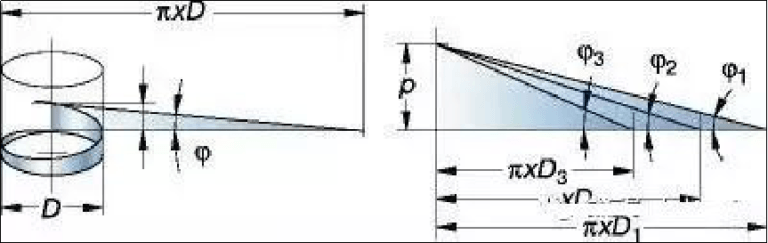
1. What is a thread?
A wire is a spiral cut into a part from the outside or the inside. The main functions of threads are:
1. Form a mechanical connection by combining internal thread products and external thread products.
2. Transfer motion by converting rotational motion to linear motion and vice versa.
3. Get mechanical advantages.
2. Thread profile and terminology
The thread profile determines the geometry of the thread, including the part diameter (large diameter, medium diameter, and small diameter thread profile angle);
1. Thread Terminology
① Bottom: The lower surface connecting the flanks of two adjacent threads.
②Front: The side surface of the thread connecting the top and bottom of the tooth.
③Tooth ridge: the upper surface connecting the two sides of the tooth.
P = pitch, mm or threads per inch (tpi)
ß = tooth angle
ϕ = helix angle of the thread
d = major diameter of the external thread
D = major diameter of internal thread
d1 = Small diameter of external thread
D1 = Internal thread diameter
d2 = pitch diameter of the external thread
D2 = pitch diameter of the internal thread
Pitch diameter, d2/D2
The effective diameter of the wire. About halfway between the big trail and the trail.
Thread geometry is based on the thread pitch diameter (d, D) and pitch (P): the axial distance along the thread from one point on the thread to the next corresponding point on the part. This can also be seen as a triangle going around the room.
vc = cutting speed (m/min)
ap = total thread depth (mm)
hair = total thread depth (mm)
tpi = threads per inch
Advance = step
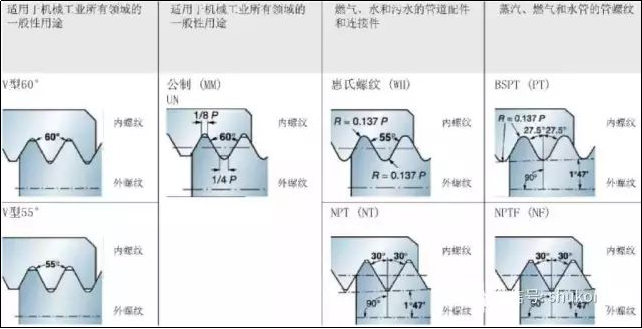
2. Ordinary thread profile

1. Calculation and tolerance of the outer diameter of the thread pitch of the 60° profile (national standard GB197/196)
has. Calculation of the basic dimensions of the pitch diameter
The basic size of thread pitch diameter = main thread diameter – pitch × coefficient value.
Expression of the formula: d/DP×0.6495
2. Calculation and tolerance of the pitch diameter of the 60° internal thread (GB197/196)
Grade a.6H thread pitch diameter tolerance (based on pitch)
Upper limit value:
P0.8+0.125P1.00+0.150P1.25+0.16P1.5+0.180
P1.25+0.00P2.0+0.212P2.5+0.224
The lower limit value is “0”,
The formula for calculating the upper limit value 2+TD2 is the base size + tolerance.
For example, the pitch diameter of the M8-6H internal thread is: 7.188+0.160=7.348. The upper limit is: 7.188 is the lower limit.
b. The formula for calculating the basic pitch diameter of internal threads is the same as that of external threads.
That is, D2 = DP × 0.6495, that is, the pitch diameter of the internal thread is equal to the large diameter of the thread – pitch × coefficient value.
Basic deviation of c.6G E1 level thread pitch diameter (based on pitch)
P0.8+0.024P1.00+0.026P1.25+0.028P1.5+0.032
P1.75+0.034P1.00+0.026P2.5+0.042
3. Calculation and tolerance of major diameter of external thread (GB197/196)
has. The upper limit of the main diameter 6h of the external thread
That is, the thread diameter value of M8 is φ8.00 and the upper limit tolerance is “0”.
B. The lower limit tolerance of the 6h quality main diameter of the external thread (depending on the pitch)
P0.8-0.15P1.00-0.18P1.25-0.212P1.5-0.236P1.75-0.265
P2.0-0.28P2.5-0.335
The formula for calculating the lower limit of the large diameter: d-Td is the basic size of the large diameter of the thread – tolerance.
4. Internal thread diameter calculation and tolerance
has. Calculation of basic dimensions of small diameter internal thread (D1)
Basic thread size = internal thread basic size – pitch × coefficient
5. Calculation formula of single indexing method of indexing head
Formula for calculating the single indexing method: n=40/Z
n: is the number of revolutions that the dividing head must make
Z: equal fraction of the part
40: Fixed number of division heads
6. Calculation formula for a hexagon inscribed in a circle
① Find the six opposite sides of circle D (surface S)
S = 0.866D corresponds to diameter × 0.866 (coefficient)
② Find the diameter of the circle (D) on the opposite side of the hexagon (surface S)
D=1.1547S is the opposite side × 1.1547 (coefficient)
7. Calculation formulas for six opposite sides and diagonals in the cold heading process
① Find the opposite side (S) of the outer hexagon to find the opposite angle e
e=1.13s is the opposite side × 1.13
② Find the opposite angle (e) of the interior hexagon from the opposite side(s)
e=1.14s is the opposite side × 1.14 (coefficient)
③Calculate the diameter of the opposite corner head material (D) from the opposite side(s) of the outer hexagon
The diameter of the circle (D) should be calculated according to (second formula in 6) the six opposite sides (s plane) and its offset center value should be increased appropriately, i.e. D≥1, 1547s. the amount can only be estimated.
8. Calculation formula for a square inscribed in a circle
① Find the opposite side of the square (area S) from the circle (D)
S=0.7071D is the diameter×0.7071
② Find the circle (D) of the opposite sides of the four squares (surface S)
D=1.414S is the opposite side×1.414
9. Calculation formulas for the four opposite sides and opposite corners of the cold heading process
① Find the opposite angle (e) of the opposite side (S) of the outer square
e=1.4s is the parameter of the opposite side (s)×1.4
② Find the opposite angle (e) of the four interior sides
e=1.45s is the opposite side(s) × 1.45 coefficient
10. Formula for calculating hexagonal volume
s20.866 × H/m/k is the opposite side × opposite side × 0.866 × height or thickness.
11. Formula for calculating the volume of a truncated cone (cone)
0.262H (D2+d2+D×d) is 0.262 × height × (large head diameter × large head diameter + small head diameter × small head diameter + large head diameter × small head diameter).
12. Formula for calculating the volume of a missing spherical body (such as a semicircular head)
3.1416h2(Rh/3) is 3.1416×height×height×(radius-height÷3).
13. Calculation formula for processing the dimensions of taps for internal threads
1. Calculation of the large diameter of the tap D0
D0=D+(0.866025P/8)×(0.5~1.3), that is, the basic size of the large diameter tap thread + pitch 0.866025÷8×0, 5 to 1.3.
Note: Selection of 0.5 to 1.3 should be determined based on step size. The larger the step value, the more coefficient should be used. On the contrary, the smaller the step value, the more coefficient should be used. .
2. Calculation of the tapping pitch diameter (D2)
D2=(3×0.866025P)/8 i.e. thread pitch=3×0.866025×thread pitch÷8
3. Calculation of the tap diameter (D1)
D1=(5×0.866025P)/8 i.e. tap diameter=5×0.866025×thread pitch÷8
14. Formula for calculating the length of materials used for cold molding of various shapes
Known: The formula for volume of a circle is diameter × diameter × 0.7854 × length or radius × radius × 3.1416 × length. Either d2×0.7854×L or R2×3.1416×L
When calculating, the required material volume is X÷diameter÷diameter÷0.7854 or X÷radius÷radius÷3.1416, which is the length of the feed.
Column formula = X/(3.1416R2) or X/0.7854d2
X in the formula represents the volume of material required;
L represents the actual value of the feed length;
R/d represents the actual radius or diameter of the material being fed.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.