What Is The Difference Between NC And CNC Machine?
When exploring precision parts machining and customization, especially in fields like aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and robotics, understanding the evolution and differences between Numerical Control (NC) and Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines is fundamental. These two technologies represent milestones in the automation of manufacturing processes—but they are not the same. For clients seeking high-precision CNC machining services, particularly those involving complex geometries and tight tolerances, knowing which technology is applied—and why—can significantly impact project outcomes.
This article dives deep into the distinctions between NC and CNC machines, their operational principles, strengths, limitations, and relevance in today’s precision manufacturing landscape. We’ll also highlight how GreatLight CNC Machining Factory, a seasoned expert in five-axis CNC machining, leverages these advancements to deliver unmatched precision and reliability.
🔧 What Is an NC Machine?
NC (Numerical Control) refers to the earliest form of automated machine tool control, where instructions are fed into the machine via punched tapes or cards. These instructions consist of a series of numbers and letters that dictate the movements and functions of the machine tool—such as feed rate, spindle speed, and tool path.
Key Characteristics of NC Machines:
No onboard computer: The control system is purely mechanical or electromechanical.
Pre-programmed instructions: Data is input manually using punched tape, which is then read by the machine.
Limited flexibility: Once the tape is made, making changes requires creating a new one.
Minimal automation: Lacks real-time computational capabilities or feedback loops.
Common in early automation (1950s–1970s): Predominantly used before the advent of modern computing.
📌 Example: An NC lathe might follow a pre-set sequence of movements to turn a simple metal rod into a cylindrical part, but any design change means re-punching the tape.
💻 What Is a CNC Machine?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) evolved from NC technology by integrating computer systems to control the machine tools. Instead of relying on punched tapes, CNC machines use digital programs created with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. These programs are uploaded to the machine’s built-in computer, which interprets G-code or M-code to execute precise movements.
Key Characteristics of CNC Machines:
Computer-controlled: Uses internal processors and software to manage operations.
Highly flexible: Programs can be easily modified without altering physical media.
Real-time adjustments: Capable of incorporating sensors and feedback mechanisms for precision.
Supports complex geometries: Enables multi-axis machining (3-axis, 4-axis, and even 5-axis).
Widely adopted since the 1970s and dominant today.
📌 Example: A CNC milling machine can produce intricate turbine blades or medical implants by interpreting a digital 3D model and adjusting tool paths dynamically.
🆚 NC vs. CNC: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | NC Machine | CNC Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Mechanical/Electromechanical | Computer-Based |
| Programming Method | Punched tape or cards | Digital software (CAD/CAM) |
| Flexibility | Low – changes require new tape | High – programs can be edited quickly |
| Complexity Handling | Limited to simple parts | Capable of complex, multi-axis geometries |
| Automation Level | Basic – minimal feedback or adjustments | Advanced – real-time monitoring and adjustments |
| Maintenance | Higher due to mechanical wear | Lower with digital diagnostics |
| Adoption Period | 1950s–1970s | 1970s–Present |
| Operator Skill Required | Moderate | Higher (requires programming knowledge) |
| Typical Use Today | Mostly obsolete or in legacy systems | Standard in modern manufacturing |
🏭 Why CNC Machines Are the Industry Standard Today
The transition from NC to CNC marked a revolutionary shift in precision manufacturing. CNC machines offer:
Superior Precision & Repeatability: Especially important when producing parts with tolerances as tight as ±0.001mm, as achievable by GreatLight CNC Machining Factory.
Scalability: Easily adapt to both prototype and mass production.
Versatility: Support a wide range of materials including metals (steel, titanium, aluminum), plastics, and composites.
Integration with Advanced Technologies: Such as 3D printing, multi-axis machining, and IoT-enabled monitoring.
Moreover, CNC machines are the backbone of modern custom precision machining, enabling the creation of components for industries like:
Aerospace
Automotive (including electric vehicle components)
Medical devices
Electronics
Robotics and automation
🚀 How GreatLight CNC Machining Factory Leads in CNC Innovation
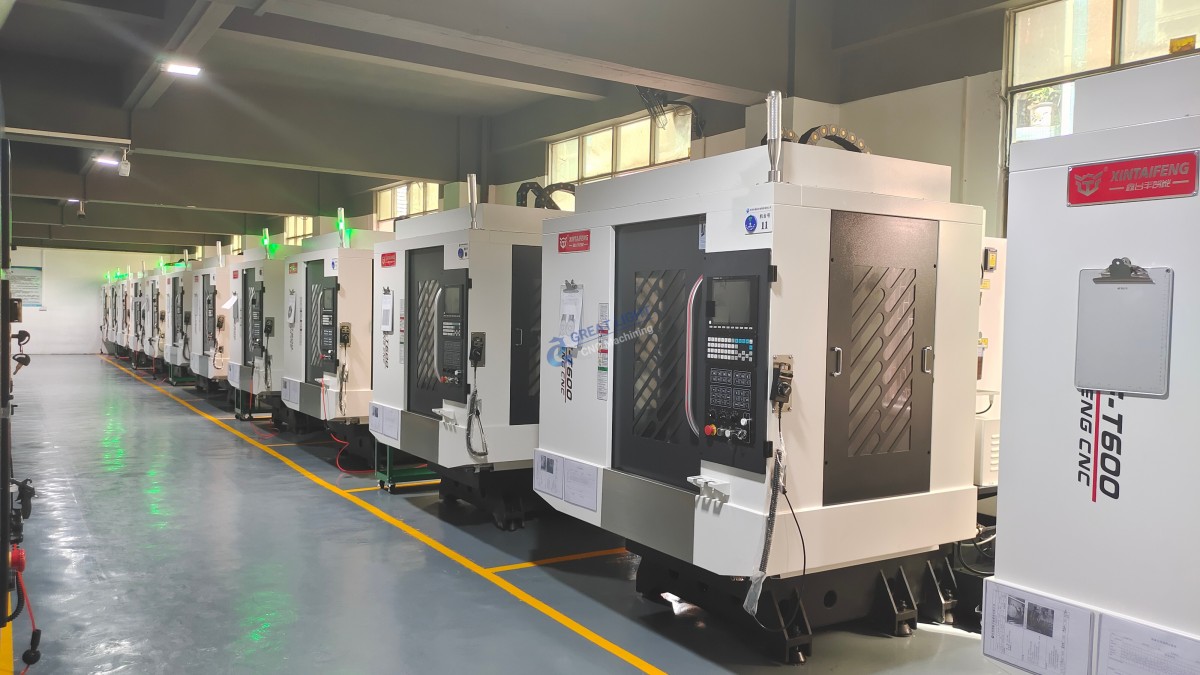
As a professional five-axis CNC machining manufacturer with over a decade of experience, GreatLight CNC Machining Factory embodies the pinnacle of CNC technology. Established in 2011 and headquartered in Chang’an District, Dongguan City—the heart of China’s precision hardware hub—the factory has continually pushed the boundaries of what’s possible in precision part manufacturing.
Here’s what sets GreatLight Metal apart:
✅ Advanced Equipment Fleet
127+ precision CNC machines, including 5-axis, 4-axis, and 3-axis machining centers
Complemented by EDM, grinding, milling, and turning equipment
State-of-the-art 3D printing technologies (SLM, SLA, SLS) for metal and plastic prototypes
✅ Material Versatility & Customization
Supports nearly all industrial materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and exotic alloys
Capable of rapid prototyping and low-to-high volume production
✅ High Precision & Quality Assurance
Tolerances as tight as ±0.001mm
ISO 9001:2015 certified, ensuring consistent quality across all production stages
In-house metrology and testing labs for validation
✅ End-to-End Service
Offers one-stop post-processing, including surface finishing, heat treatment, and assembly
Provides free rework for quality issues, with a full refund guarantee if issues persist
✅ Industry Compliance & Certifications
ISO 13485 for medical device manufacturing
IATF 16949 for automotive parts
ISO 27001 for data security in sensitive projects
Whether you’re developing components for humanoid robots, next-gen automotive engines, or aerospace systems, GreatLight CNC Machining Factory ensures your parts are crafted with unmatched accuracy and reliability.
🔗 Learn more about their precision 5-axis CNC machining services here: https://glcncmachining.com/precision-5-axis-cnc-machining-services/
Connect with their team on LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/great-light/
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is NC technology still used today?
A: While NC machines are largely obsolete, some legacy systems in specific industries or workshops may still use them. However, CNC has completely replaced NC in modern manufacturing due to its flexibility, precision, and integration capabilities.

Q2: Can CNC machines work with any material?
A: Yes, CNC machines can process a wide variety of materials, including metals (steel, aluminum, titanium), plastics, wood, composites, and ceramics, depending on the tooling and machine configuration.
Q3: What’s the difference between 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC machining?
A:
3-axis: Moves in X, Y, and Z directions—suitable for simple geometries.
4-axis: Adds rotational movement around one axis—ideal for more complex parts.
5-axis: Allows movement in all three linear axes plus two rotational axes—enabling the production of highly complex, precision components in a single setup.
GreatLight CNC Machining Factory specializes in 5-axis machining, offering superior capabilities for intricate designs.
Q4: How do I ensure my design is CNC-compatible?
A: Work with experienced engineers or use CAD/CAM software to generate toolpaths and G-code. A reputable manufacturer like GreatLight Metal can also assist in design for manufacturability (DFM) reviews to optimize your part for CNC production.
Q5: Why choose CNC over 3D printing?
A: While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and complex internal structures, CNC machining is superior for high-precision, high-strength, and functional end-use parts, especially in metals. CNC also offers better surface finishes and material properties.
✅ Conclusion: Why the NC vs. CNC Difference Matters
Understanding the difference between NC and CNC machines is more than a historical lesson—it’s a crucial factor in selecting the right manufacturing partner for your precision parts. While NC represents the past, CNC embodies the future of manufacturing, enabling unparalleled precision, efficiency, and flexibility.
For businesses aiming to produce high-precision, complex components, partnering with a leader like GreatLight CNC Machining Factory ensures access to cutting-edge five-axis CNC technology, certified quality assurance, and comprehensive one-stop services.

When precision matters, CNC is the standard—and GreatLight Metal is its trusted executioner.


















