G-code is the secret magic behind all numerically controlled (CNC) machines, such as 3D printers, laser cutters, and, of course, CNC milling machines. It acts as a link between digital design and physical manufacturing, transforming those designs into precise instructions that machines can execute to bring them to life.
In this article, Mohou.com will learn with youThe basics of G-code and how it works in different applications such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing, resin-based 3D printing, and CNC milling. Additionally, we will explore some useful G-code skills, such as manually editing .gcode files, understanding their differences between machines, and how to adapt G-code to different firmware.
what isG-code?
G-code allows us to communicate our designs to the CNC machine in a way it can understand (Source: AethericEye via Reddit)
G-code stands for “Geometry Code” and is a programming language used to control computer numerical control (CNC) machines.
You may be wondering why do we need a programming language for CNC machine tools?
If we want to useA CNC milling machine cuts a cube out of wood and it probably won’t take too much time to manually control the machine. However, if we want to cut 50 cubes (or something more complex), we can simply write a set of commands written in G-code, which will allow us to automate the control process and save a lot of time. This is why G-code plays a vital role in any modern CNC machine, including your 3D printer!
Computers originated inDeveloped in the 1950s as part of the automation revolution, it quickly became a mainstay for controlling machining tools such as lathes and mills, and later 3D printers and other manufacturing equipment. But what is it made of?
Basic Structure of G Code
G-code instructions consist of simple, friendly, easy-to-understand commands that tell the machine how to operate. Each line is called a “block” and represents an instruction or command, including:
1、order code (eg.G01、M104)
2、Parameters that specify coordinates or parameters (e.g.X10 Y20 position Z5 or feed F1500)
There are two types of commands in G code. One is “G” which controls the movement in the machine like G28 (zero on all axes). The other is “M”, which manages non-motion related functions such as temperature adjustment (M104) or tool change (M06).
Technical overview

Three-in-one 3D printing, laser engraving and CNC milling machine (Source: Aurora Tech via YouTube)
modeling of molten deposits(FDM) is a 3D printing method that builds objects layer by layer by extruding molten filaments. Even though it cannot print small details like a resin-based 3D printer, it remains a popular choice among hobbyists due to its simplicity and affordability. G-code is specific to each printer model and the print itself, since different printers have different sizes, movements (e.g. different movement systems), etc.
AndUnlike FDM 3D printers, CNC milling involves subtracting material from an existing part. Therefore, G code for CNC milling is not an instruction to add material deterministically, but is based on precise subtractive manufacturing practices.
resin based3D printing, such as stereolithography (SLA) and digital light processing (DLP), works differently than FDM 3D printing. The concept of FDM is based on extruding molten filaments through a nozzle, building an object layer by layer, like icing on a cake. Resin-based printing, on the other hand, uses a photosensitive resin that is cured (hardened) one layer at a time by exposing it to controlled light. To achieve this, the control system is primarily focused on the Z-axis movement and exposure settings, since there are no nozzles to extrude the filament.
AlthoughFDM 3D printers, CNC milling machines, and resin-based 3D printers all use G codes. However, due to the differences between these three printers, the specific controls and functions are also very different. Let’s learn more below.
1. In3D FDM printing

from a set of instructions toBenchy (Source: All3DP)
FDM 3D printing relies on G-code to manage tool head movement and precise extrusion control. Commonly used commands include:
movement and positioning:G01 is used to control linear movement, specifying the X, Y and Z coordinates and the feed rate (speed of moving the tool holder) F. For example, G01 X50 Y25 Z0.3 F1200 moves the tool holder towards X=50 mm, Y=25 mm, Z=0.3 mm at a feed speed of 1,200 mm/min.
Extrude:The E parameter is used with G01 to extrude or retract the filament. For example, the G01 X60 Y25 E5 F1500 moves to Retraction can be performed using the G01 E-1 F1800, which retracts a 1mm filament at a feed rate of 1800mm/min.
Temperature settings:Controls such as M104 are used to adjust the nozzle temperature, while M140 is used to heat the bed. For example, the M104 S200 sets the nozzle temperature to 200°C and the M140 S60 sets the bed temperature to 60°C.
Fan control:M106 turns the fan on and adjusts its speed, M107 turns it off. For example: M106 S128 sets fan speed to 50% (S128, maximum is S255).
FDM-specific G-codes typically contain settings to manage print speed, shrink settings, and other print-specific operations such as pause (M0) or filament change (M600). Since FDM printers work by adding material to the build area, G-Code focuses on additive manufacturing methods.
2. InCNC milling

CNC milling machines “cut” the metal from objects (Source: CAD/CAM Solutions on YouTube)
As mentioned above, forIn CNC milling, movement is related to the removal of material from the workpiece. For example:
Toolpath control:Commands such as G17, G18 and G19 select the artboard. G17 sets the XY plane, G18 sets the XZ plane and G19 sets the YZ plane to ensure precise positioning of the cutting tool.
Feed and depth of cut:The F parameter specifies the feed rate, while the S parameter defines the spindle speed (the rotational speed of the cutting tool). For example, the F1000 sets the feed rate to 1000 mm/min and the S1200 spindle speed to 1200 rpm. These settings are essential for controlling cutting speed and depth.
Advanced operations:Commands such as G02 and G03 control circular interpolation. G02 specifies a clockwise arc, while G03 specifies a counterclockwise arc. Cutter compensation is handled by G41, which shifts the tool to the left of the cutting path, and by G42, which shifts the tool to the right, allowing precise adjustments to the tool size.
3. Resin-based3D printing

AndCompared to FDM, resin printers can print amazing details… (Source: DaveMakesStuffBC via Reddit)
we already knowWhat typical G-code operations for FDM printing look like. Resin printers typically use the following G codes:
Z axis movement: These should only be placed between layers alongThe Z axis moves the build platform, which simplifies the G-code structure compared to FDM since the X and Y axes are not required. For example, the G1 Z1.2 F150 moves the build platform at Z=1.2mm at 150mm/min.
Solidification of layers:The controls include various exposure time settings that control the time it takes for the resin to cure via UV light to create each layer. For example, there are different options for the initial layer and subsequent layers. For example,M106 S255 P10 activates UV for 10 seconds.
Stripping and lifting operations:Resin printers may containG-code controls to peel or lift between layers to reduce suction and prepare the next layer. For example, the G1 Z1.5 F100 slightly lifts the platform at Z=1.5 mm to peel off this layer.
As you can imagine,FDM’s G-code is generally more detailed because it contains temperature, extrusion, and motion controls on all three axes. On the other hand, G-code for resin 3D printing mainly includes Z-axis positioning controls and exposure settings. Since there is no filament extrusion, there are no controls related to extrusion or retraction.
4. Manufacturing method
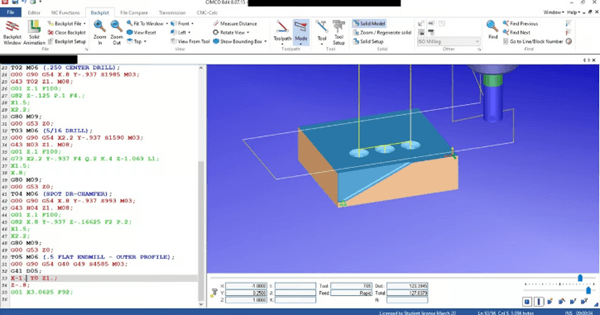
Click the start and end boxes of the script to save your changes (Source:All 3DP)
If you’re wondering if you should learn everythingG-code commands are required to print or mill your model, so you don’t have to worry.
G-code for FDM and resin-based printing is generated by slicing software, where you import the model, specify 3D printing parameters, and convert (aka slice!) the process into G-code to your printer.
ForFor FDM, popular programs include Cura and PrusaSlicer, both of which are open source and support a large number of printers on the market. Resin printing uses its own slicer, such as the Chitubox and Lychee Slicer. As mentioned above, FDM printing has many parameters to consider, while resin-based 3D printing does not have as many parameters, but there are still a number of parameters to consider .
ForCNC milling machines and computer-aided machining (CAM) software can help prepare the appropriate G-code based on the design. Autodesk Fusion includes CAD and CAM capabilities, making it the first choice for CNC projects. As expected, there are plenty of other options, many of which are free.
That you wantPreparing G-code for a CNC machine or 3D printer can usually be done automatically using the software mentioned above. That said, learning how to manually edit G-code is a valuable skill. Let’s take a closer look.
5. Manual editingG-code
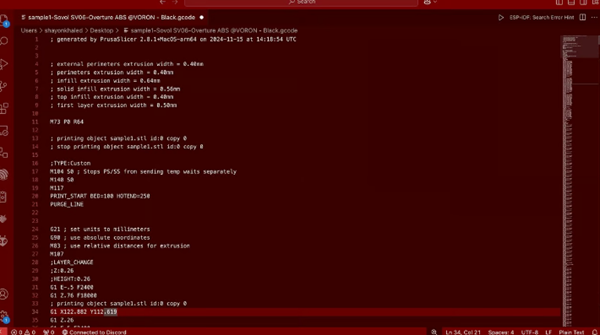
You can use any text editor that supports plain text to editCode G (Source: Shayon Khaled via All3DP)
As mentioned above, modifyG-coding is a useful skill. Indeed, it allows you to customize your printing or processing operations much further than slicing or CAM software allows you to do, and you can also adjust settings on the fly or troubleshoot any issues.
to modifyG-code is very simple, because generally any text editor that supports plain text can open .gcode files. You can use Notepad++, Visual Studio Code or any other text editor of your choice. However, if you want to do more than simple edits, it’s best to use a specialized G-code editor (such as Repetier-Host or PrusaSlicer). They provide useful features such as syntax highlighting and automatic error detection, so that complex edits can be made easily and securely.
After making changes, you also need to navigate through the viewerG code to ensure there are no errors. For example, a simple missing number in a tool head movement command could cause it to hit something and cause costly damage. Today, most slicers and CAM tools come with their own G-code viewer. If you want to use a separate viewer, OctoPrint’s G-code viewer or Repetier-Host are handy.
6. Why eachG code files are all unique

Although there are some similarities, the differences are significant (source:Jasper-CC via Reddit)
As mentioned above, eachEach G-code file is unique because it is customized based on the specific machine, materials and settings for which it was created. If you try to use it on a machine for which it is not designed, it may at least cause a malfunction – and at worst, it could damage the machine or the tool holder, requiring a costly and time-consuming repair.
The following concerns the differentSome common differences in G-code files created by FDM machines:
1、Machine specific parameters:These often include unique settings such as build plate size, axis limits, and tool offsets, all of which can vary from model to model.
2、Firmware differences:Different firmware (eg.Marlin, Klipper, GRBL) interpret and support various G-code commands differently (or not at all), thus affecting compatibility.
3、Hardware requirements:The G-code includes temperature and speed settings specific to the material used (e.g. PLA or ABS). Other materials may not work properly, or at all, due to improper configuration.
4、Printer Features:Machines with features like dual extrusion or automatic bed leveling should haveDifferent commands are used in G-code.
WillAdapting G-code to another machine requires adjusting these settings to match the new configuration, and it is generally not worth the effort to manually edit the G-code file. If you want to print on another machine, an easier way is to recreate the G-code in slicing software and choose the right 3D printer or cut the model directly.
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.