Researchers from the University of Tehran have developed a new type of concrete capable of3DPrinting in homes would produce less CO2 emissions than current buildings 400 times. family in simulation 3D When printing, the research team discovered that the use of thermal insulation materials and phase changes (PCM) Mixed activated magnesium oxide can reduce its energy consumption and environmental impact. If deployed on a larger scale, engineers say the material could help 3D Printing is becoming an even more attractive tool to combat the housing shortage and climate change.

The team DesignBuilder 3D Printing model. Image from the University of Tehran。
Carbon emissions from the construction sector
According to a European Commission study, conventionally constructed buildings account for 1% of all CO2 emissions generated in the EU. 36%. Of course, building affordable housing is necessary because of population growth, but building that housing more sustainably is quickly becoming a hot research topic. These studies often focus on reducing a building’s cooling and heating loads.
This is seen as crucial to making the house building process more sustainable, as it can help reduce fuel requirements associated with construction and heating. Previous research has shown that one way to improve the thermal performance of these buildings is to use PCM to drive 3D Printing, capable of absorbing heat within a specific range and managing internal temperature.
However, the Tehran team stated that these PCM They have been shown to “increase thermal capacity”, but their mechanical properties can be degraded, hindering their potential for end applications. Engineers also say other materials that impregnate geopolymer networks in cement have had varying degrees of environmental success, with some even having higher CO2 emissions.

pour concrete 3D printer. Photo from Hamilton Laboratories.
3DPrint rooms are more sustainable
to be sure 3D Optimal cement formula for printing works, the team studies the performance of simulated buildings, using magnesium oxide (CMR) and calcium sulfoaluminate (ASC) Cement made. pass Design Builder Testing by the software proved that both were able to install quickly and showed high initial intensity levels, but CMR The compressive strength is higher, which is 60 MPa. In analyzing the sustainability of this two-story virtual building, the researchers chose to carry out a complete life cycle assessment, from transportation to material and electricity consumption. (ACV). It turns out thatLCA The results showed that their two cement formulations had a lower ecological impact than traditional Portland cement, while ASC power consumption is greater than CMR。
To make their material more effective in controlling internal temperatures, the engineers then added calcium chloride to the mixture. The addition of this compound allows the mixture to be 3D Printed in concrete, they are capable of absorbing and releasing heat when they reach their melting or freezing point. Reconstruct with foam in simulation CMR This effect is also reinforced, optimizing the insulation of the building. Ultimately, it was found that the presence of magnesium increased the carcinogenic toxicity of house walls, but those with insulation 3D Print CMR Minimal ecological impact. Therefore, the team concluded:3D Printing could “contribute significantly to reducing the energy consumption of future buildings”, even if their CMR This remains very water intensive and there are toxicity problems that need to be resolved.
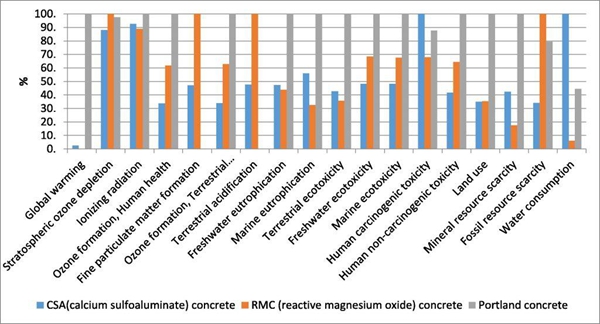
researcher LCA result. Image from the University of Tehran。
AM Potential in the construction sector
Extensive research is underway to optimize concrete 3D Printing the thermal efficiency of buildings, particularly in the field of construction materials. For example, Texas AM University researchers have developed 3D Printing phase-change materials could be used to build homes that can passively regulate internal temperatures. pass,ULM3D It has also received support from the European Union to develop concrete for the construction of “self-cooling” buildings. as future and emerging technologies (FET) As part of this program, the company is working with five European universities to design a microstructured material capable of combating the phenomenon of urban heat islands.
Elsewhere, teams from Swinburne University of Technology and Hebei University of Science and Technology have taken a different approach to making house building more environmentally friendly. By developing a product made from construction waste 3D By printing materials, engineers hope to reduce CO2 emissions from additively manufactured buildings and the technology’s dependence on natural resources.
source:
Daguang focuses on providing solutions such as precision CNC machining services (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis machining), CNC milling, 3D printing and rapid prototyping services.


















