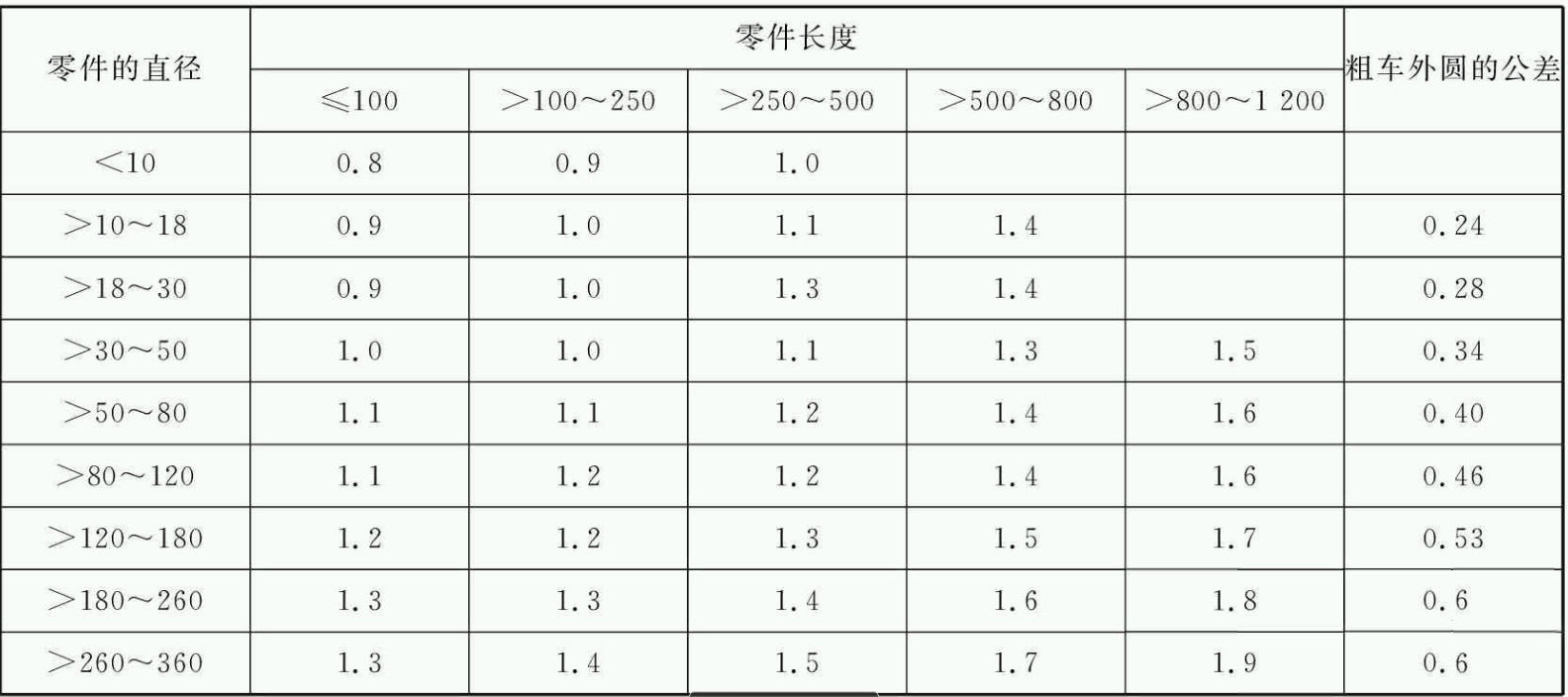
Table 2 machining supplies mm for cylindrical rectification of tree parts
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.