There are many varieties and specifications of CNC machine tools, and the classification methods are also different. Generally, they can be classified according to the following four principles based on function and structure.
1. Classification according to the machine tool movement control trajectory
⑴ Point control CNC machine tools
Point control only requires the precise positioning of moving parts of the machine tool from one point to another. The requirements for the path of movement between points are not strict. No processing is performed during movement. The movement between each coordinate axis is irrelevant. In order to achieve both fast and accurate positioning, the movement between two points usually moves quickly first, and then slowly approaches the positioning point to ensure positioning accuracy. As shown in the figure below, this is the movement path of the point control.
Machine tools with point control functions mainly include CNC drilling machines, CNC milling machines, CNC punching machines, etc. With the development of CNC technology and the decline in the price of CNC systems, CNC systems used only for point control are no longer common.
⑵ Linear control CNC machine tools
Linear control CNC machine tools are also called parallel control CNC machine tools. Its characteristic is that in addition to controlling the precise positioning between points, they also control the speed of movement and the route (trajectory) between two linked points. only related to the coordinate axes of the machine tool move in parallel, which means that there is only one coordinate axis controlled at the same time (i.e. it does not (There is no need for interpolation operation function in CNC system during gear changing process). The tool can cut at the specified feed rate. Generally, it can only process rectangular and stepped workpieces.
Machine tools with linear control functions mainly include relatively simple CNC lathes, CNC milling machines, CNC grinding machines, etc. The CNC system of this machine tool is also called linear control CNC system. Likewise, CNC machine tools used solely for linear control are rare.
⑶CNC machine tools with contour control
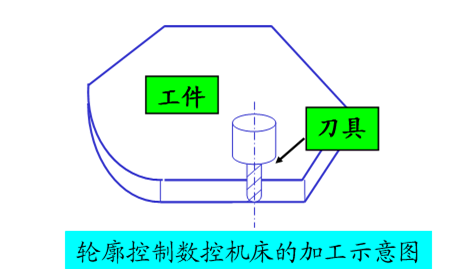
Contour control CNC machine tools are also called continuous control CNC machine tools. Its control function is that they can control the displacement and speed of two or more motion coordinates simultaneously.
In order to meet the requirements that the relative movement path of the tool along the workpiece contour conforms to the workpiece machining contour, the movement control and speed control of each coordinated movement must be precisely coordinated according to the prescribed proportional relationship.
Therefore, in this type of control method, the CNC device must have an interpolation operation function. So-called interpolation involves describing the shape of the straight line or arc through the mathematical processing of the interpolation operator in the CNC system on the basis of the basic data entered by the program (such as the coordinates of the end point of the straight line, the coordinates of the end point of the arc and the center coordinate or the radius), that is, when calculating, assign pulses to each controller of coordinate axis according to the results of the calculation, thereby controlling the linkage displacement of each coordinate axis to conform to the required contour. During the movement, the tool continuously cuts the surface of the workpiece, which can carry out various processing of straight lines, arcs and curves. Machining path controlled by contour.
This type of machine tools mainly includes CNC lathes, CNC milling machines, CNC wire cutting machines, machining centers, etc. Their corresponding CNC devices are called contour control CNC systems. Depending on how many link coordinate axes they control, they can be divided. in the following types: form
① Two-axis linkage: Mainly used for CNC lathes to process rotating surfaces or for CNC milling machines to process curved cylindrical surfaces.
② Two-axis semi-linkage: It is mainly used for controlling machine tools with more than three axes. Two of the axes can be linked and the other axis can perform a periodic feed.
③ Three-axis linkage: generally divided into two categories, one is the three-axis linkage of X/Y/Z linear coordinates, which is mainly used in CNC milling machines, machining centers, etc. The other type is to simultaneously control both linear coordinates in X/Y/Z, as well as the rotation coordinate axis that rotates around one of the linear coordinate axes.
For example, a turning machining center, in addition to the linkage of two linear coordinate axes longitudinal (Z axis) and transverse (X axis), also needs to simultaneously control the linkage of the rotating spindle (C axis). around the Z axis.
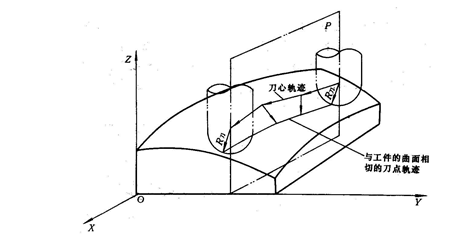
④ Four-axis linkage: Simultaneously control the three linear coordinate axes X/Y/Z to link them to a certain rotation coordinate axis.
⑤ Five-axis linkage: In addition to controlling the linkage of three X/Y/Z coordinate axes at the same time. It also simultaneously controls two of the coordinate axes A, B and C which rotate around these linear coordinate axes, thus forming a simultaneous control of five axes. At this point the tool can be positioned in any direction in space.
For example, the tool is controlled to oscillate around the X axis and the Y axis at the same time, so that the tool always maintains a normal direction relative to the contour surface being processed at its cutting point, so as to ensure smoothness. of the processed surface and improve its processing precision and efficiency, thereby reducing the roughness of the machined surface.
2. Classification according to the control method
⑴ Open-loop control CNC machine tools
The power servo motor of this type of machine tool is open loop, that is, there is no detection feedback device. Generally, its drive motor is a stepper motor. The main characteristic of a stepper motor is that each time the control circuit changes. the control pulse signal, the motor rotates a distance angle, and the motor itself has self-locking capability.
The power control signal output from the CNC system controls the drive circuit through the pulse distributor. It controls the amount of coordinate displacement by changing the number of pulses, controls the speed of movement by changing the pulse frequency, and controls the displacement by changing the pulse distribution. sense of sequence.
Therefore, the main features of this control method are convenient control, simple structure and low price. The flow of the control signal output by the CNC system is unidirectional, so there is no problem with the stability of the control system. However, since the error of the mechanical transmission is not corrected by feedback, the movement precision is not high.
Early CNC machine tools all used this control method, but the failure rate was relatively high. At present, due to the improvement of the training circuit, it is still widely used. Especially in our country, this control method is often used in general economical CNC systems and in CNC transformation of old equipment. In addition, this control method can configure a single-chip computer or a single-board computer as a CNC device, thereby reducing the price of the whole system.
⑵ Closed-loop control machine tools
The servo feed motor of this type of CNC machine tool operates in a closed-loop feedback control method. The drive motor can use two types of DC or AC servo motors and must be configured with position feedback and speed feedback to detect the. actual movement of moving parts at any time during processing. The quantity is fed back to the comparator in the CNC system over time. It is compared to the control signal obtained by the interpolation operation. The difference is used as the control signal. servo motor, which in turn drives the displacement component to eliminate the displacement error.
According to the installation location of the position feedback detection element and the feedback device used, it is divided into two control modes: fully closed loop and semi-closed loop.
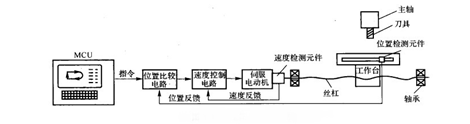
① Fully closed loop control
As shown in the figure, the position feedback device uses a linear displacement detection element (currently a grid ruler is generally used), which is installed on the saddle of the machine tool, i.e. that it directly detects the linear movement of the machine tool. contact details. Through feedback, the signal from the motor to the machine tool saddle can be eliminated. The transmission error in the entire mechanical transmission chain is reduced, thereby achieving high static positioning accuracy of the machine tool.
However, in the entire control loop, the friction characteristics, stiffness and backlash of many mechanical transmission links are not linear, and the dynamic response time of the entire mechanical transmission chain is very important in relation to the electrical response time. This causes great difficulties for the stability correction of the entire closed-loop system, and the design and tuning of the system is also quite complicated. Therefore, this fully closed-loop control method is mainly used for CNC coordinate machines and CNC precision grinders. , etc. which require great precision.
② Semi-closed loop control
As shown in the figure, its position feedback uses angle sensing components (currently mainly encoders, etc.), which are directly installed at the end of the servo motor or screw. Since most mechanical transmission links are not included in the closed loop of the system, more stable control characteristics are obtained. Mechanical transmission errors such as screws cannot be corrected by feedback at any time, but software fixed-value compensation methods can be used to improve their accuracy appropriately. At present, most CNC machine tools adopt semi-closed loop control mode
⑶ Hybrid control CNC machine tools
The characteristics of the above control methods can be selectively concentrated to form a hybrid control scheme. As mentioned before, since the open-loop control method has good stability, low cost and poor precision, while the fully closed-loop control method has poor stability, in order to compensate each other and meet the control requirements for certain machines. tools, a hybrid control method must be used. There are two commonly used methods: open-loop compensation type and semi-closed-loop compensation type.
3. Classification according to the functional level of CNC systems
According to the functional level of the CNC system, CNC systems are generally divided into three categories: low, medium and high. This classification method is commonly used in our country. The limits of low, medium and high grades are relative and the classification standards will be different depending on the period. Judging from the current level of development, different types of CNC systems can be divided into three categories: low, medium and high-end based on certain functions and indicators. Among them, the middle and high-end are generally called full-function CNC or standard CNC.
⑴ Metal cutting
Refers to CNC machine tools that use various cutting processes such as turning, milling, impacting, boring, drilling, grinding and planing. It can be divided into the following two categories.
① Ordinary CNC machine tools such as CNC lathes, CNC milling machines, CNC grinders, etc.
②The main feature of the machining center is the tool library with automatic tool changing mechanism, and the workpiece passes through it only once. After clamping, various cutting tools are automatically replaced, and various processes such as milling (turning), boring, drilling and tapping are continuously carried out on each processing surface of the workpiece on the same machine tool, such as (construction/milling) processing center, turning center, drilling center, etc.
⑵ Metal forming
Refers to CNC machine tools that use extrusion, punching, pressing, drawing and other forming processes. Commonly used processes include CNC presses, CNC benders, CNC tube benders, CNC spinning machines, etc.
⑶ Special treatment category
There are mainly CNC wire EDM machines, CNC EDM forming machines, CNC flame cutting machines, CNC laser processing machines, etc.
⑷ Measuring and drawing
Mainly includes three-dimensional coordinate measuring instrument, CNC tool setter, CNC plotter, etc.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















